RevOps CRM Architecture: Entities, Stages, and SLAs is a deep dive into optimizing your customer relationship management. This guide will help you understand how to build a RevOps CRM architecture, focusing on its core purpose and how it differs from traditional CRM approaches. We’ll explore the key benefits of a RevOps approach, including how it can drive revenue growth and improve operational efficiency.
This guide will also cover critical components of a RevOps CRM, like defining the essential data entities (Leads, Contacts, Accounts, Opportunities, and Deals) and their relationships. We’ll also analyze the customer lifecycle stages within a RevOps framework (Lead Generation, Qualification, Sales, Onboarding, Adoption, Expansion, and Renewal), along with the key metrics to track at each stage. Furthermore, we’ll discuss Service Level Agreements (SLAs), data flow, integration methods, technology, implementation, best practices, measuring success, and future trends.
Defining RevOps CRM Architecture
The landscape of customer relationship management (CRM) is evolving, and with it, the need for a more strategic and integrated approach. RevOps CRM architecture is a key element in this evolution, moving beyond traditional CRM to focus on revenue generation and alignment across the entire customer lifecycle. This approach emphasizes process optimization, data-driven decision-making, and a unified view of the customer.
Core Purpose and Objectives of RevOps CRM Architecture, RevOps CRM Architecture: Entities, Stages, and SLAs
The primary aim of a RevOps CRM architecture is to streamline and optimize the entire revenue lifecycle, from lead generation to customer retention. This architecture acts as a central hub, integrating various systems and data sources to provide a holistic view of the customer journey.The objectives include:
- Driving Revenue Growth: By aligning sales, marketing, and customer success efforts, RevOps CRM architecture aims to increase revenue generation. This involves optimizing lead qualification, improving sales cycle efficiency, and maximizing customer lifetime value.
- Improving Operational Efficiency: Automation and streamlined processes are key components. The architecture seeks to reduce manual tasks, eliminate data silos, and provide a single source of truth for customer data.
- Enhancing Customer Experience: A unified view of the customer enables personalized interactions and proactive support. This leads to increased customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: RevOps CRM architecture provides robust analytics and reporting capabilities, enabling data-driven decision-making across all revenue-generating functions.
- Process Standardization: Standardized processes ensure consistency and scalability. This leads to improved predictability and reduced errors.
How RevOps Differs from Traditional CRM Approaches
Traditional CRM often focuses on siloed departmental functions, such as sales or marketing, without a holistic view of the customer journey. RevOps, on the other hand, takes a cross-functional approach, breaking down silos and aligning all revenue-generating activities.Key differences include:
- Focus: Traditional CRM primarily focuses on managing customer interactions, while RevOps centers on revenue generation and business outcomes.
- Scope: Traditional CRM often concentrates on specific departments, whereas RevOps encompasses the entire customer lifecycle.
- Alignment: Traditional CRM may lack alignment between departments, while RevOps emphasizes cross-functional collaboration and shared goals.
- Data Utilization: Traditional CRM may not fully leverage data for decision-making, while RevOps relies heavily on data analysis and insights.
- Process Orientation: Traditional CRM may have fragmented processes, while RevOps strives for streamlined and optimized processes across the revenue lifecycle.
Key Benefits of Implementing a RevOps CRM Architecture
Implementing a RevOps CRM architecture offers a multitude of benefits, leading to improved business performance and customer satisfaction. The focus on alignment and optimization translates into tangible results.
- Increased Revenue: By streamlining processes, improving sales efficiency, and maximizing customer lifetime value, RevOps can significantly boost revenue. For example, companies that have implemented RevOps often see a 10-20% increase in sales productivity within the first year.
- Improved Customer Experience: A unified view of the customer allows for personalized interactions and proactive support, leading to higher customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Automation, data integration, and process optimization reduce manual tasks and improve efficiency across all revenue-generating functions. This can lead to a reduction in operational costs by up to 15%.
- Better Data-Driven Decisions: Robust analytics and reporting capabilities enable data-driven decision-making, leading to improved forecasting, resource allocation, and strategic planning.
- Increased Sales and Marketing Alignment: RevOps fosters collaboration between sales and marketing teams, leading to improved lead qualification, higher conversion rates, and a more efficient sales cycle. A common outcome of such alignment is a 20-30% increase in lead-to-opportunity conversion rates.
- Improved Scalability: Standardized processes and integrated systems enable businesses to scale their revenue operations more effectively as they grow.
- Faster Time to Market: By optimizing processes and improving collaboration, RevOps can help companies bring products and services to market faster.
CRM Entities in RevOps
The cornerstone of any effective RevOps CRM architecture lies in understanding and managing the core data entities that represent your business interactions. These entities are the building blocks upon which all RevOps processes are built, from lead generation to deal closure and beyond. A well-defined entity structure allows for streamlined data flow, improved reporting, and ultimately, better decision-making across the revenue lifecycle.
Primary Data Entities
The following are the fundamental data entities that form the backbone of a RevOps CRM. These entities, when correctly defined and interconnected, provide a comprehensive view of the customer journey.
- Leads: Represent potential customers who have shown some interest in your product or service but haven’t yet been qualified. They are typically the starting point of the sales process.
- Contacts: Individual people associated with a company, often representing decision-makers or influencers. Contacts are linked to Accounts.
- Accounts: Represent the companies or organizations you do business with. Accounts provide a holistic view of the relationship with a specific business entity.
- Opportunities: Represent potential sales deals or revenue-generating activities. They are associated with an Account and often involve multiple Contacts.
- Deals: This entity is often synonymous with “Opportunities,” but in some systems, it might represent a more concrete, closed deal. It encompasses all the details of a finalized transaction.
Relationships Between Entities
Understanding the relationships between these entities is crucial for effective RevOps. These relationships enable you to track the progression of a lead through the sales funnel and gain insights into customer behavior.
- Leads to Contacts: A lead can be converted into a Contact when qualified. This usually involves verifying the lead’s information and assigning them to an Account.
