First-Party Data Strategy: Using CRM with a CDP is your gateway to mastering customer relationships and driving unparalleled marketing success. Dive into the world of data-driven strategies, where you’ll discover the power of owning your customer information and transforming it into actionable insights. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to leverage your data, personalize customer experiences, and optimize your marketing efforts for maximum impact.
We’ll explore the core concepts of first-party data, delve into the capabilities of CRM and CDP systems, and unveil a synergistic approach that combines these powerful technologies. Learn how to collect data ethically, segment your audience effectively, and personalize your marketing campaigns to resonate with each customer. Prepare to unlock the full potential of your customer data and achieve remarkable results.
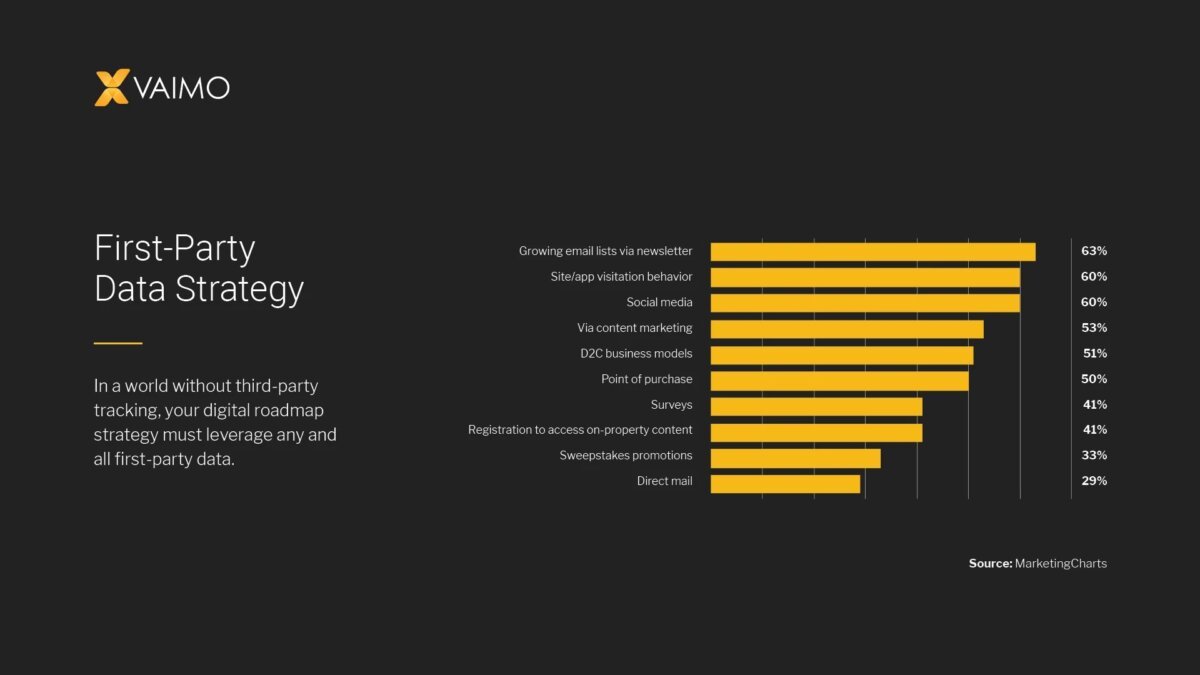
Understanding First-Party Data: The Foundation
First-party data is becoming increasingly critical for businesses aiming to create personalized customer experiences and maintain a competitive edge. This section delves into the core definition of first-party data, explores its diverse types, and highlights its advantages over other data sources in the current marketing environment. The effective utilization of first-party data forms the bedrock of a successful customer relationship management (CRM) and customer data platform (CDP) strategy.
Defining First-Party Data
First-party data is information a company collects directly from its own customers. This data is owned by the business and gathered through direct interactions, without relying on third-party sources. This direct ownership gives companies complete control over the data, ensuring its accuracy and relevance.
Types of First-Party Data
First-party data encompasses a wide range of information collected through various channels. Understanding these different types of data and their sources is crucial for building a comprehensive customer profile.
- Website Interactions: This includes data collected from a company’s website, such as browsing history, time spent on pages, content downloads, and search queries. For example, a user who frequently visits the “Running Shoes” section of an e-commerce site and searches for “trail running shoes” provides valuable data about their interests and needs.
- Purchase History: This includes all past purchase data, such as products bought, transaction dates, amounts spent, and payment methods. Analyzing purchase history allows businesses to identify customer preferences, predict future purchases, and tailor product recommendations. A customer who consistently buys organic groceries might be targeted with promotions for new organic products.
- Customer Service Interactions: This encompasses data collected through customer service channels, including emails, phone calls, and live chat transcripts. Information gathered from these interactions, such as the nature of inquiries, problem resolutions, and customer feedback, provides insights into customer satisfaction and pain points. For example, a customer repeatedly contacting customer service about a product defect signals a potential need for product improvement or replacement.
