Lead Scoring Models: From MQL to PQL, duh, judulnya udah bikin penasaran, kan? Nah, pokoknya kita mau ngobrolin gimana caranya ngurutin calon pelanggan biar gak buang-buang waktu, fokus ke yang potensial aja. Bayangin, sales jadi makin efektif, marketing makin nge-hits, duit masuk terus! Gak pake ribet, kita bedah mulai dari MQL (Marketing Qualified Leads) sampe PQL (Product Qualified Leads).
Kita bakal kupas tuntas gimana bikin model lead scoring yang pas buat bisnis kamu, mulai dari nyari data yang penting, nentuin skor buat tiap kriteria, sampe gimana caranya nge-integrasiin semua ini ke CRM dan platform marketing automation. Plus, kita kasih bocoran gimana caranya ngatur strategi buat beda-beda industri, biar gak salah sasaran. Penasaran, kan? Yuk, lanjut!
Introduction to Lead Scoring Models
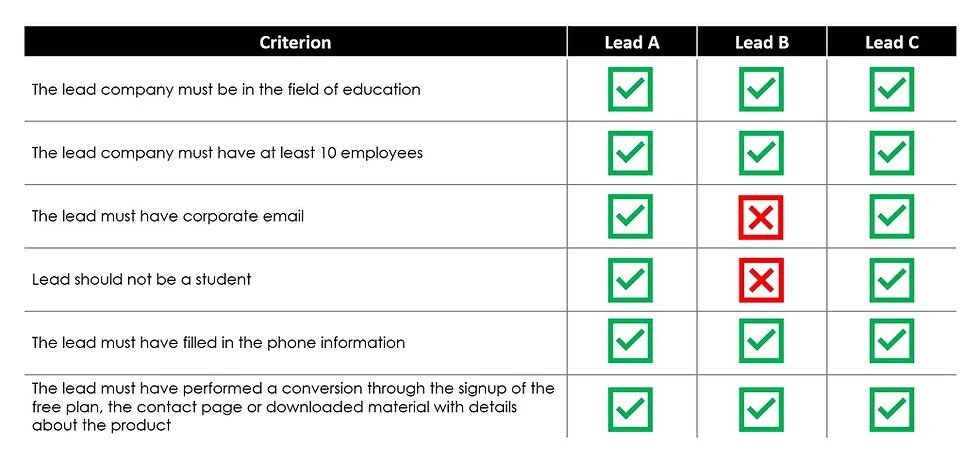
Source: wixstatic.com
Lead scoring models are indispensable tools in modern sales and marketing strategies, acting as a compass to guide efforts towards the most promising prospects. They streamline the process of identifying, qualifying, and prioritizing leads, ultimately leading to more efficient resource allocation and improved conversion rates. This section will delve into the core purpose, definition, and benefits of lead scoring, showcasing its significance in enhancing sales efficiency and marketing return on investment.
Core Purpose in Sales and Marketing
Lead scoring models serve as a vital mechanism for prioritizing leads based on their likelihood to convert into customers. This prioritization enables sales and marketing teams to focus their time and resources on the most promising prospects, thereby increasing the efficiency of their outreach efforts. The models help to identify individuals or companies who are most likely to make a purchase, allowing teams to avoid wasting time on those who are not yet ready or unlikely to buy.
This strategic approach maximizes the chances of converting leads into paying customers.
Definition of Lead Scoring and Its Benefits
Lead scoring is a methodology that assigns numerical values to leads based on their behavior, demographics, and engagement with a company’s marketing and sales activities. This scoring system allows businesses to rank leads, indicating their readiness to move through the sales funnel. The higher the score, the more qualified the lead is considered to be.The benefits of implementing lead scoring are numerous:
- Improved Lead Qualification: Lead scoring helps distinguish between Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs) and Sales Qualified Leads (SQLs), ensuring that sales teams only engage with leads who have a higher probability of converting.
- Enhanced Sales Efficiency: By prioritizing high-scoring leads, sales representatives can focus their efforts on the most promising prospects, reducing the time spent on less likely opportunities and improving overall sales productivity.
- Personalized Marketing: Lead scoring provides insights into lead behavior and preferences, enabling marketing teams to tailor their messaging and content to specific segments of the lead base, resulting in higher engagement rates.
- Increased Conversion Rates: By focusing on qualified leads and providing relevant content, lead scoring helps increase the conversion rate from leads to customers.
- Better Alignment between Sales and Marketing: Lead scoring fosters a shared understanding of what constitutes a qualified lead, improving communication and collaboration between sales and marketing teams.
Improving Sales Efficiency and Marketing ROI
Lead scoring directly impacts sales efficiency by allowing sales teams to concentrate on the most promising leads. This strategic approach leads to a reduction in wasted time and resources, as sales representatives no longer need to sift through a large volume of unqualified leads. Instead, they can prioritize those with the highest scores, which increases the probability of a successful conversion.Marketing ROI is also significantly improved through lead scoring.
By providing valuable insights into lead behavior and engagement, lead scoring enables marketing teams to optimize their campaigns and content. This targeted approach ensures that marketing efforts are aligned with the interests and needs of the leads, leading to higher engagement rates, improved conversion rates, and a greater return on marketing investments. For instance, a company using lead scoring might find that leads who download a specific whitepaper are more likely to convert.
They can then focus marketing efforts on promoting this whitepaper and similar content to attract more high-scoring leads, ultimately improving ROI.
Defining MQLs and PQLs
Understanding the distinctions between Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs) and Product Qualified Leads (PQLs) is crucial for aligning marketing and sales efforts, optimizing the customer journey, and ultimately, driving revenue growth. These lead classifications help businesses focus their resources on the most promising prospects. This section clarifies the definitions of MQLs and PQLs, providing insights into the criteria used to identify them and comparing their roles within the sales funnel.
Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs)
MQLs represent leads who have shown interest in a company’s products or services, but are not yet ready for a direct sales conversation. They have engaged with marketing content or activities, signaling a higher level of interest than a general lead. The criteria used to identify MQLs typically revolve around online behavior and content interaction.The following are common criteria used to identify MQLs:
- Content Engagement: This involves downloading ebooks, registering for webinars, or visiting specific website pages (e.g., pricing, product demos). The more content a lead consumes, the more qualified they become. For example, a lead who downloads a case study, attends a webinar, and requests a product demo is likely a higher-quality MQL than someone who only downloads a single ebook.
- Demographic and Firmographic Data: This involves information such as job title, company size, industry, and location. Businesses often define MQL criteria based on their ideal customer profile (ICP). For instance, a company selling enterprise software might prioritize leads from companies with over 500 employees.
- Behavioral Scoring: Assigning points to different actions. This method involves scoring leads based on their engagement with marketing activities. For example, a lead might receive 10 points for downloading a whitepaper, 20 points for attending a webinar, and 30 points for requesting a demo. Leads who reach a predetermined score threshold are then classified as MQLs.
- Lead Source: Leads originating from specific channels, such as paid advertising campaigns, may be considered MQLs based on the campaign’s targeting and messaging. For instance, leads generated from a high-converting Google Ads campaign targeting a specific industry segment might be automatically classified as MQLs.
Product Qualified Leads (PQLs)
PQLs are users who have demonstrated product-market fit by engaging with a product or service. They have experienced the product and shown behaviors that suggest they are likely to become paying customers. This lead qualification approach is particularly relevant for product-led growth (PLG) companies.Key behaviors that qualify a user as a PQL include:
- Product Usage: Frequent or consistent use of specific product features. This demonstrates an understanding of the product’s value. For example, a user of a project management software who regularly creates projects, assigns tasks, and collaborates with team members is likely a PQL.
- Feature Adoption: The utilization of key product features that are associated with successful customer outcomes. The more of these key features are used, the higher the likelihood of conversion. For instance, a user of a data analytics platform who actively uses data visualization tools, creates custom reports, and shares insights with their team is a strong PQL.
- Product-Market Fit Signals: Users who reach key “aha” moments within the product. These are moments when a user understands the core value proposition of the product. For example, a user of a video conferencing tool who successfully hosts a meeting with multiple participants and utilizes screen sharing is experiencing an “aha” moment.
- Trial Duration and Engagement: For companies with free trials, the duration and level of engagement during the trial period are important. Longer trial periods and more active engagement with the product increase the likelihood of conversion.
Comparing and Contrasting MQLs and PQLs
MQLs and PQLs represent different stages of the customer journey and are qualified based on distinct criteria. Understanding their differences and similarities is vital for effective lead management.The table below Artikels the key differences and similarities:
| Feature | Marketing Qualified Lead (MQL) | Product Qualified Lead (PQL) |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Interest in the company and its offerings. | Product usage and value realization. |
| Primary Qualification Criteria | Content engagement, demographic/firmographic data, behavioral scoring, lead source. | Product usage, feature adoption, product-market fit signals, trial duration. |
| Stage in the Funnel | Top of the funnel (awareness, interest). | Middle to bottom of the funnel (consideration, decision). |
| Sales Involvement | Typically passed to sales for follow-up. | Often directly contacted by sales or offered a sales conversation. |
| Ideal for | Companies with longer sales cycles, content-driven marketing. | Product-led growth (PLG) companies, freemium or trial-based models. |
While distinct, MQLs and PQLs are not mutually exclusive. A lead can become an MQL through marketing efforts and later become a PQL by experiencing the product. A well-defined lead scoring system often incorporates both MQL and PQL criteria, allowing for a comprehensive view of a lead’s readiness to convert. For example, a lead who downloads a whitepaper (MQL) and then signs up for a free trial of the product (potential PQL) would be a highly qualified lead.
Building a Lead Scoring Model: The Process
Designing and implementing a lead scoring model is a strategic endeavor that can significantly improve sales and marketing efficiency. This process requires careful planning, data analysis, and continuous refinement to ensure optimal performance. The following steps Artikel a comprehensive approach to building a successful lead scoring model.
Defining Objectives and Setting Goals
Before embarking on the technical aspects of lead scoring, it’s crucial to establish clear objectives and goals. This involves aligning the lead scoring model with the overall business strategy and defining what constitutes a “qualified” lead.
- Identify Business Goals: Determine how lead scoring will contribute to overarching business objectives. This could include increasing sales revenue, improving conversion rates, or reducing the sales cycle length.
- Define Ideal Customer Profile (ICP): Develop a detailed profile of the ideal customer, including demographics, firmographics, behaviors, and pain points. This profile will guide the scoring criteria.
- Establish Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Define measurable KPIs to track the success of the lead scoring model. Examples include lead-to-opportunity conversion rate, cost per lead, and sales cycle length.
Data Collection and Analysis
Effective lead scoring relies on a solid foundation of data. This step involves gathering and analyzing relevant information to identify patterns and trends that can be used to score leads accurately.
- Gather Data Sources: Identify all relevant data sources, including CRM systems (e.g., Salesforce, HubSpot), marketing automation platforms (e.g., Marketo, Pardot), website analytics (e.g., Google Analytics), and social media platforms.
- Data Cleansing and Standardization: Ensure data quality by cleaning and standardizing data across all sources. This includes removing duplicates, correcting errors, and formatting data consistently.