- Contacts to Accounts: Contacts are always associated with an Account, indicating the company they work for.
- Accounts to Opportunities: Opportunities are always associated with an Account, signifying a potential deal with that company.
- Contacts to Opportunities: Contacts can be linked to Opportunities, indicating their involvement in a specific deal.
- Opportunities to Deals: When an Opportunity is won, it is typically converted into a Deal, representing a closed sale.
Common Entity Attributes
Each entity is defined by a set of attributes that describe its characteristics. These attributes are crucial for data organization, segmentation, and reporting. Below is a table showcasing common entity attributes with their data types.
| Entity Name | Attribute | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead | First Name | Text | The lead’s first name. |
| Lead | Last Name | Text | The lead’s last name. |
| Lead | Text | The lead’s email address. | |
| Lead | Company | Text | The lead’s company name. |
| Lead | Lead Source | Picklist | The source from which the lead originated (e.g., Website, Trade Show, Referral). |
| Contact | First Name | Text | The contact’s first name. |
| Contact | Last Name | Text | The contact’s last name. |
| Contact | Text | The contact’s email address. | |
| Contact | Account Name | Lookup | The account the contact is associated with. |
| Account | Account Name | Text | The company’s name. |
| Account | Industry | Picklist | The industry the company operates in (e.g., Technology, Healthcare). |
| Account | Website | Text | The company’s website URL. |
| Account | Number of Employees | Number | The number of employees at the company. |
| Opportunity | Opportunity Name | Text | A descriptive name for the opportunity. |
| Opportunity | Account Name | Lookup | The account associated with the opportunity. |
| Opportunity | Stage | Picklist | The current stage of the opportunity in the sales process (e.g., Qualification, Proposal, Negotiation). |
| Opportunity | Close Date | Date | The expected close date of the opportunity. |
| Opportunity | Amount | Currency | The estimated value of the opportunity. |
| Deal | Deal Name | Text | A descriptive name for the closed deal. |
| Deal | Account Name | Lookup | The account associated with the deal. |
| Deal | Close Date | Date | The actual close date of the deal. |
| Deal | Amount | Currency | The actual value of the deal. |
RevOps Stages within the CRM: RevOps CRM Architecture: Entities, Stages, And SLAs
In a RevOps-driven CRM, the customer journey is meticulously mapped and managed across distinct stages. Each stage represents a crucial phase in the customer lifecycle, from initial awareness to long-term advocacy. This structured approach allows for optimized processes, improved collaboration between teams, and data-driven decision-making, ultimately leading to increased revenue and customer satisfaction.
Lead Generation
Lead Generation focuses on attracting potential customers and capturing their interest in a company’s products or services. This stage involves various marketing activities aimed at generating leads and building a database of potential customers.The primary activities include:
- Content Marketing: Creating and distributing valuable content (blog posts, ebooks, webinars) to attract and engage potential customers. This content is designed to address their pain points and position the company as a thought leader.
- Search Engine Optimization (): Optimizing website content and structure to improve search engine rankings and drive organic traffic. This increases the visibility of the company’s website to potential customers searching for relevant information.
- Paid Advertising: Utilizing paid advertising platforms (Google Ads, social media ads) to target specific audiences and drive traffic to the company’s website or landing pages.
- Social Media Marketing: Building a presence on social media platforms to engage with potential customers, share content, and drive traffic to the website.
- Email Marketing: Building an email list and sending targeted email campaigns to nurture leads and promote products or services.
Key metrics and KPIs to track in the Lead Generation stage include:
- Website Traffic: The total number of visitors to the company’s website.
- Lead Volume: The total number of leads generated through various channels.
- Conversion Rate (Lead to MQL): The percentage of leads that convert into Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs).
- Cost Per Lead (CPL): The cost associated with acquiring each lead.
- Lead Source Performance: The performance of different lead generation channels (e.g., organic search, paid advertising, social media) in terms of lead volume, conversion rates, and cost.
Qualification
The Qualification stage involves assessing leads to determine their fit with the company’s ideal customer profile (ICP) and their likelihood of becoming paying customers. This process helps sales teams prioritize their efforts and focus on the most promising leads.Activities in this stage involve:
- Lead Scoring: Assigning points to leads based on their demographics, behavior, and engagement with marketing materials. This helps prioritize leads based on their perceived level of interest and fit.
- Lead Enrichment: Gathering additional information about leads through data enrichment tools to gain a deeper understanding of their needs and challenges.
- Initial Contact: Sales representatives reaching out to leads via phone, email, or other channels to qualify them and assess their needs.
- Needs Analysis: Identifying the lead’s pain points, goals, and budget to determine if the company’s products or services are a good fit.
Key metrics and KPIs for the Qualification stage:
- MQL Volume: The total number of Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs) generated.
- SQL Volume: The total number of Sales Qualified Leads (SQLs) generated.
- Conversion Rate (MQL to SQL): The percentage of MQLs that convert into SQLs.
- Time to SQL: The average time it takes for a lead to become an SQL.
- Lead Qualification Rate: The percentage of leads that are successfully qualified.
Sales
The Sales stage encompasses the activities involved in converting qualified leads into paying customers. This stage involves sales representatives engaging with prospects, presenting solutions, and closing deals.Key activities include:
- Product Demos and Presentations: Demonstrating the value of the company’s products or services to potential customers.
- Proposal Generation: Creating customized proposals that Artikel the proposed solutions and pricing.
- Negotiation: Negotiating terms and conditions with potential customers to reach a mutually agreeable agreement.
- Closing the Deal: Finalizing the sale and securing a contract or purchase order.
- CRM Updates: Sales representatives meticulously updating the CRM with all interactions, communications, and deal stages.
Key metrics and KPIs for the Sales stage:
- Conversion Rate (SQL to Opportunity): The percentage of SQLs that convert into sales opportunities.
- Win Rate: The percentage of opportunities that are successfully closed.
- Average Deal Size: The average revenue generated from each closed deal.