- CRM Data: This data resides within the Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system and includes customer demographics (age, location, gender), contact information (email, phone number), and interactions with sales and marketing teams. A CRM system can track a customer’s journey from lead to purchase, providing valuable insights into their behavior.
- Social Media Interactions: This includes data from a company’s owned social media channels, such as likes, shares, comments, and direct messages. Social media data provides insights into customer preferences, brand sentiment, and engagement levels. Analyzing social media data can help identify trending topics and tailor content accordingly.
- Mobile App Data: If a company has a mobile app, it can collect data on user behavior within the app, such as feature usage, in-app purchases, and location data (with user consent). This data helps personalize the mobile experience and deliver targeted promotions.
- Surveys and Feedback: Data gathered from customer surveys, feedback forms, and reviews provides direct insights into customer satisfaction, product preferences, and areas for improvement. This data is often qualitative and can be used to supplement other data sources.
Advantages of First-Party Data
Leveraging first-party data offers significant advantages compared to relying on second-party or third-party data. These advantages relate to control, cost, and compliance.
- Control: Businesses have complete control over first-party data, including how it’s collected, stored, and used. This allows for greater accuracy, reliability, and relevance. Unlike third-party data, which can be outdated or inaccurate, first-party data is directly sourced from the customer, ensuring its quality.
- Cost: Collecting first-party data is generally more cost-effective than purchasing second-party or third-party data. It relies on existing channels and interactions with customers, reducing the need for external data providers. This helps to streamline marketing budgets.
- Compliance: First-party data collection aligns with data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA, as it’s collected with explicit consent. This reduces the risk of legal issues and builds trust with customers. The emphasis on transparency and consent helps foster a positive brand image.
The core benefit of first-party data is the ability to personalize the customer experience. By understanding individual customer preferences, behaviors, and needs, businesses can deliver targeted messaging, relevant product recommendations, and seamless interactions across all touchpoints.
CRM: The Central Hub for Customer Information
Source: vaimo.com
A Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is a cornerstone of any effective first-party data strategy. It serves as a centralized repository for customer information, facilitating a 360-degree view of each customer and enabling personalized interactions. By effectively leveraging a CRM, businesses can collect, organize, and utilize customer data to improve customer relationships, drive sales, and enhance overall business performance.
The Role of a CRM System, First-Party Data Strategy: Using CRM with a CDP
The primary function of a CRM system is to centralize customer data. This involves collecting, storing, and managing all interactions and information related to customers. It goes beyond simple contact management, encompassing a wide range of data points, from basic contact details to detailed purchase history, communication logs, and marketing interactions.A CRM system’s core functions include:
- Data Collection: CRM systems collect data from various sources, including website interactions, email communications, social media, sales transactions, and customer service interactions. This data is typically gathered through web forms, email tracking, phone calls, and direct data entry by sales and customer service representatives.
- Data Storage: The CRM stores this collected data in a structured and organized manner, often using a relational database. This allows for efficient data retrieval and analysis. Data is usually categorized into different fields, such as contact information, account details, sales opportunities, and service requests.
- Data Management: CRM systems provide tools for managing customer data, including data cleansing, deduplication, and enrichment. This ensures data accuracy and consistency. Data cleansing involves identifying and correcting errors in the data, while deduplication removes duplicate entries. Data enrichment involves supplementing existing data with additional information from external sources, such as demographic data or social media profiles.
- Data Analysis: CRM systems offer reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing businesses to analyze customer data to gain insights into customer behavior, preferences, and trends. These insights can be used to inform marketing campaigns, sales strategies, and customer service initiatives. Common analyses include customer segmentation, churn prediction, and sales forecasting.
Key Features and Functionalities of a CRM
The effectiveness of a CRM system for first-party data collection hinges on its features and functionalities. These capabilities enable businesses to gather, manage, and utilize customer data effectively.The essential features and functionalities relevant to first-party data collection include:
- Contact Management: This feature allows for the storage and management of individual customer contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses.
- Lead Management: CRM systems track leads through the sales funnel, from initial contact to conversion. This involves capturing lead information, scoring leads based on their engagement, and assigning leads to sales representatives.
- Sales Force Automation (SFA): SFA features automate sales processes, such as opportunity tracking, quote generation, and order management. This data can be used to understand customer purchase behavior and sales cycles.
- Marketing Automation: This functionality enables the automation of marketing campaigns, including email marketing, social media marketing, and lead nurturing. Data from these campaigns, such as open rates, click-through rates, and conversions, provides valuable insights into customer engagement and preferences.
- Customer Service and Support: CRM systems often include features for managing customer service interactions, such as case management, knowledge bases, and live chat. This data can be used to understand customer issues and improve customer satisfaction.
- Reporting and Analytics: CRM systems provide dashboards and reports that allow businesses to visualize and analyze customer data. This includes metrics such as customer lifetime value, customer acquisition cost, and churn rate.
- Integration Capabilities: A crucial feature is the ability to integrate with other systems, such as e-commerce platforms, marketing automation tools, and social media platforms. This allows for the seamless flow of data between different systems, providing a more comprehensive view of the customer.