- Conduct Data Analysis: Analyze historical data to identify correlations between lead characteristics and conversion rates. This involves looking at demographic information, website activity, content engagement, and other relevant factors. For example, a study by MarketingSherpa found that companies using lead scoring experienced a 77% increase in lead generation ROI.
Selecting Scoring Criteria and Weighting
This is the core of the lead scoring process, where specific criteria are selected and weighted based on their predictive power. The criteria are the specific characteristics or behaviors that indicate a lead’s likelihood to convert.
- Choose Scoring Criteria: Based on data analysis, select criteria that are most predictive of conversion. These can be categorized into demographic, firmographic, behavioral, and engagement factors.
- Assign Weights to Criteria: Assign weights to each criterion based on its relative importance. Higher weights should be assigned to criteria that are strongly correlated with conversion. The weighting process can be based on statistical analysis, such as regression analysis, or on expert judgment.
- Develop a Scoring Scale: Define a scoring scale (e.g., 0-100) and assign points to each criterion based on its weight. This scale should be clear and easy to understand.
- Example: A lead who is a decision-maker (demographic) at a company with over 100 employees (firmographic) who has downloaded a pricing guide (behavioral) and visited the pricing page on the website (engagement) would receive a higher score than a lead who has only downloaded a whitepaper.
Implementing the Lead Scoring Model
Once the scoring criteria and weights have been determined, the model needs to be implemented within the chosen marketing and sales platforms.
- Choose Lead Scoring Software: Select a lead scoring software solution that meets the specific business needs. Consider factors such as integration capabilities, ease of use, and reporting features. This is discussed in detail in the next section.
- Configure the Software: Configure the software to apply the scoring criteria and weights to incoming leads.
- Integrate with CRM and Sales Tools: Integrate the lead scoring software with the CRM system and other sales tools to ensure that sales representatives have access to lead scores in real-time.
- Set Up Notifications and Alerts: Configure notifications and alerts to notify sales representatives when leads reach a certain score threshold.
Testing and Validation
Before fully relying on the lead scoring model, it’s crucial to test and validate its accuracy. This involves comparing the lead scores with actual conversion outcomes.
- Test the Model: Run the model on a sample of existing leads and compare the scores with their actual conversion outcomes.
- Analyze Results: Analyze the results to identify any discrepancies or areas for improvement.
- Refine the Model: Based on the analysis, refine the scoring criteria, weights, or thresholds to improve accuracy. This is an iterative process.
- Monitor and Track Performance: Continuously monitor the model’s performance using the established KPIs. Track the lead-to-opportunity conversion rate, cost per lead, and sales cycle length.
- Iterate and Improve: Regularly review and update the lead scoring model based on performance data and changing business needs.
Choosing the Right Lead Scoring Software
Selecting the right lead scoring software is critical to the success of the lead scoring model. Different software solutions offer various features and capabilities. The selection process should align with the business’s specific requirements and resources.
- Assess Business Needs: Determine the specific needs and requirements of the business. Consider factors such as the size of the sales and marketing team, the complexity of the sales process, and the existing technology infrastructure.
- Evaluate Software Features: Evaluate the features offered by different software solutions. Key features to consider include:
- Integration Capabilities: The ability to integrate with existing CRM, marketing automation, and other sales tools.
- Customization Options: The flexibility to customize scoring criteria, weights, and thresholds.
- Reporting and Analytics: Robust reporting and analytics capabilities to track performance and identify areas for improvement.
- Ease of Use: A user-friendly interface that is easy to learn and use.
- Scalability: The ability to scale the software as the business grows.
- Consider Budget and Resources: Determine the budget and resources available for implementing and maintaining the lead scoring software.
- Research and Compare Options: Research different lead scoring software solutions and compare their features, pricing, and reviews.
- Examples:
- HubSpot: Offers comprehensive marketing automation and lead scoring capabilities, suitable for businesses of all sizes.
- Marketo: A powerful marketing automation platform with advanced lead scoring features, ideal for larger enterprises.
- Pardot (Salesforce): Integrates seamlessly with Salesforce CRM and provides robust lead scoring functionality.
- Leadfeeder: Focuses on identifying website visitors and scoring them based on their behavior.
- Conduct Trials and Demos: Conduct free trials or request demos of the software solutions being considered.
- Make a Decision: Based on the assessment, evaluation, and trials, make a decision on the best lead scoring software for the business.
Scoring Criteria: Behavioral Data
Understanding and leveraging behavioral data is crucial for effective lead scoring. By analyzing how leads interact with your online assets and communications, you can gain valuable insights into their interests, needs, and likelihood of conversion. This data allows for a more nuanced and accurate assessment of lead quality, enabling targeted marketing efforts and improved sales efficiency.
Scoring Leads Based on Website Visits
Website visits provide a wealth of information about a lead’s interests. The pages a lead views, the frequency of their visits, and the time they spend on each page all contribute to a comprehensive understanding of their engagement.To score leads based on website behavior, consider the following factors:
- Page Views: Assign points based on the specific pages visited. For example, visiting the “Pricing” page could receive a higher score than visiting the “About Us” page, indicating a stronger interest in making a purchase.
- Frequency of Visits: Reward leads who frequently visit your website. This demonstrates ongoing engagement and interest.
- Time on Site: Longer session durations can indicate deeper engagement with your content.
- Pages Visited per Session: Leads who explore multiple pages within a single session are likely more engaged.
- Content Downloads: Downloading valuable resources, such as white papers or case studies, is a strong indicator of interest.
For instance, a lead who visits the pricing page (5 points), downloads a product demo (10 points), and frequently visits the blog (2 points per visit) would accumulate a significant score, indicating a highly qualified lead.