- Sales Cycle Length: The average time it takes to close a deal.
- Revenue Generated: The total revenue generated from closed deals.
Onboarding
Onboarding is the process of integrating new customers into the company’s systems and ensuring they can successfully use the product or service. This stage is crucial for setting the foundation for long-term customer satisfaction and retention.Key activities include:
- Welcome and Introduction: Welcoming new customers and introducing them to the onboarding process.
- Product Training: Providing training on how to use the product or service effectively.
- Account Setup: Assisting customers with setting up their accounts and configuring the product or service.
- Implementation: Helping customers implement the product or service within their own workflows.
- Ongoing Support: Providing ongoing support to help customers resolve any issues or questions they may have.
Key metrics and KPIs for the Onboarding stage:
- Time to Value: The time it takes for customers to experience the value of the product or service.
- Onboarding Completion Rate: The percentage of customers who successfully complete the onboarding process.
- Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT): Measuring customer satisfaction with the onboarding experience.
- Churn Rate (Early): The percentage of customers who churn within a specific timeframe after onboarding.
- Product Usage: Tracking customer usage of the product or service.
Adoption
Adoption focuses on encouraging customers to actively use the product or service and derive value from it. This stage is critical for driving customer satisfaction, retention, and expansion opportunities.Key activities include:
- User Education: Providing ongoing education and resources to help customers get the most out of the product or service.
- Feature Adoption: Encouraging customers to adopt new features and functionalities.
- Best Practice Guidance: Providing guidance on best practices for using the product or service.
- Proactive Support: Proactively reaching out to customers to offer assistance and support.
- Customer Success Management: Assigning customer success managers (CSMs) to help customers achieve their goals.
Key metrics and KPIs for the Adoption stage:
- Active User Rate: The percentage of customers who actively use the product or service.
- Feature Adoption Rate: The percentage of customers who adopt specific features.
- Customer Health Score: Assessing the overall health and satisfaction of customers.
- Product Usage Frequency: How often customers use the product or service.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS): Measuring customer loyalty and willingness to recommend the company.
Expansion
The Expansion stage focuses on identifying and capitalizing on opportunities to increase revenue from existing customers. This stage involves upselling, cross-selling, and identifying new use cases for the product or service.Key activities include:
- Upselling: Selling higher-value products or services to existing customers.
- Cross-selling: Selling complementary products or services to existing customers.
- Account Reviews: Conducting regular account reviews to identify opportunities for expansion.
- Needs Assessment: Understanding the evolving needs of customers and identifying new solutions.
- Customer Advocacy: Encouraging customers to become advocates for the company.
Key metrics and KPIs for the Expansion stage:
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): The predicted revenue a customer will generate over their relationship with the company.
- Expansion Revenue: The revenue generated from upselling and cross-selling activities.
- Net Revenue Retention (NRR): The percentage of revenue retained from existing customers, including expansion and churn.
- Average Revenue Per Account (ARPA): The average revenue generated from each customer account.
- Customer Advocacy Rate: Measuring the number of customers who actively advocate for the company.
Renewal
The Renewal stage focuses on retaining existing customers and ensuring they continue to use the product or service. This stage is crucial for long-term revenue stability and growth.Key activities include:
- Contract Management: Managing contracts and ensuring timely renewals.
- Customer Communication: Communicating with customers about their upcoming renewals.
- Value Validation: Demonstrating the ongoing value of the product or service.
- Renewal Negotiations: Negotiating renewal terms with customers.
- Churn Prevention: Proactively addressing any concerns or issues that could lead to churn.
Key metrics and KPIs for the Renewal stage:
- Renewal Rate: The percentage of customers who renew their contracts.
- Churn Rate: The percentage of customers who do not renew their contracts.
- Customer Retention Rate: The percentage of customers retained over a specific period.
- Renewal Revenue: The revenue generated from contract renewals.
- Renewal Cycle Time: The average time it takes to renew a contract.
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) in RevOps CRM
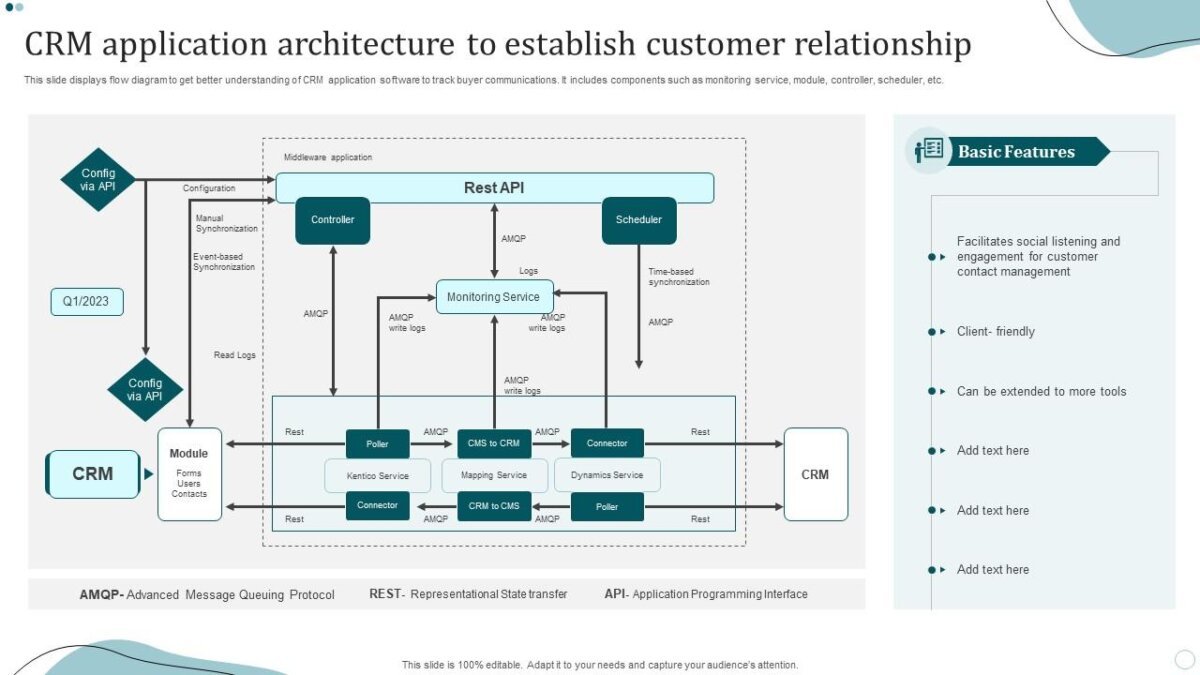
Source: slideteam.net
SLAs are critical in a RevOps CRM architecture. They define the expectations and commitments for service delivery, ensuring accountability and driving efficiency across teams. Well-defined SLAs help to align teams, improve customer satisfaction, and optimize the overall performance of the CRM system.