Customer Segmentation Scenario
CRM systems are powerful tools for segmenting customers based on their behavior and demographics. This segmentation allows for targeted marketing campaigns, personalized customer experiences, and improved customer engagement.Consider the following scenario: A retail company uses a CRM to segment its customers. The company has collected data on customer purchase history, demographics, and website activity.The company might segment its customers into the following groups:
- High-Value Customers: Customers who have made frequent purchases, spent a significant amount of money, and have a high customer lifetime value. The CRM would identify these customers based on their purchase history and spending habits.
- Loyal Customers: Customers who have made repeat purchases and have a long relationship with the company. The CRM would track the number of purchases and the time since the last purchase to identify these customers.
- New Customers: Customers who have made their first purchase within a specific timeframe. The CRM would track the date of the first purchase to identify these customers.
- Customers Interested in Specific Products: Customers who have shown interest in specific product categories or have browsed specific product pages on the company’s website. The CRM would track website activity and purchase history to identify these customers.
- Demographic-Based Segments: Customers segmented based on demographic data, such as age, gender, location, and income. This data can be collected through web forms, surveys, or third-party data sources.
The company can then use these segments to create targeted marketing campaigns. For example:
- High-Value Customers: Offer exclusive discounts, early access to new products, and personalized recommendations.
- Loyal Customers: Send thank-you notes, offer loyalty rewards, and provide special promotions.
- New Customers: Send welcome emails, offer introductory discounts, and provide product recommendations.
- Customers Interested in Specific Products: Send targeted emails promoting related products and offer personalized content.
- Demographic-Based Segments: Tailor marketing messages and product offerings to match the specific interests and needs of each demographic group.
By leveraging its CRM system, the company can deliver more relevant and personalized experiences to its customers, leading to increased customer engagement, improved customer satisfaction, and higher sales. This approach highlights the practical application of a CRM in harnessing first-party data for strategic advantage.
CDP: Enhancing Data Capabilities
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) is a critical component of a modern first-party data strategy, serving as a centralized hub for customer information from various sources. Its primary function is to collect, unify, and activate customer data, enabling businesses to create more personalized and effective customer experiences. By integrating data from disparate systems, CDPs provide a comprehensive view of each customer, empowering businesses to make data-driven decisions across marketing, sales, and customer service.
CDP: Purpose and Benefits
The primary purpose of a Customer Data Platform (CDP) is to create a unified and persistent customer database by ingesting data from numerous sources. This unified view allows businesses to understand their customers more comprehensively and tailor their interactions accordingly. CDPs offer several key benefits, including enhanced personalization, improved customer segmentation, and streamlined marketing efforts.The benefits of using a CDP can be summarized as follows:
- Data Unification: CDPs collect and integrate data from various sources, such as CRM systems, marketing automation platforms, website analytics, and social media. This consolidation creates a single, unified view of each customer.
- Customer Profiling: By combining data from different sources, CDPs enable the creation of detailed customer profiles, including demographics, behaviors, preferences, and purchase history.
- Enhanced Personalization: With a comprehensive understanding of each customer, businesses can personalize their marketing messages, product recommendations, and website experiences.
- Improved Segmentation: CDPs allow for the creation of more granular customer segments based on various criteria, enabling targeted marketing campaigns.
- Real-time Data Activation: CDPs can activate customer data in real-time, enabling businesses to deliver personalized experiences across multiple channels.
- Increased Marketing ROI: By targeting the right customers with the right messages at the right time, CDPs can improve marketing campaign performance and increase ROI.
- Data Governance and Compliance: CDPs often include features for data governance and compliance with privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
CDP vs. CRM: Core Functionalities and Target Users
While both Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems and Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) deal with customer data, they serve different purposes and are designed for different user groups. Understanding the core functionalities and target users of each system is crucial for building an effective first-party data strategy.The differences between CRM and CDP can be explained as follows:
- Core Functionality: CRM systems primarily focus on managing customer interactions and sales processes, providing a centralized repository for sales, marketing, and customer service activities. CDPs, on the other hand, specialize in collecting, unifying, and activating customer data from various sources, creating a single customer view.
- Data Focus: CRMs typically store structured data related to customer interactions, such as contact information, sales leads, and support tickets. CDPs handle both structured and unstructured data, including website behavior, social media activity, and offline interactions.
- Data Sources: CRM data primarily comes from direct interactions with customers, such as sales calls and email correspondence. CDPs integrate data from a wider range of sources, including CRM, marketing automation platforms, website analytics, and external data providers.
- Target Users: CRM systems are primarily used by sales, marketing, and customer service teams to manage customer relationships and track interactions. CDPs are used by data analysts, marketers, and IT professionals to collect, analyze, and activate customer data.
- Data Activation: CRMs primarily activate data within the CRM system itself, such as for sales follow-ups and customer service interactions. CDPs activate data across multiple channels, including marketing automation platforms, advertising platforms, and website personalization tools.
- Data Persistence: CRM data typically persists for the duration of the customer relationship. CDP data persists across the customer lifecycle, even after the customer is no longer actively engaged.