Scoring Leads Based on Email Campaign Engagement
Email campaigns offer another rich source of behavioral data. Tracking how leads interact with your emails can reveal their level of interest and inform your lead scoring model.Key email engagement metrics to consider include:
- Open Rate: Indicates whether a lead is receiving and acknowledging your emails. A higher open rate suggests a greater level of engagement.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Measures the percentage of recipients who click on links within your emails. A high CTR suggests that the email content is relevant and engaging.
- Click-Throughs on Specific Links: Clicking on specific links, such as those related to product features or pricing, can be weighted more heavily.
- Replies: Responding to an email demonstrates active engagement and a willingness to communicate.
- Unsubscribes: While not positive, unsubscribes provide important feedback and should be considered in the lead scoring model.
For example, a lead who opens multiple emails (2 points per open), clicks on a link to a product page (5 points), and replies to an email (10 points) would be considered a highly engaged lead. Conversely, a lead who consistently ignores emails or unsubscribes might receive a negative score.
Designing a System for Scoring Leads Based on Product or Service Interactions
For businesses with active product or service offerings, incorporating interaction data is critical for accurate lead scoring. Analyzing how leads utilize your product or service provides valuable insights into their level of engagement and potential for conversion.Consider these factors when designing a scoring system based on product interactions:
- Product Usage Frequency: Assign points based on how often a lead uses the product or service. Frequent usage indicates a higher level of engagement.
- Feature Usage: Reward leads who actively utilize key features of your product or service. This demonstrates a deeper understanding and investment.
- Time Spent Using the Product: Longer sessions or periods of use often correlate with greater engagement.
- Account Activity: Track activities such as logins, data uploads, and interactions with customer support.
- Purchase History: For existing customers, purchase history provides a strong indicator of value and potential for upselling or cross-selling.
For instance, a lead who logs into a software platform daily (3 points per day), uses a premium feature (5 points per use), and uploads significant data (10 points) would receive a high score. This indicates a highly engaged user who is likely deriving significant value from the product.In a real-world example, a SaaS company could use product usage data to identify “power users” who are highly likely to renew their subscriptions or upgrade to a higher tier.
These power users would receive a high lead score, prompting targeted marketing efforts to nurture their relationship and increase customer lifetime value.
Lead Scoring Models
Lead scoring models are powerful tools for prioritizing leads and improving sales and marketing efficiency. They assign numerical values to leads based on their behavior and demographics, allowing businesses to focus their efforts on the most promising prospects. This section explores the crucial aspects of implementing, integrating, and optimizing lead scoring models.
Lead Scoring Models: Implementation and Integration
Integrating lead scoring models with existing CRM and marketing automation platforms is essential for their effectiveness. This integration enables the automatic assignment of scores, the segmentation of leads, and the triggering of targeted actions.To implement and integrate lead scoring models effectively, consider the following steps:
- Choose the Right Platforms: Select CRM and marketing automation platforms that support lead scoring. Popular choices include Salesforce, HubSpot, Marketo, and Pardot. Ensure these platforms can integrate with your data sources and the data warehouse.
- Data Synchronization: Establish seamless data synchronization between your lead scoring model and your chosen platforms. This ensures that lead scores are updated in real-time across all systems. Utilize APIs or pre-built integrations to facilitate data transfer.
- Configure Lead Scoring Rules: Define the rules for calculating lead scores within your CRM or marketing automation platform. These rules should align with the criteria defined in your lead scoring model. For example, a lead who visits a pricing page might receive a higher score.
- Automate Lead Segmentation: Use lead scores to segment leads into different categories. This enables targeted marketing campaigns and sales efforts. For example, leads with high scores can be routed to sales representatives immediately.
- Set Up Triggered Actions: Configure automated actions based on lead scores. This might include sending personalized emails, enrolling leads in specific workflows, or notifying sales representatives when a lead reaches a certain score threshold.
- Test and Refine: Thoroughly test the integration to ensure that lead scores are calculated and applied correctly. Continuously monitor and refine the integration based on performance data.
Tracking the Performance of a Lead Scoring Model
Tracking the performance of a lead scoring model is vital to ensure its effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. Key performance indicators (KPIs) help to assess the model’s accuracy and its impact on business outcomes.To effectively track the performance, consider the following:
- Lead Conversion Rate: Track the conversion rate of leads at different score levels. This metric indicates how well the model predicts which leads will convert into customers. Higher-scoring leads should ideally have a higher conversion rate.
- Sales Cycle Length: Measure the average sales cycle length for leads at different score levels. A shorter sales cycle for high-scoring leads suggests that the model is effectively prioritizing qualified leads.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): Analyze the CPA for leads at different score levels. The model should help reduce the CPA by focusing marketing and sales efforts on the most promising leads.
- Lead Quality: Evaluate the quality of leads generated by the model. This can be assessed by examining the win rate, average deal size, and customer lifetime value (CLTV) of converted leads.
- Accuracy and Precision: Calculate the accuracy and precision of the lead scoring model. These metrics assess the model’s ability to correctly identify leads that will convert and avoid false positives.
- Reporting and Dashboards: Create reports and dashboards to visualize the performance of the lead scoring model. These reports should include key metrics and trends over time.
Analyzing Lead Scoring Data to Optimize the Model
Analyzing lead scoring data is an ongoing process that helps to refine and optimize the model for improved performance. Regular analysis of key metrics and feedback from sales and marketing teams can reveal areas for improvement.Optimizing the lead scoring model through data analysis involves the following actions:
- Identify High-Performing Behaviors: Analyze which behaviors and characteristics are most strongly correlated with conversion. This information can be used to adjust the scoring criteria and give more weight to the most impactful factors. For example, if downloading a specific white paper consistently leads to conversions, increase the points assigned to that action.