Role of SLAs in RevOps CRM Architecture
SLAs play a vital role in a RevOps CRM architecture by setting clear expectations and ensuring accountability. They establish measurable standards for service delivery, which allows for consistent performance and improved customer satisfaction. By defining specific metrics, SLAs provide a framework for monitoring, evaluating, and optimizing CRM processes. This leads to better resource allocation, proactive issue resolution, and ultimately, a more efficient and effective RevOps operation.
Sample SLA Structure for a Sales Team
Creating an effective SLA structure involves defining specific performance targets. This includes response times, resolution times, and escalation procedures. A well-defined SLA for a sales team helps to manage expectations, prioritize tasks, and ensure timely service delivery.
- Response Times: Define the acceptable timeframes for responding to different types of requests.
- Lead Qualification Requests: Respond within 1 hour.
- Technical Support Requests: Acknowledge within 30 minutes.
- High-Priority Sales Inquiries: Respond within 15 minutes.
- Resolution Times: Specify the target time to resolve different issues.
- Bug Fixes: Resolve within 24 hours.
- Account Setup: Complete within 2 hours.
- Data Entry Errors: Correct within 1 hour.
- Escalation Procedures: Artikel the steps to escalate issues that cannot be resolved within the defined timeframes.
- Level 1: Sales Representative -> Sales Manager (if resolution time is exceeded).
- Level 2: Sales Manager -> RevOps Team (if the Sales Manager can’t resolve the issue).
- Level 3: RevOps Team -> IT Department/Vendor (if the issue requires technical intervention).
Differences Between Internal and External SLAs in RevOps
Internal and external SLAs differ in their scope and focus. Internal SLAs govern the service levels within an organization, focusing on the relationship between different departments or teams. External SLAs, on the other hand, are legally binding agreements with external customers. Understanding these differences is crucial for effectively managing and optimizing a RevOps CRM.
- Internal SLAs: These are agreements between departments within a company. They define the service levels that one team provides to another.
- Example: The RevOps team has an internal SLA with the Sales team to resolve data entry errors within one hour.
- Focus: Improving internal efficiency, aligning teams, and streamlining processes.
- External SLAs: These are contracts between a company and its customers. They define the service levels that the company promises to deliver.
- Example: A SaaS company’s SLA with its customers guarantees 99.9% uptime of its CRM platform.
- Focus: Customer satisfaction, legal compliance, and maintaining a positive brand reputation.
Data Flow and Integration
Understanding how data flows between different systems and integrating data from various departments is crucial for a successful RevOps CRM architecture. This ensures a unified view of the customer, enables informed decision-making, and streamlines processes.
Data Flow in RevOps CRM
The data flow in a RevOps CRM architecture describes how information moves between different systems and departments. This flow is designed to create a cohesive and efficient operational environment.* Lead Generation to Sales: Data originates from marketing efforts, such as website forms, advertising campaigns, and content downloads. This information flows into the CRM, where leads are qualified and assigned to sales representatives.
Sales to Customer Success
Once a deal is closed, the sales data (deal size, product purchased, contract terms) is passed to customer success. This enables the customer success team to onboard the customer effectively and manage their ongoing relationship.
Customer Success to Marketing
Customer success teams gather data on customer usage, satisfaction, and churn. This information feeds back to marketing to refine messaging, target upsell opportunities, and improve customer retention strategies.
Financial Data Integration
Integration with financial systems (e.g., accounting software) provides visibility into revenue, payment status, and contract renewals, supporting accurate forecasting and financial reporting.
Product Usage Data
Integrating with product analytics platforms provides insights into customer product usage, which can be used to personalize customer interactions and identify opportunities for product adoption.
Importance of Integrating Sales, Marketing, and Customer Success Data
Integrating data from sales, marketing, and customer success departments provides a 360-degree view of the customer, enabling better decision-making and improved customer experiences. This integration facilitates alignment across teams, leading to more effective operations.* Improved Customer Understanding: A unified view of the customer’s journey, including their interactions with marketing, sales, and customer success, provides a comprehensive understanding of their needs and preferences.
Enhanced Personalization
Access to complete customer data enables personalized interactions, tailored product recommendations, and targeted marketing campaigns.
Increased Efficiency
Automated data sharing reduces manual data entry and the need for multiple systems, saving time and resources.
Better Forecasting and Reporting
Consolidated data provides a single source of truth for revenue forecasting, sales performance analysis, and customer retention metrics.
Reduced Churn
By understanding customer behavior and proactively addressing issues, businesses can reduce churn and increase customer lifetime value.
Integration Methods
Several methods can be employed to integrate data between different systems within a RevOps CRM architecture. The choice of method depends on the specific systems involved, the volume of data, and the desired level of real-time integration.* APIs (Application Programming Interfaces): APIs allow different software systems to communicate with each other, exchanging data in real-time. For example, a CRM can use an API to pull lead information from a marketing automation platform or push deal information to a financial system.
APIs are like the translators of the digital world, enabling different software applications to “speak” the same language and exchange information seamlessly.