Consider this:
A CRM is like a detailed address book and interaction log, while a CDP is like a comprehensive library and research center, providing a holistic understanding of customer behavior and preferences.
CDP: Enriching CRM Data
A CDP can significantly enhance the data held within a CRM by enriching existing customer profiles with additional insights. This enrichment process involves integrating data from various sources, such as website behavior, social media activity, and offline interactions, to provide a more comprehensive view of each customer. This expanded data view allows for improved segmentation, personalization, and targeting, ultimately leading to more effective customer engagement.Here’s an example of how a CDP can enrich data within a CRM:
- CRM Data: A company’s CRM contains basic customer information, such as name, email address, phone number, and purchase history.
- CDP Integration: The CDP integrates with the company’s website analytics platform, social media accounts, and email marketing platform.
- Data Collection: The CDP collects data on customer website behavior (e.g., pages visited, products viewed), social media engagement (e.g., likes, shares, comments), and email interactions (e.g., opens, clicks).
- Data Enrichment: The CDP uses this data to enrich the customer profiles in the CRM. For example, the CDP might add information about a customer’s preferred product categories, their level of engagement with the company’s social media content, and their responsiveness to email campaigns.
- CRM Update: The enriched customer profiles are then updated in the CRM, providing sales and marketing teams with a more complete understanding of each customer.
- Improved Targeting: As a result, the sales team can personalize their outreach based on the customer’s interests and behaviors, and the marketing team can create more targeted email campaigns based on the customer’s website activity and social media engagement.
For example, consider an e-commerce company using a CRM to track customer purchases. By integrating a CDP, the company can add data about which products a customer has viewed on their website, which items they’ve added to their cart, and which content they’ve engaged with on social media. This enriched data allows the company to send personalized product recommendations, target customers with relevant ads, and improve the overall customer experience.
This enrichment process allows for more effective marketing campaigns and improved customer relationship management.
Integrating CRM and CDP: A Synergistic Approach
The integration of a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system with a Customer Data Platform (CDP) creates a powerful synergy, allowing businesses to leverage the strengths of both platforms. This integration enables a unified view of the customer, facilitates personalized experiences, and improves marketing efficiency. Successfully integrating these systems requires careful planning, execution, and ongoing maintenance to maximize their combined value.
Process of CRM and CDP Integration
The integration process involves several key steps, each crucial for a seamless and effective connection. The goal is to establish a two-way data flow, allowing information to move freely between the CRM and CDP.The key steps involved are:
- Defining Objectives and Scope: The initial step involves clearly defining the goals of the integration. What specific business outcomes are expected? Identifying the specific data points that need to be shared between the CRM and CDP is essential. For example, a company might want to synchronize customer purchase history from the CRM with the CDP to enhance personalized product recommendations. This stage also involves defining the scope of the integration, including which CRM and CDP modules will be involved and the target user groups.
- Data Mapping and Schema Design: This step involves mapping the data fields between the CRM and CDP. Data fields with similar meanings must be identified and matched. This process requires careful consideration of data types, formats, and naming conventions to ensure data consistency. For example, a customer’s email address in the CRM might need to be mapped to the corresponding email field in the CDP.
A well-defined data mapping schema minimizes data discrepancies and ensures accurate data flow.
- Choosing an Integration Method: There are several methods for integrating CRM and CDP systems, including:
- Native Integrations: Some CRM and CDP vendors offer pre-built integrations. This is often the simplest and most efficient method, requiring minimal configuration.
- API-Based Integrations: Using Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) allows for a more customized integration, providing greater flexibility and control. This approach typically requires more technical expertise.
- Third-Party Integration Platforms: Several platforms specialize in integrating different software systems, offering a user-friendly interface and pre-built connectors.
The chosen method should align with the organization’s technical capabilities and integration requirements.
- Data Synchronization and Testing: Once the integration method is selected, the next step is to establish the data synchronization process. This involves determining the frequency and direction of data flow (e.g., real-time, batch). Thorough testing is crucial to ensure that data is transferred accurately and consistently between the systems. Testing should cover various scenarios, including data updates, deletions, and new data entries.
- Deployment and Monitoring: After successful testing, the integration is deployed. Ongoing monitoring is essential to identify and address any issues that may arise. This includes monitoring data synchronization logs, identifying errors, and ensuring data quality. Regular audits can help ensure the integration continues to meet business needs.
Challenges in Integrating CRM and CDP Systems
Integrating CRM and CDP systems can present several challenges. Anticipating these challenges and developing strategies to mitigate them is essential for a successful integration.The key challenges include:
- Data Silos and Inconsistent Data: One of the most significant challenges is dealing with data silos. Data may reside in different formats, use different naming conventions, or have varying levels of quality. Inconsistent data can lead to inaccurate customer profiles and ineffective marketing campaigns.
- Technical Complexity: Integrating two complex systems requires technical expertise and a thorough understanding of both platforms. Compatibility issues between the CRM and CDP, especially when dealing with custom implementations, can pose significant challenges.