- Refine Scoring Weights: Adjust the weights assigned to different scoring criteria based on their impact on conversion rates. Use data to determine which factors are most predictive of success and adjust their scores accordingly.
- Monitor and Adjust Thresholds: Regularly review the lead score thresholds used to segment leads and trigger actions. Adjust these thresholds based on performance data to ensure that leads are being qualified and routed appropriately.
- Analyze Sales Team Feedback: Gather feedback from sales representatives on the quality of leads generated by the model. Sales reps can provide valuable insights into which leads are truly qualified and which are not.
- Conduct A/B Testing: Experiment with different lead scoring criteria and weights through A/B testing. This can help identify the most effective approach for scoring leads.
- Retrain the Model: Regularly retrain the lead scoring model with new data to ensure its accuracy and relevance. The effectiveness of a model can diminish over time as market conditions and customer behavior change.
Iteration and Optimization of Lead Scoring Models
Source: influno.com
Regularly refining lead scoring models is crucial for their sustained effectiveness. The business landscape evolves, customer behavior shifts, and marketing strategies adapt. A static lead scoring model quickly becomes outdated, leading to inaccurate lead qualification, wasted sales efforts, and ultimately, a decline in conversion rates. Continuous monitoring and adjustment are therefore essential for maximizing the return on investment in lead scoring.
The Importance of Regular Review and Refinement
Lead scoring models require ongoing attention because of several factors that can impact their performance. This includes changes in product offerings, shifts in target audience demographics, and modifications to marketing campaigns. To ensure the model continues to accurately identify high-potential leads, regular reviews and adjustments are necessary.
- Data Drift: Over time, the data used to train the model can change, leading to decreased accuracy. For example, a new product launch might attract a different customer profile than the existing products, rendering the original scoring criteria less relevant.
- Changing Customer Behavior: Consumer preferences and online behavior are constantly evolving. What constitutes a “qualified lead” today may differ significantly from what it was a year ago. A model that doesn’t adapt to these changes will miss valuable opportunities.
- Marketing Campaign Performance: The success of marketing campaigns directly influences lead quality. If a campaign attracts a different type of lead than anticipated, the scoring model needs to reflect this.
- Business Objectives: Changes in company goals, such as a shift in focus to a new market segment, necessitate adjustments to the lead scoring model to align with the new priorities.
Adjusting Scoring Criteria Based on Performance Data, Lead Scoring Models: From MQL to PQL
Analyzing performance data is the cornerstone of optimizing lead scoring models. By tracking key metrics, such as conversion rates, sales cycle length, and customer lifetime value (CLTV) for leads generated through the model, businesses can identify areas for improvement and refine the scoring criteria.
Consider a scenario where a lead scoring model initially assigns high points to leads who download a specific whitepaper. After analyzing the data, it’s discovered that while many leads download the whitepaper, few convert into paying customers. In contrast, leads who attend a webinar on a related topic show a significantly higher conversion rate.
Based on this analysis, the scoring model should be adjusted. Here’s how:
- Increase the score for attending the webinar: This reflects the higher probability of conversion associated with this action.
- Decrease the score for downloading the whitepaper: This acknowledges the lower conversion rate associated with this action.
- Introduce new scoring criteria: If the analysis reveals that leads from a specific industry or with a certain job title are more likely to convert, add these as scoring criteria.
The process of adjustment often involves the following steps:
- Gather Data: Collect data on lead behavior, conversion rates, sales outcomes, and other relevant metrics.
- Analyze Data: Identify patterns, correlations, and insights that reveal the effectiveness of the current scoring criteria.
- Adjust Scoring Criteria: Modify the points assigned to different lead behaviors and attributes based on the data analysis.
- Test and Validate: Implement the changes and monitor the results to ensure they improve the model’s performance.
Using A/B Testing to Optimize Lead Scoring Effectiveness
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is a powerful method for optimizing lead scoring models. This involves creating two or more versions of the model with different scoring criteria and comparing their performance to determine which version performs best.
For example, a company might create two versions of its lead scoring model:
- Version A: The existing model.
- Version B: A modified model that assigns more points to leads who visit the pricing page.
The company would then apply each model to a random subset of leads and track the conversion rates for each group. The model that generates a higher conversion rate is considered the more effective version.
Benefits of A/B Testing:
- Data-Driven Decisions: A/B testing provides concrete data to support decisions about which scoring criteria are most effective.
- Continuous Improvement: A/B testing enables a cycle of continuous improvement, allowing businesses to constantly refine their lead scoring models.
- Reduced Risk: A/B testing allows businesses to test changes to their lead scoring models without risking a complete overhaul of the existing system.
A Real-World Example:
A software company uses A/B testing to optimize its lead scoring model. They initially assign a high score to leads who request a product demo. After A/B testing, they discover that leads who watch a specific explainer video on their website have a higher conversion rate than those who request a demo. The company then adjusts its model to give more weight to watching the video, leading to a significant increase in qualified leads and sales.
Lead Scoring and Sales Alignment: Lead Scoring Models: From MQL To PQL
Lead scoring models are not just about identifying potential customers; their true power lies in bridging the gap between marketing and sales. Successful implementation hinges on a strong alignment between these two crucial teams. This alignment ensures that marketing efforts are directly contributing to sales revenue and that sales representatives are focusing their time and energy on the most promising leads.
The synergy created through this collaboration maximizes the efficiency of the entire sales and marketing funnel.