Webhooks
Webhooks are automated notifications sent from one application to another when a specific event occurs. For example, a webhook can notify a CRM when a new lead submits a form on a website, triggering an automated workflow.
Data Connectors
Data connectors are pre-built integrations that connect different systems, often provided by third-party vendors. These connectors simplify the integration process by providing a ready-made solution for data transfer.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Tools
ETL tools are used to extract data from various sources, transform it into a usable format, and load it into a central data warehouse or CRM. This is useful for batch processing and integrating data from multiple sources.
Custom Integrations
In some cases, custom integrations may be necessary to connect specific systems that do not have readily available connectors or APIs. This often involves developing custom code to facilitate data transfer.
Technology and Tools for RevOps CRM
The right technology stack is crucial for successfully implementing a RevOps CRM architecture. It’s not just about having the latest and greatest tools; it’s about choosing the right combination of technologies that work together seamlessly to support the entire customer lifecycle and align sales, marketing, and customer success efforts. This section explores the different technology categories that support RevOps CRM, emphasizing the importance of tool selection and how these tools contribute to each stage of the customer journey.
Technology Categories Supporting RevOps CRM
Various technology categories underpin a RevOps CRM architecture. These categories need to integrate and work in harmony to achieve the desired results.
- CRM Platforms: These are the central hubs for customer data and interactions. They manage contact information, track deals, and provide a 360-degree view of the customer. Examples include Salesforce, HubSpot, and Zoho CRM.
- Marketing Automation Platforms: These tools automate marketing tasks, such as email campaigns, lead nurturing, and social media management. They help generate leads and move them through the sales funnel. Popular examples include Marketo, Pardot (Salesforce), and HubSpot Marketing Hub.
- Sales Enablement Tools: These tools equip sales teams with the resources they need to succeed, including content management, sales analytics, and training. Examples include Seismic, Outreach, and Salesloft.
- Data Integration and Management Tools: These tools ensure that data flows seamlessly between different systems, providing a unified view of customer data. They handle data cleansing, transformation, and synchronization. Examples include Zapier, Tray.io, and MuleSoft.
- Business Intelligence (BI) and Analytics Tools: These tools analyze data to provide insights into sales performance, marketing effectiveness, and customer behavior. They help identify trends and make data-driven decisions. Examples include Tableau, Power BI, and Looker.
- Communication and Collaboration Tools: These tools facilitate communication and collaboration between teams, ensuring everyone is on the same page. Examples include Slack, Microsoft Teams, and Zoom.
Importance of Selecting the Right Tools
Choosing the right tools is essential for a successful RevOps CRM implementation. Selecting tools that align with the business’s specific needs, goals, and budget is crucial. The wrong tools can lead to data silos, inefficiencies, and a poor customer experience.
- Alignment with Business Needs: Tools should support the specific processes and workflows of the business. A company focused on high-volume, transactional sales might need a different CRM and sales enablement stack than a company focused on enterprise-level deals.
- Integration Capabilities: The chosen tools must integrate with each other and other existing systems. Data silos can hinder RevOps efforts, so seamless data flow is essential.
- Scalability: The tools should be able to scale as the business grows. This means they should be able to handle increasing data volumes and user numbers.
- User Adoption: The tools should be user-friendly and easy to adopt. If the tools are too complex or difficult to use, adoption rates will be low, and the investment will be wasted.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Consider the total cost of ownership, including licensing fees, implementation costs, and ongoing maintenance.
Tool Contributions to the Customer Lifecycle
Various tools contribute to each stage of the customer lifecycle, from initial awareness to post-sale support. The correct implementation of these tools is key to achieving a smooth customer journey.
- Awareness: Marketing automation tools play a crucial role in generating awareness. They can be used to create targeted advertising campaigns, manage social media, and track website traffic.
- Interest/Consideration: Lead nurturing campaigns and content marketing efforts are key at this stage. Marketing automation tools are used to nurture leads with targeted email sequences and personalized content. Sales enablement tools can provide sales teams with the resources they need to engage with prospects.
- Decision/Conversion: CRM platforms are central to managing the sales process at this stage. Sales teams use the CRM to track deals, manage communication with prospects, and generate quotes. Sales enablement tools can provide sales teams with the information and resources they need to close deals.
- Retention/Loyalty: Customer success platforms and CRM platforms are essential for managing customer relationships after the sale. They are used to provide customer support, track customer satisfaction, and identify opportunities for upselling and cross-selling.
- Advocacy: Customer advocacy programs and feedback mechanisms are crucial at this stage. CRM platforms and customer success tools can be used to identify and engage with brand advocates.
Example: A company uses HubSpot Marketing Hub to create a series of blog posts and social media campaigns to attract potential customers interested in their software. They track website visits and content downloads to measure campaign effectiveness.
Example: A lead downloads a white paper from a company’s website. They are then added to a lead nurturing sequence in Marketo, receiving emails with relevant case studies and product demos. The sales team uses Salesloft to access relevant content and track prospect engagement.
Example: A sales rep uses Salesforce to manage a deal, track communication with a prospect, and send a proposal. They use Seismic to access and share the latest product pricing and specifications.
Example: A customer uses Zendesk for customer support. The customer success team uses Gainsight to track customer health scores and identify opportunities to expand the account.
Example: A customer who is very satisfied with a product is identified in the CRM system. The customer success team reaches out to the customer and asks if they would be willing to participate in a case study or provide a testimonial.
Implementing RevOps CRM Architecture
Implementing a RevOps CRM architecture is a transformative process, demanding careful planning and execution. It’s not simply about adopting new software; it’s about redesigning how your organization operates to align sales, marketing, and customer success efforts. This section provides a structured approach to guide you through the implementation process, ensuring a smooth transition and maximizing the benefits of your RevOps CRM.
Step-by-Step Implementation Process
The implementation of a RevOps CRM architecture involves several key phases. Each phase is critical to the overall success of the project. Adhering to a well-defined process minimizes risks and maximizes the chances of achieving the desired outcomes.