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, is crucial. Protecting sensitive customer data during the integration process and ensuring data security across both systems is paramount.
- Budget and Resource Constraints: Integrating CRM and CDP systems can be costly, involving expenses for software, implementation, and ongoing maintenance. Limited resources, including budget and skilled personnel, can hinder the integration process.
- Vendor Lock-in and Compatibility: Choosing the right vendors and ensuring their systems are compatible is critical. Vendor lock-in can limit flexibility and make it difficult to switch to a different system in the future.
Strategies to overcome these challenges include:
- Data Standardization: Implement data standardization processes to ensure consistency in data formats, naming conventions, and data quality across both systems.
- API Documentation and Expertise: Utilize comprehensive API documentation and skilled technical resources to address technical complexities.
- Data Governance: Establish a data governance framework that includes data quality checks, data privacy policies, and security measures.
- Phased Implementation: Adopt a phased approach to implementation, starting with a pilot project to test the integration and gradually expanding its scope.
- Vendor Selection and Evaluation: Carefully evaluate vendors based on their integration capabilities, support, and compliance with data privacy regulations.
Best Practices for Data Accuracy and Consistency
Maintaining data accuracy and consistency across both CRM and CDP systems is crucial for maximizing the benefits of integration. Following best practices ensures that the data is reliable, up-to-date, and usable for business purposes.The best practices include:
- Establish Data Governance Policies: Implement clear data governance policies that define data ownership, data quality standards, and data update procedures. These policies should be consistently applied across both the CRM and CDP.
- Implement Data Validation Rules: Utilize data validation rules within both systems to ensure that data entered is accurate and complete. For example, require email addresses to be in a valid format and phone numbers to have the correct number of digits.
- Data Deduplication and Cleansing: Implement data deduplication processes to identify and merge duplicate records. Regularly cleanse data to correct errors and remove outdated information.
- Real-Time Data Synchronization: Where possible, synchronize data in real-time to ensure that both systems have the most up-to-date information. This is particularly important for critical data points like customer contact information.
- Regular Audits and Monitoring: Conduct regular audits of the data to identify and address any inconsistencies or errors. Monitor data synchronization logs to ensure data is flowing correctly between the systems.
- Define Clear Data Ownership: Establish clear ownership of data fields and ensure that the responsible parties are accountable for data accuracy and maintenance.
- Use Unique Identifiers: Implement a unique identifier, such as a customer ID, to link records across both systems. This ensures that data is accurately matched and prevents data discrepancies.
- Provide User Training: Train users on the importance of data accuracy and the proper procedures for entering and updating data.
By implementing these best practices, organizations can ensure that the data in their CRM and CDP systems is accurate, consistent, and reliable, leading to improved customer experiences and more effective marketing campaigns.
Data Segmentation and Personalization: Tailoring the Experience
The combined power of a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system and a Customer Data Platform (CDP) unlocks unprecedented opportunities for segmenting customers and delivering highly personalized experiences. This ability to tailor interactions drives engagement, fosters loyalty, and ultimately, increases revenue. The following sections delve into how to leverage the integrated data to achieve these goals.
Customer Segmentation Strategies
Effective segmentation is the cornerstone of targeted marketing. By analyzing data from both CRM and CDP, marketers can create granular customer segments based on various criteria.To illustrate the potential of segmentation, consider a retail company.
- Demographic Segmentation: This involves grouping customers based on age, gender, location, income, and other demographic factors. Data for this often resides in the CRM. For example, a luxury goods retailer might segment customers by income level to tailor offers for high-end products to affluent segments.
- Behavioral Segmentation: This focuses on customer actions, such as purchase history, website browsing behavior, app usage, and email engagement. The CDP excels at capturing this real-time behavioral data. A streaming service, for instance, could segment users based on the genres they watch most frequently to recommend similar content.
- Psychographic Segmentation: This delves into customer lifestyles, values, attitudes, and interests. While more complex, a CDP can enrich CRM data with insights from surveys, social media activity, and third-party data providers to create segments based on personality traits or brand affinity. An outdoor apparel company might identify segments interested in adventure travel versus casual hiking.
- RFM (Recency, Frequency, Monetary Value) Segmentation: This classic segmentation method, easily achievable with data from both CRM and CDP, ranks customers based on how recently they made a purchase, how often they purchase, and how much they spend. This enables the company to prioritize communications and offers to high-value customers.
These segmentation strategies can be combined. For instance, a company might create a segment of “high-value, frequent purchasers” (RFM) who are also “interested in sustainable products” (psychographic).
Personalizing Customer Experiences Across Touchpoints
Once customer segments are defined, the next step is to personalize the customer experience across various touchpoints. This involves tailoring content, offers, and interactions to resonate with individual customer needs and preferences.
- Email Marketing: CRM data, such as purchase history and demographics, can be used to personalize email subject lines, content, and product recommendations. The CDP can provide real-time behavioral data, such as abandoned cart information, to trigger timely and relevant email reminders. For example, an e-commerce store might send an email to a customer who abandoned their cart with a specific product, including an incentive such as free shipping to encourage completion of the purchase.