Importance of Aligning Sales and Marketing Teams
The alignment of sales and marketing teams around lead scoring is paramount for achieving optimal business outcomes. It fosters a shared understanding of what constitutes a qualified lead, leading to improved lead quality and increased conversion rates. Without this alignment, marketing may generate leads that sales deems unqualified, leading to wasted resources and frustration. Sales teams, conversely, might miss out on high-potential leads that marketing has successfully nurtured.
- Shared Definitions: Establishing a common language around lead definitions (MQLs, SQLs, etc.) is fundamental. Both teams must agree on the criteria that define a qualified lead. This includes demographics, firmographics, and behavioral data.
- Improved Lead Quality: When both teams understand the lead scoring model, marketing can focus on attracting and nurturing leads that fit the ideal customer profile. Sales, in turn, receives a stream of leads that are more likely to convert.
- Increased Sales Efficiency: Sales representatives can prioritize their efforts on the highest-scoring leads, those most likely to close. This leads to a more efficient use of sales resources and a higher return on investment (ROI).
- Enhanced Communication: Regular communication and feedback loops between sales and marketing are crucial. Sales can provide feedback on the quality of leads, which marketing can use to refine the lead scoring model and improve lead generation efforts.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Lead scoring provides data that both teams can use to make informed decisions. Marketing can track the performance of different lead generation campaigns, and sales can analyze which types of leads are converting best.
Creating a Service Level Agreement (SLA) Based on Lead Scores
A Service Level Agreement (SLA) between sales and marketing, built upon lead scores, formalizes the relationship and sets expectations for lead handling and follow-up. This agreement clarifies responsibilities and ensures accountability, ultimately streamlining the lead-to-customer journey.
- Defining Lead Qualification Thresholds: The SLA should clearly define the lead score required for a lead to be considered an MQL (Marketing Qualified Lead) and an SQL (Sales Qualified Lead). For instance, an MQL might be a lead with a score of 50 or higher, indicating they’ve shown interest in specific content or engaged with the company. An SQL might require a score of 80 or higher, coupled with a specific interaction, such as requesting a demo or contacting sales directly.
- Lead Acceptance Timeframe: The SLA should specify the time frame within which sales must accept or reject a lead. This ensures that leads are followed up promptly, capitalizing on their interest while it is fresh. A common timeframe is within 24-48 hours.
- Lead Follow-up Requirements: The SLA should Artikel the required follow-up actions by sales representatives for different lead scores. For example, a high-scoring lead might require a personalized phone call, while a lower-scoring lead might warrant an email sequence or further nurturing from marketing.
- Reporting and Accountability: The SLA should include provisions for reporting on lead performance and holding both teams accountable for their responsibilities. This includes tracking lead conversion rates, sales cycle length, and the ROI of marketing campaigns.
- Regular Review and Adjustment: The SLA should be reviewed and adjusted regularly, typically quarterly or semi-annually, to reflect changes in the business environment, lead scoring model, and sales processes. This ensures the SLA remains relevant and effective.
Role of Lead Scoring in Improving the Sales and Marketing Handoff Process
Lead scoring significantly enhances the sales and marketing handoff process, creating a smoother transition and increasing the likelihood of conversion. It ensures that sales representatives receive qualified leads equipped with relevant information, allowing them to engage prospects effectively.
- Improved Lead Qualification: Lead scoring ensures that sales receives only qualified leads, those that have demonstrated sufficient interest and meet the predetermined criteria. This eliminates wasted time and resources on unqualified leads.
- Enhanced Lead Intelligence: Lead scoring provides sales representatives with valuable insights into a lead’s behavior, interests, and engagement with marketing content. This information allows sales to personalize their outreach and tailor their messaging to the lead’s specific needs.
- Streamlined Handoff Process: The lead scoring model automates the handoff process, triggering alerts and notifications when a lead reaches a specific score threshold. This ensures that leads are routed to the appropriate sales representative promptly.
- Increased Sales Efficiency: By prioritizing high-scoring leads, sales representatives can focus their efforts on the most promising prospects, leading to a higher conversion rate and a shorter sales cycle.
- Better Communication and Collaboration: Lead scoring facilitates better communication and collaboration between sales and marketing. Sales can provide feedback on lead quality, which marketing can use to refine the lead scoring model. This feedback loop ensures that both teams are working together to achieve the same goals.
Challenges and Common Pitfalls in Lead Scoring
Implementing lead scoring models, while offering significant benefits, isn’t without its hurdles. Successfully navigating these challenges requires a proactive approach, careful planning, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Failing to address these issues can lead to inaccurate scores, wasted resources, and ultimately, a less effective sales and marketing alignment. Understanding and mitigating these potential pitfalls is crucial for maximizing the value of lead scoring.
Data Quality and Availability Issues
The foundation of any effective lead scoring model rests on the quality and availability of data. Without reliable and comprehensive data, the model’s accuracy and predictive power are severely compromised. This involves the sources, the data types collected, and how often it is updated.
- Insufficient Data Volume: If the dataset is too small, the model may struggle to identify meaningful patterns and correlations. This can result in inaccurate scores and a model that doesn’t generalize well to new leads.
- Data Silos: When data is fragmented across different systems (CRM, marketing automation, website analytics), it becomes difficult to get a holistic view of the lead’s behavior and engagement. This limits the information available for scoring.
- Data Inconsistencies: Inaccurate or inconsistent data, such as typos, outdated information, or conflicting values, can skew the model’s results. For example, different formatting for the same information in various sources.
- Lack of Data Integration: The inability to seamlessly integrate data from various sources can hinder the model’s effectiveness. If data from different platforms cannot be combined, it becomes challenging to gain a comprehensive understanding of a lead’s behavior.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA adds complexity. Organizations must ensure they collect and use data ethically and transparently, which can impact the types of data available for scoring.