- Planning and Assessment: This initial phase sets the foundation for the entire project. It involves a thorough assessment of the current state of your CRM, identifying pain points, and defining clear objectives for the RevOps implementation.
- Define Objectives: Clearly articulate the goals of the RevOps CRM. Examples include improving lead conversion rates, increasing customer lifetime value, or streamlining sales processes.
- Assess Current State: Analyze existing CRM systems, data quality, and workflows. Identify areas for improvement and potential roadblocks.
- Stakeholder Alignment: Engage with stakeholders from sales, marketing, and customer success to gather requirements and ensure alignment on the project’s scope.
- Select CRM Platform (if needed): If you’re not already using a CRM, research and choose a platform that aligns with your business needs and RevOps strategy. Consider factors such as scalability, integration capabilities, and user-friendliness.
- Data Migration and Cleansing: This phase focuses on migrating data from existing systems to the new RevOps CRM. Data quality is crucial for the success of the implementation.
- Data Mapping: Define how data from legacy systems will be mapped to the new CRM’s fields and objects.
- Data Cleansing: Cleanse and standardize data to ensure accuracy and consistency. This includes removing duplicates, correcting errors, and updating outdated information.
- Data Migration Execution: Migrate data in batches, testing the process at each stage to identify and resolve any issues. Consider using specialized data migration tools to streamline the process.
- System Configuration: Configure the CRM to align with your RevOps processes and workflows. This involves setting up user roles, permissions, automation rules, and integrations.
- User Roles and Permissions: Define user roles and assign appropriate permissions to control access to data and functionality.
- Workflow Automation: Implement automated workflows to streamline processes, such as lead routing, task assignments, and email sequences.
- Integration Setup: Integrate the CRM with other essential business systems, such as marketing automation platforms, communication tools, and financial systems.
- Testing and Validation: Thoroughly test the implemented CRM to ensure it functions as expected and meets the defined objectives.
- Unit Testing: Test individual components and functionalities of the CRM.
- Integration Testing: Test the integration between the CRM and other systems.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involve end-users in testing the system to ensure it meets their needs and expectations.
- Performance Testing: Evaluate the system’s performance under different load conditions.
- Training and Onboarding: Provide comprehensive training to users on how to use the new CRM and its features.
- Training Materials: Develop training materials, such as user guides, videos, and online tutorials.
- Training Sessions: Conduct training sessions for different user groups.
- Ongoing Support: Provide ongoing support and resources to help users adopt and effectively use the new CRM.
- Deployment and Go-Live: Deploy the implemented CRM to the production environment and make it available to users.
- Deployment Plan: Develop a detailed deployment plan that Artikels the steps involved in deploying the CRM.
- Go-Live Checklist: Create a go-live checklist to ensure all necessary steps are completed before launching the new system.
- Post-Deployment Monitoring: Monitor the system’s performance and address any issues that arise after deployment.
- Ongoing Optimization and Improvement: Continuously monitor the performance of the CRM and make adjustments as needed to optimize its effectiveness.
- Performance Monitoring: Track key metrics, such as lead conversion rates, sales cycle length, and customer satisfaction.
- Feedback Collection: Gather feedback from users to identify areas for improvement.
- Iterative Updates: Implement iterative updates and enhancements to the CRM based on performance data and user feedback.
Guidelines for Data Migration and System Configuration
Data migration and system configuration are critical aspects of a successful RevOps CRM implementation. Proper planning and execution of these tasks are essential to ensure data integrity and system functionality.
Data Migration Guidelines
- Plan Thoroughly: Develop a detailed data migration plan that Artikels the scope of the migration, the data sources, the target CRM, and the migration process.
- Cleanse and Standardize Data: Cleanse and standardize data to ensure accuracy and consistency. This includes removing duplicates, correcting errors, and updating outdated information. For example, standardize phone number formats (e.g., +1-555-123-4567) and address formats.
- Map Data Fields: Define how data from legacy systems will be mapped to the new CRM’s fields and objects. This requires careful consideration of the data structure and relationships between data elements.
- Choose the Right Migration Method: Select the appropriate data migration method based on the volume of data, the complexity of the data structure, and the desired level of downtime. Options include:
- Big Bang Migration: Migrating all data at once. Suitable for smaller datasets or less complex migrations.
- Phased Migration: Migrating data in stages. Allows for testing and validation at each stage, reducing the risk of major issues.
- Trickle Migration: Migrating data continuously over time. Ideal for large datasets or systems with minimal downtime requirements.
- Test and Validate: Thoroughly test the data migration process to ensure data accuracy and integrity. Validate the migrated data against the source data to identify and resolve any discrepancies.
- Document the Process: Document the entire data migration process, including the data mapping, cleansing rules, and migration steps. This documentation is essential for troubleshooting and future migrations.
System Configuration Guidelines
- Define User Roles and Permissions: Define user roles and assign appropriate permissions to control access to data and functionality. This ensures that users only have access to the information they need and that sensitive data is protected.
- Configure Workflows and Automations: Implement automated workflows to streamline processes, such as lead routing, task assignments, and email sequences. Automation can significantly improve efficiency and reduce manual effort.
- Integrate with Other Systems: Integrate the CRM with other essential business systems, such as marketing automation platforms, communication tools, and financial systems. Integrations enable data to flow seamlessly between systems, providing a unified view of the customer.
- Customize the User Interface: Customize the user interface to align with your branding and user preferences. This includes customizing the layout, colors, and logos.
- Set Up Reporting and Dashboards: Configure reporting and dashboards to track key performance indicators (KPIs) and provide insights into business performance. This enables data-driven decision-making.
- Test and Validate: Thoroughly test the system configuration to ensure that all features and functionalities work as expected. Validate the configuration against your business requirements to identify and resolve any issues.
Checklist for Testing and Validating the Implemented Architecture
Testing and validation are critical steps to ensure that the implemented RevOps CRM architecture functions correctly and meets your business requirements. A comprehensive checklist helps ensure that all aspects of the system are thoroughly tested.