- Website Personalization: Dynamic website content can be displayed based on customer segment. This includes personalized product recommendations, tailored landing pages, and targeted promotions. A travel website could display different flight deals and hotel options based on a customer’s past travel destinations or preferred travel style (e.g., luxury vs. budget).
- In-App Messaging: Mobile apps can utilize data from both CRM and CDP to deliver personalized in-app messages, such as welcome messages, onboarding tutorials, and promotional offers. A fitness app could send personalized workout recommendations based on a user’s fitness level, goals, and activity history.
- Social Media Advertising: Customer segments created in the CRM and CDP can be used to target specific audiences with personalized ads on social media platforms. A fashion retailer could show ads featuring different clothing styles based on a customer’s browsing history and purchase preferences.
The key to effective personalization is to ensure that the customer data is accurate, up-to-date, and integrated across all touchpoints. This requires a robust data infrastructure, including a well-integrated CRM and CDP.
Successful Personalization Examples
Several companies have demonstrated the power of personalization driven by integrated CRM and CDP data. These examples highlight the impact of these strategies.
- Netflix: Netflix uses a sophisticated recommendation engine, powered by data from its CDP and CRM, to personalize the content it suggests to each user. This includes analyzing viewing history, ratings, search queries, and device information to predict what a user will enjoy. The result is increased engagement and subscriber retention. This is evident in their personalized home screen displays.
- Amazon: Amazon’s website is a prime example of personalization. They leverage data from their CRM and CDP to provide personalized product recommendations, tailored search results, and targeted email promotions. This data includes purchase history, browsing behavior, and customer demographics. The result is a highly relevant shopping experience that drives sales.
- Spotify: Spotify personalizes music recommendations through its “Discover Weekly” playlist, curated playlists, and tailored radio stations. The data is collected through listening history, artist preferences, and social media activity. This drives user engagement and subscription growth. The personalized playlists and curated content contribute significantly to the platform’s stickiness.
These examples demonstrate that effective personalization is not about simply adding a customer’s name to an email. It’s about using data to understand customer needs and preferences and then tailoring the entire customer experience to meet those needs.
Measuring and Optimizing: Continuous Improvement
A robust first-party data strategy is not a set-it-and-forget-it endeavor. Instead, it requires ongoing measurement, analysis, and optimization to ensure its effectiveness and alignment with evolving business goals. Regularly assessing performance, identifying areas for improvement, and implementing data-driven adjustments are crucial for maximizing the value of first-party data and achieving desired outcomes. This section details the essential elements of a continuous improvement framework.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Measuring Effectiveness
Defining and tracking relevant KPIs is fundamental to evaluating the success of a first-party data strategy. These metrics provide quantifiable insights into various aspects of the strategy, allowing for a data-driven assessment of its impact. The selection of KPIs should align with the specific objectives of the strategy and the overall business goals.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): This KPI measures the total cost incurred to acquire a new customer. By analyzing CAC, businesses can determine the efficiency of their marketing efforts and identify channels that yield the most cost-effective customer acquisition. Lowering CAC is a primary goal, demonstrating that marketing investments are yielding positive returns.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV): CLTV estimates the total revenue a customer is expected to generate throughout their relationship with the business. A higher CLTV indicates greater customer loyalty and profitability. This metric helps prioritize customer segments and optimize strategies to retain high-value customers. For example, if a company knows that customers acquired through a specific first-party data-driven campaign have a CLTV of $1,000 compared to a baseline CLTV of $500, the campaign’s effectiveness is clearly demonstrated.
- Conversion Rate: This KPI measures the percentage of users who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or requesting a demo. Tracking conversion rates across different marketing channels and customer segments provides insights into campaign effectiveness and user behavior. Optimizing conversion rates is essential for maximizing revenue generation.
- Website Traffic and Engagement Metrics: Analyzing website traffic (e.g., page views, sessions, unique visitors) and engagement metrics (e.g., bounce rate, time on site, pages per session) reveals how users interact with a website and its content. These metrics provide valuable insights into user experience and content effectiveness, which can be improved using data-driven adjustments.
- Email Marketing Performance Metrics: Email marketing performance is assessed through metrics such as open rates, click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, and unsubscribe rates. These metrics help gauge the effectiveness of email campaigns, identify areas for improvement in content and targeting, and assess the impact of personalized messaging. For example, an email campaign targeting a specific customer segment using personalized product recommendations might achieve a CTR of 10%, significantly higher than the average CTR of 3% for generic email blasts.
- Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) and Net Promoter Score (NPS): CSAT and NPS are crucial for understanding customer sentiment and loyalty. CSAT measures customer satisfaction with specific interactions or experiences, while NPS gauges the likelihood of customers recommending the business to others. High CSAT scores and NPS ratings indicate strong customer relationships and brand advocacy, which are essential for long-term success. A company implementing a first-party data-driven loyalty program might see an increase in its NPS from 60 to 75 within a year, demonstrating a positive impact on customer loyalty.