Model Complexity and Maintenance Challenges
Building a lead scoring model is not a “set it and forget it” endeavor. It requires ongoing maintenance, adjustments, and a deep understanding of the business and its customers. Ignoring these aspects can lead to model decay and decreased effectiveness.
- Overly Complex Models: Complex models with too many variables can be difficult to understand, maintain, and interpret. This can lead to challenges in identifying the factors driving the scores and making necessary adjustments.
- Lack of Regular Model Review: The business environment, customer behavior, and marketing strategies evolve over time. If the model isn’t regularly reviewed and updated, it can become outdated and inaccurate.
- Insufficient Resources for Maintenance: Without dedicated resources (personnel, tools, budget), the model may not receive the necessary attention for ongoing monitoring, analysis, and refinement.
- Difficulty in Interpreting Results: If the scoring criteria are not transparent or easily understood, it can be difficult to interpret the scores and understand why certain leads are ranked higher than others. This can undermine sales and marketing alignment.
- Failure to Adapt to Changing Market Conditions: Changes in the market, such as new competitors, evolving customer needs, or shifts in buying behavior, require the model to be adjusted to remain relevant. Failure to do so can render the model ineffective.
Sales and Marketing Misalignment
Effective lead scoring requires a strong partnership between sales and marketing. When these teams are not aligned, the model can fail to deliver the expected results, leading to frustration and inefficiencies.
- Lack of Agreement on Lead Definitions: Disagreement on what constitutes a qualified lead (MQL, SQL, PQL) can lead to conflicting expectations and wasted resources.
- Poor Communication and Feedback Loops: Without clear communication channels and feedback loops, it’s difficult to understand how the model is performing in practice and make necessary adjustments.
- Sales Resistance to the Model: If the sales team doesn’t trust the model or doesn’t understand how to use it, they may ignore the lead scores, rendering the model ineffective.
- Misalignment on Scoring Criteria: If the scoring criteria don’t align with the sales team’s priorities or the sales process, the model may not effectively identify leads that are likely to convert.
- Failure to Integrate Lead Scoring into Sales Workflows: If the lead scores aren’t integrated into the sales team’s CRM and workflows, it can be difficult for them to prioritize leads effectively.
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Here’s a list of common pitfalls in lead scoring and actionable strategies to mitigate them:
- Pitfall: Building a model without clear business objectives.
- Solution: Define specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) goals before building the model. For instance, increase sales qualified leads (SQLs) by 15% in the next quarter.
- Pitfall: Using only demographic data for scoring.
- Solution: Incorporate behavioral data (website visits, content downloads, email engagement) to understand lead intent and engagement levels.
- Pitfall: Creating an overly complex model with too many variables.
- Solution: Start with a simple model and gradually add complexity as needed. Focus on the most impactful variables.
- Pitfall: Neglecting data quality and cleansing.
- Solution: Implement data validation rules, regular data cleansing processes, and ensure data consistency across all systems.
- Pitfall: Failing to regularly review and update the model.
- Solution: Schedule regular reviews (e.g., quarterly or semi-annually) to assess model performance and make necessary adjustments based on data and feedback.
- Pitfall: Lack of sales and marketing alignment.
- Solution: Foster open communication, establish clear lead definitions, and involve both teams in the model-building and review process.
- Pitfall: Ignoring feedback from the sales team.
- Solution: Create a feedback loop where sales representatives can provide insights and suggestions on lead quality and scoring accuracy.
- Pitfall: Not tracking and measuring the model’s performance.
- Solution: Track key metrics (e.g., lead conversion rates, sales cycle length, revenue generated) to assess the model’s effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
- Pitfall: Failing to communicate the model’s purpose and benefits to the sales team.
- Solution: Provide training and documentation to help the sales team understand how to use the lead scores and prioritize their efforts.
- Pitfall: Not adapting the model to changing market conditions and customer behavior.
- Solution: Continuously monitor market trends, customer behavior, and sales performance to identify areas where the model needs to be adjusted.
Lead Scoring Models in Different Industries
Lead scoring models are not one-size-fits-all. The optimal approach varies significantly depending on the industry, business model, and target audience. Understanding these nuances is crucial for building effective lead scoring systems that drive conversions and maximize ROI. Adapting lead scoring strategies to specific industry contexts allows businesses to prioritize leads more accurately, personalize marketing efforts, and ultimately, improve sales performance.
Adapting Lead Scoring Models
Adapting lead scoring models requires a deep understanding of the specific industry dynamics, customer journey, and sales cycle. This adaptation process involves customizing scoring criteria, weighting factors, and lead qualification thresholds to align with industry-specific behaviors and conversion patterns.For instance, a SaaS company might prioritize leads based on product usage metrics, such as feature adoption or login frequency. Conversely, an e-commerce business could focus on purchase history, average order value, and browsing behavior.
Tailoring the model to the industry’s unique characteristics ensures that the lead scoring system accurately reflects the likelihood of conversion.
Lead Scoring Strategies Across Industries
Lead scoring strategies vary considerably across different industries. The key differences often stem from the nature of the product or service, the length of the sales cycle, and the typical customer journey.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): SaaS companies often focus on product usage, engagement, and feature adoption.
- Example: A lead who frequently uses core features, attends webinars, and interacts with customer support is assigned a higher score, indicating a strong likelihood of conversion.
- E-commerce: E-commerce businesses prioritize purchase history, browsing behavior, and cart abandonment.
- Example: A lead who has previously purchased products, frequently views product pages, and abandons a shopping cart is assigned a high score, signaling a high purchase intent.
- Financial Services: Financial service providers often consider factors such as creditworthiness, income, and financial goals.