- Data Migration Validation:
- Verify that all data has been successfully migrated from legacy systems.
- Check for data accuracy and completeness.
- Ensure data integrity by verifying data relationships.
- Validate data mapping rules.
- Test data cleansing and standardization processes.
- System Functionality Testing:
- Test all core CRM functionalities, such as lead management, contact management, opportunity management, and sales forecasting.
- Verify that user roles and permissions are correctly configured.
- Test workflow automation rules and triggers.
- Validate the integration with other systems.
- Test the user interface and user experience.
- Integration Testing:
- Test the integration between the CRM and other systems, such as marketing automation platforms, communication tools, and financial systems.
- Verify that data is flowing seamlessly between systems.
- Test the synchronization of data between systems.
- Validate the data transformation rules.
- Test error handling and logging.
- Performance Testing:
- Test the system’s performance under different load conditions.
- Measure response times and identify any performance bottlenecks.
- Test the system’s scalability.
- Monitor resource utilization.
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT):
- Involve end-users in testing the system to ensure it meets their needs and expectations.
- Gather feedback from users on the usability and functionality of the system.
- Identify and address any user-reported issues.
- Conduct training sessions for users.
- Security Testing:
- Test the security of the system to ensure that data is protected.
- Verify that access controls are correctly implemented.
- Test for vulnerabilities.
- Reporting and Analytics Validation:
- Validate the accuracy of reports and dashboards.
- Verify that key performance indicators (KPIs) are correctly calculated.
- Test the data visualization and reporting capabilities.
Best Practices for RevOps CRM
Optimizing your RevOps CRM architecture is crucial for driving efficiency, improving data accuracy, and fostering collaboration across your revenue teams. Implementing these best practices will help you unlock the full potential of your CRM and achieve your revenue goals.
Optimizing Performance of RevOps CRM Architecture
A well-performing RevOps CRM architecture is the backbone of a successful revenue operation. This requires proactive monitoring and continuous improvement.
- Regular Audits and Performance Reviews: Conduct periodic audits of your CRM to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. Review key performance indicators (KPIs) such as data entry speed, report generation time, and the overall user experience. Regularly assess CRM performance against defined SLAs and business objectives.
- Workflow Automation and Optimization: Automate repetitive tasks and workflows within the CRM to free up your team’s time and reduce errors. Optimize existing workflows to improve efficiency and streamline processes. Examples include automated lead assignment, deal stage progression, and notification triggers.
- User Training and Onboarding: Provide comprehensive training to all CRM users to ensure they understand how to effectively use the system. Ongoing training should be offered to address new features, updates, and best practices. A well-trained user base leads to better data quality and increased adoption.
- System Integrations and API Management: Seamless integration with other business systems, such as marketing automation platforms, sales enablement tools, and financial systems, is essential. Effectively manage APIs to ensure data flows smoothly between systems. This reduces manual data entry and improves data accuracy.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Design your CRM architecture to accommodate future growth and changing business needs. Choose a CRM platform that can scale with your business and adapt to evolving requirements. This includes the ability to add new users, data fields, and integrations without significant disruption.
Improving Data Quality and Data Governance
Data quality is paramount for making informed decisions and driving revenue growth. Implementing robust data governance practices is essential.
- Data Cleansing and Standardization: Implement processes to cleanse and standardize your data. This includes removing duplicates, correcting errors, and ensuring consistent formatting. Data cleansing should be performed regularly, using automated tools and manual reviews.
- Data Validation Rules: Establish data validation rules to ensure that data entered into the CRM meets specific criteria. These rules can prevent incorrect data from being entered, such as requiring a valid email address or phone number format.
- Data Governance Policies and Procedures: Define clear data governance policies and procedures that Artikel how data is collected, stored, used, and protected. This should include data ownership, access controls, and data retention policies. These policies help ensure data accuracy, consistency, and compliance.
- Regular Data Audits: Conduct regular data audits to identify and correct data quality issues. These audits should involve reviewing data for accuracy, completeness, and consistency. The audit findings should be used to improve data quality processes and procedures.
- Data Enrichment: Leverage data enrichment tools to supplement your CRM data with additional information, such as company size, industry, and contact information. This enhances the value of your data and provides a more complete view of your customers and prospects.
Aligning Sales, Marketing, and Customer Success Teams within the CRM
Effective collaboration between sales, marketing, and customer success teams is essential for driving revenue growth. The CRM serves as the central hub for these teams.
- Shared Data and Visibility: Ensure that all relevant teams have access to the same data within the CRM. This includes lead information, customer interactions, deal stages, and customer success metrics. This transparency fosters collaboration and alignment.
- Defined Lead and Account Hand-offs: Establish clear processes for lead hand-offs from marketing to sales and account hand-offs from sales to customer success. Define specific criteria for qualifying leads and accounts. Document these processes within the CRM to ensure consistency.
- Common Metrics and KPIs: Align sales, marketing, and customer success teams around common metrics and KPIs. Track metrics such as customer acquisition cost (CAC), customer lifetime value (CLTV), and churn rate. Use these metrics to measure the effectiveness of each team and identify areas for improvement.
- Collaborative Workflows and Processes: Implement collaborative workflows and processes within the CRM. For example, create workflows that trigger notifications to the customer success team when a deal closes or when a customer is at risk of churn.
- Regular Communication and Feedback Loops: Foster regular communication and feedback loops between sales, marketing, and customer success teams. Encourage teams to share insights, best practices, and customer feedback. Use the CRM to facilitate this communication, such as by using shared dashboards and reports.
Measuring the Success of RevOps CRM
Source: bytestechnolab.ca
Measuring the success of your RevOps CRM implementation is crucial to understanding its impact and ensuring continuous improvement. This involves tracking specific Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), regularly reviewing the architecture, and adapting strategies based on performance data. The goal is to validate the investment in RevOps CRM and demonstrate its contribution to overall business objectives.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to Track
Several KPIs can be used to gauge the effectiveness of a RevOps CRM implementation. These KPIs should be aligned with the business’s overarching goals, such as revenue growth, customer satisfaction, and operational efficiency. Monitoring these metrics regularly helps identify areas of strength and weakness within the RevOps CRM architecture.