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): This KPI measures the revenue generated for every dollar spent on advertising. A high ROAS indicates efficient ad spending and effective campaign performance. Tracking ROAS allows businesses to optimize their advertising strategies and allocate budget to the most profitable channels. If a first-party data-driven campaign generates a ROAS of 5:1 (meaning $5 in revenue for every $1 spent), it indicates a strong return on investment.
Using Data Insights to Optimize Marketing Campaigns and Improve Customer Engagement
Data insights gleaned from the analysis of KPIs are invaluable for optimizing marketing campaigns and enhancing customer engagement. This involves a continuous cycle of data collection, analysis, interpretation, and action. The goal is to make informed decisions that improve campaign performance, personalize customer experiences, and drive business growth.
Here’s a framework for utilizing data insights:
- Identify Trends and Patterns: Analyze the data to identify emerging trends, patterns, and anomalies. This could involve looking at changes in conversion rates, customer behavior, or campaign performance.
- Segment and Target: Use data to segment customers into distinct groups based on their demographics, behaviors, and preferences. Then, tailor marketing messages and offers to each segment for increased relevance and effectiveness.
- Personalize Content and Experiences: Leverage data to personalize website content, email communications, product recommendations, and other customer interactions. Personalization can significantly improve engagement and conversion rates.
- Test and Iterate: Conduct A/B testing to compare different versions of marketing materials (e.g., email subject lines, ad copy, landing pages) and identify the most effective approaches. Continuously iterate and refine campaigns based on the results of these tests.
- Optimize Channels and Budgets: Analyze the performance of different marketing channels and allocate budget to the most effective ones. This might involve shifting resources from underperforming channels to those that generate higher returns.
- Improve Customer Journey: Map the customer journey and identify points of friction or drop-off. Use data to optimize the customer experience at each touchpoint, making it more seamless and enjoyable.
Example:
A retailer analyzing its first-party data might discover that customers who have previously purchased a specific product category are more likely to respond to promotions for related items. They can then use this insight to create targeted email campaigns featuring personalized product recommendations, resulting in higher click-through rates and increased sales. For instance, if data reveals that customers who purchased running shoes also frequently buy running apparel, the retailer can automatically send personalized emails featuring new arrivals in running shorts or shirts.
Tools for Data Analysis and Reporting
A variety of tools are available to facilitate data analysis and reporting, enabling businesses to gain actionable insights from their first-party data. The choice of tools should be based on factors such as the size and complexity of the data, the technical expertise of the team, and the specific analytical needs.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: CRM systems, such as Salesforce, HubSpot, and Microsoft Dynamics 365, serve as central repositories for customer data and provide built-in reporting and analytics capabilities. They enable businesses to track customer interactions, manage sales pipelines, and generate reports on key metrics.
- Customer Data Platforms (CDPs): CDPs, like Segment, Tealium, and Adobe Experience Platform, are designed to collect, unify, and activate customer data from various sources. They offer advanced segmentation, personalization, and reporting features, enabling businesses to create a unified view of the customer and deliver more targeted marketing campaigns.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools: BI tools, such as Tableau, Power BI, and Looker, allow businesses to visualize and analyze data from multiple sources. They provide dashboards, reports, and interactive visualizations that help users understand trends, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions.
- Web Analytics Tools: Web analytics tools, such as Google Analytics, provide insights into website traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates. They track metrics such as page views, bounce rates, time on site, and goal completions, enabling businesses to optimize their website and improve user experience.
- Email Marketing Platforms: Email marketing platforms, such as Mailchimp, Sendinblue, and Klaviyo, offer robust analytics features for tracking email campaign performance. They provide data on open rates, click-through rates, conversion rates, and unsubscribe rates, enabling businesses to optimize their email marketing efforts.
- Spreadsheet Software: Tools like Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets can be used for basic data analysis, reporting, and visualization. They are accessible and easy to use for smaller datasets or simpler analyses.
- Data Visualization Tools: Tools such as Datawrapper and Infogram focus specifically on creating compelling data visualizations. These tools allow users to transform complex data into easily understandable charts, graphs, and other visual formats, facilitating the communication of key findings.
Data Governance and Privacy: Building Trust: First-Party Data Strategy: Using CRM With A CDP
Data governance and privacy are paramount in any first-party data strategy. They establish the framework for responsible data handling, ensuring customer trust and compliance with evolving regulations. A robust data governance program safeguards data integrity, minimizes risks, and fosters a positive brand reputation. Neglecting these crucial aspects can lead to legal penalties, reputational damage, and ultimately, the loss of customer loyalty.
Importance of Data Governance in First-Party Data Management
Data governance provides the structure for managing and utilizing first-party data effectively and ethically. It ensures data quality, security, and compliance with relevant privacy regulations. This framework encompasses policies, processes, and responsibilities that guide how data is collected, stored, used, and shared.
- Data Quality: Data governance establishes standards for data accuracy, completeness, and consistency. This ensures that the data used for analysis and personalization is reliable and actionable. For example, regular data cleansing processes can identify and correct errors in customer contact information, preventing inaccurate marketing campaigns and improving deliverability.