- Example: A lead who demonstrates a strong credit history, a high income, and a clear financial need (e.g., home purchase, investment) is assigned a high score, indicating a good fit for financial products.
- Real Estate: Real estate businesses may focus on location preferences, budget, and property viewing activity.
- Example: A lead who frequently views properties in a specific neighborhood, has a defined budget, and attends open houses is assigned a high score, suggesting a strong interest in purchasing a property.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers can use lead scoring based on symptoms, insurance, and appointment scheduling.
- Example: A lead who searches for specific medical conditions, has insurance coverage, and schedules an initial consultation is assigned a high score, indicating a need for medical services.
Tailoring Lead Scoring Models
Tailoring lead scoring models to specific business types requires a detailed analysis of customer data, sales cycles, and conversion patterns. This involves identifying the key behaviors and attributes that correlate with successful conversions and assigning appropriate weights to each criterion.Here’s a breakdown of how to tailor lead scoring models:
- Define Ideal Customer Profile (ICP): Understand the characteristics of the most successful customers.
- Analyze Customer Data: Examine historical data to identify commonalities among converted leads.
- Identify Key Scoring Criteria: Determine the most relevant attributes and behaviors to score.
- Weight Scoring Criteria: Assign weights based on the impact of each criterion on conversions.
- Set Lead Qualification Thresholds: Define the score required to qualify a lead as an MQL or PQL.
- Continuously Monitor and Refine: Regularly evaluate the model’s performance and make adjustments as needed.
For instance, a business targeting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) might prioritize lead attributes such as company size, industry, and job title. The model would then assign higher weights to leads that match these criteria, ensuring that marketing efforts are focused on the most promising prospects.By implementing these steps, businesses can create highly effective lead scoring models that drive conversions and improve sales performance across different industries.
The Future of Lead Scoring
Lead scoring, a cornerstone of modern marketing and sales, is poised for significant evolution. Driven by technological advancements and shifting consumer behaviors, the future of lead scoring promises more sophisticated, personalized, and predictive models. This evolution will not only improve efficiency but also reshape how businesses engage with potential customers.
Emerging Trends in Lead Scoring
Several trends are shaping the future of lead scoring, promising to refine the process and enhance its effectiveness. These trends are geared towards greater accuracy, personalization, and integration across various marketing and sales platforms.
- Hyper-Personalization: The ability to tailor lead scoring models to individual customer segments or even specific leads is increasing. This goes beyond broad demographics and leverages detailed behavioral data, such as content consumption patterns, website interactions, and social media engagement.
- Predictive Analytics: Lead scoring models are increasingly incorporating predictive analytics. This allows businesses to forecast the likelihood of a lead converting into a customer, going beyond simply assessing current engagement to anticipate future behavior.
- Cross-Channel Integration: Lead scoring is no longer confined to a single channel. The future involves seamless integration across various platforms, including marketing automation, CRM systems, social media, and even offline interactions. This provides a holistic view of the customer journey.
- Focus on Privacy and Data Ethics: With growing concerns around data privacy, lead scoring models are evolving to be more transparent and ethical. This includes obtaining explicit consent for data collection and providing users with greater control over their data.
- Emphasis on Account-Based Scoring: For businesses focusing on B2B sales, account-based lead scoring is gaining traction. This approach prioritizes scoring entire accounts rather than individual leads, aligning sales and marketing efforts to target high-value accounts.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Lead Scoring Models
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are revolutionizing lead scoring, offering capabilities that were previously unimaginable. These technologies enable more accurate, dynamic, and adaptable scoring models.
- Enhanced Data Analysis: AI and ML algorithms can process vast amounts of data from various sources, identifying patterns and correlations that humans might miss. This allows for more sophisticated lead scoring criteria.
- Dynamic Scoring: ML models can continuously learn and adapt to changing customer behavior and market trends. This results in more dynamic lead scores that reflect the current likelihood of conversion.
- Predictive Capabilities: AI-powered lead scoring can predict future customer behavior with greater accuracy, allowing businesses to proactively engage with leads and optimize their sales efforts. For example, an AI model might predict that a lead who has downloaded three specific whitepapers and attended a webinar is highly likely to convert within the next month.
- Automated Segmentation: AI can automate the process of segmenting leads based on their behavior and characteristics. This allows businesses to personalize their marketing and sales efforts more effectively.
- Reduced Bias: By using objective data and algorithms, AI can help reduce bias in lead scoring models, leading to fairer and more accurate assessments. However, it’s important to note that the data used to train these models must be carefully curated to avoid perpetuating existing biases.
Vision of Lead Scoring in the Future
The future of lead scoring paints a picture of a highly integrated, intelligent, and personalized system that is seamlessly interwoven into the entire customer journey. This vision anticipates a level of sophistication that will drastically improve the efficiency and effectiveness of sales and marketing efforts.
- Real-time Scoring: Lead scores will be updated in real-time, reflecting the latest interactions and behaviors. This allows sales teams to engage with leads at the optimal moment.
- AI-Driven Insights: AI will provide actionable insights into lead behavior, enabling sales teams to understand the “why” behind the scores and tailor their outreach accordingly. This could include suggesting specific content or messaging based on a lead’s interests and past interactions.
- Hyper-Personalized Journeys: Marketing and sales efforts will be fully personalized, with each lead receiving a tailored experience based on their individual score and behavior. This will be enabled by sophisticated marketing automation systems.
- Seamless Integration: Lead scoring will be seamlessly integrated with all relevant platforms, including CRM, marketing automation, and sales enablement tools, creating a unified view of the customer.
- Focus on Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): Lead scoring models will go beyond predicting conversions and will also incorporate factors that predict customer lifetime value, enabling businesses to prioritize leads with the highest potential long-term value.