- Revenue Growth: This is a primary indicator of success. Track the increase in revenue generated by deals managed within the CRM.
- Sales Cycle Length: A shorter sales cycle often indicates improved efficiency. Monitor the average time it takes to close a deal.
- Conversion Rates: This measures the percentage of leads that convert into opportunities, opportunities into customers, and so on.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): Evaluate the cost of acquiring new customers. A well-implemented RevOps CRM can help optimize marketing and sales efforts, leading to a lower CAC.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): This measures the predicted revenue a customer will generate throughout their relationship with the company. An effective RevOps CRM should contribute to a higher CLTV.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) and Net Promoter Score (NPS): These metrics assess customer satisfaction levels. A CRM that improves customer experience can lead to higher CSAT and NPS scores.
- Lead Qualification Rate: This measures the percentage of leads that meet the criteria for being considered qualified.
- Sales Team Productivity: Track metrics such as the number of calls made, emails sent, and meetings held by sales representatives.
- Data Quality: Assess the accuracy, completeness, and consistency of data within the CRM. High-quality data is essential for effective decision-making.
- Process Automation Efficiency: Monitor the time saved through automated workflows and tasks.
Framework for Regularly Reviewing and Improving the Architecture
A structured approach to reviewing and improving the RevOps CRM architecture is vital for maintaining its effectiveness over time. This process should involve regular assessments, data analysis, and continuous refinement.
- Regular Audits: Conduct periodic audits of the CRM system. These audits should assess data quality, workflow efficiency, and compliance with SLAs.
- Performance Reviews: Schedule regular reviews of the KPIs. These reviews should involve the RevOps team, sales, marketing, and customer success teams.
- Feedback Collection: Gather feedback from users across different departments. This feedback can provide valuable insights into the usability and effectiveness of the CRM.
- Data Analysis: Analyze the collected data to identify trends, patterns, and areas for improvement. This analysis should drive decision-making.
- Iterative Improvements: Implement improvements based on the findings of the reviews and data analysis. This may involve adjusting workflows, updating data models, or integrating new tools.
- Technology Updates: Keep the CRM system and related technologies up-to-date. This includes applying security patches, installing new features, and integrating with other systems.
- Training and Enablement: Provide ongoing training to users on new features and best practices. This helps ensure that users are effectively leveraging the CRM.
Example: A company implements a RevOps CRM to improve sales efficiency. After six months, they review the KPIs and find that the sales cycle length has decreased by 15% and the conversion rate has increased by 10%. This indicates a positive impact, but further analysis reveals that lead qualification is still a bottleneck. The company then focuses on improving lead scoring and qualification processes within the CRM, further optimizing their sales process.
Future Trends in RevOps CRM
The landscape of RevOps CRM is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting business needs. Understanding these emerging trends is crucial for organizations aiming to optimize their revenue generation processes and stay ahead of the competition. This section will explore some of the most significant future trends shaping RevOps CRM architecture.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning on RevOps
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to revolutionize how RevOps teams operate within the CRM environment. These technologies offer powerful capabilities to automate tasks, improve decision-making, and personalize customer experiences.
- Predictive Analytics: AI and ML algorithms can analyze vast amounts of CRM data to predict future customer behavior, identify potential churn risks, and forecast revenue with greater accuracy. For example, a CRM system could analyze a customer’s interactions, purchase history, and support tickets to predict the likelihood of them renewing their subscription. This information enables proactive outreach and targeted interventions to prevent churn.
- Automated Task Management: AI can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up RevOps professionals to focus on more strategic initiatives. This includes tasks like data entry, lead scoring, and opportunity qualification. For instance, an AI-powered CRM can automatically score leads based on their demographics, website activity, and engagement with marketing materials, ensuring sales reps prioritize the most promising prospects.
- Personalized Customer Experiences: AI can personalize customer interactions across all touchpoints. By analyzing customer data, AI can tailor marketing messages, product recommendations, and support interactions to individual preferences and needs. Consider a scenario where a CRM system uses AI to recommend relevant products to a customer based on their past purchases and browsing history, leading to increased sales.
- Improved Data Quality: AI can help to clean and maintain the accuracy of CRM data. This includes identifying and correcting errors, filling in missing information, and removing duplicate records. Clean data is essential for accurate reporting and effective decision-making.
Role of Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) in Future RevOps CRM Models
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are becoming increasingly important in the RevOps landscape. CDPs centralize customer data from various sources, providing a unified view of the customer and enabling more effective marketing, sales, and customer service.
- Unified Customer View: CDPs integrate data from various sources, including CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, e-commerce platforms, and social media channels, to create a single, comprehensive view of each customer. This unified view allows RevOps teams to understand the entire customer journey and tailor interactions accordingly.
- Enhanced Personalization: By providing a 360-degree view of the customer, CDPs enable more personalized marketing and sales efforts. For example, a CDP can identify a customer’s preferred communication channel, purchase history, and browsing behavior, allowing marketers to send targeted messages and sales reps to provide relevant product recommendations.
- Improved Data Segmentation: CDPs allow for more sophisticated customer segmentation, enabling RevOps teams to target specific customer groups with tailored campaigns and offers. This leads to higher conversion rates and improved customer engagement. For example, a CDP could segment customers based on their lifetime value, purchase frequency, or product usage, enabling targeted campaigns.
- Real-time Data Activation: CDPs can activate customer data in real-time, allowing for immediate responses to customer behavior. For example, if a customer abandons their shopping cart, the CDP can trigger an automated email to remind them of their purchase.
- Seamless Integration: CDPs are designed to integrate seamlessly with other marketing and sales technologies, including CRM systems. This integration allows for the seamless flow of data between different systems, ensuring that all teams have access to the same customer information.