- Data Security: Robust security measures are a cornerstone of data governance. These measures protect customer data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse. Encryption, access controls, and regular security audits are essential components. The implementation of multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all systems accessing customer data is a key security practice.
- Compliance: Data governance ensures adherence to relevant privacy regulations, such as GDPR, CCPA, and other regional laws. This includes obtaining proper consent for data collection, providing transparency about data usage, and respecting customer rights related to data access, rectification, and deletion. A well-defined compliance program minimizes the risk of legal penalties and builds customer trust.
- Data Ethics: Data governance promotes ethical data practices, including transparency, fairness, and accountability. This involves considering the potential impact of data usage on customers and making responsible decisions about how data is used for personalization and targeting. For example, avoid using sensitive personal data, such as health information, without explicit consent and a clear understanding of its intended use.
Creating a Data Privacy Policy Aligned with Regulations
A comprehensive data privacy policy is essential for communicating data handling practices to customers and demonstrating compliance with privacy regulations. The policy should be clear, concise, and easily accessible. It should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect changes in data practices and evolving legal requirements.
- Transparency: The policy must clearly state what data is collected, how it is collected (e.g., website forms, cookies), and the purpose for which it is used. Explain how data is used for personalization, marketing, and other business activities. Provide specific examples of data usage.
- Legal Basis for Processing: Specify the legal basis for processing customer data, such as consent, legitimate interest, or contract. When relying on consent, ensure it is freely given, specific, informed, and unambiguous. For example, if using data for direct marketing, obtain explicit consent through a clear opt-in mechanism.
- Data Subject Rights: Clearly Artikel the rights of data subjects, including the right to access, rectify, erase, restrict processing, and data portability. Provide clear instructions on how customers can exercise these rights. For example, include a dedicated email address or online form for data subject requests.
- Data Retention: State the retention period for customer data. This should be based on the purpose for which the data was collected and legal requirements. Define a schedule for data deletion or anonymization. For example, data collected for marketing purposes might be retained for a specified period after the last customer interaction.
- Data Security Measures: Describe the security measures implemented to protect customer data, such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. This demonstrates a commitment to data protection. For instance, describe the use of firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and regular security assessments.
- Third-Party Data Sharing: Disclose any third parties with whom data is shared, such as marketing platforms or analytics providers. Explain the purpose of the data sharing and ensure that appropriate data processing agreements are in place. For example, clearly state which data is shared with a marketing automation platform and how it is used.
- Policy Updates: Include a statement about how the privacy policy will be updated and when the last update was made. This ensures that customers are informed of any changes to data handling practices. Indicate the effective date of the policy.
Procedures for Ensuring Data Security and Protecting Customer Information
Implementing robust security procedures is crucial to safeguarding customer data from unauthorized access and breaches. This involves a multi-layered approach that includes technical, administrative, and physical security measures. Regular monitoring and audits are essential to ensure the effectiveness of these measures.
- Access Controls: Implement strict access controls to limit access to customer data to authorized personnel only. Use role-based access control (RBAC) to grant access based on job responsibilities. Regularly review and update access permissions. For example, only marketing team members should have access to customer contact information, and only customer service representatives should have access to customer support tickets.
- Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both in transit and at rest. This protects data from unauthorized access even if systems are compromised. Use strong encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, for encrypting sensitive data stored in databases and cloud storage.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in security systems. These assessments should be performed by qualified security professionals. Address any identified vulnerabilities promptly.
- Data Minimization: Collect and store only the data that is necessary for the stated purpose. Avoid collecting unnecessary data, which reduces the risk of a data breach. Review data collection practices regularly to ensure that only essential data is being collected.
- Data Anonymization and Pseudonymization: Use data anonymization and pseudonymization techniques to protect sensitive data. Anonymization completely removes identifying information, while pseudonymization replaces identifying information with pseudonyms. These techniques can be used to enable data analysis while protecting customer privacy.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and maintain an incident response plan to address data breaches or security incidents. This plan should Artikel the steps to be taken in the event of a breach, including containment, investigation, notification, and recovery. Regularly test and update the incident response plan.
- Employee Training: Provide regular data security and privacy training to all employees who have access to customer data. This training should cover topics such as data handling best practices, phishing awareness, and data breach prevention. Conduct annual refresher training to reinforce these principles.
- Vendor Management: Implement a vendor management program to ensure that third-party vendors who have access to customer data also comply with data security and privacy requirements. Conduct due diligence on vendors before sharing data and include data processing agreements in contracts.
Use Cases: Real-World Applications
Implementing a first-party data strategy using a Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system and a Customer Data Platform (CDP) offers significant advantages across various industries. This approach enables businesses to deeply understand their customers, personalize their interactions, and optimize marketing efforts, ultimately leading to improved customer lifetime value (CLTV). The following sections explore specific industries where this strategy is particularly effective, showcasing successful use cases with quantifiable results and key takeaways.
Industries Where the Strategy is Most Effective
Several industries benefit significantly from integrating CRM and CDP. These industries often have a high volume of customer interactions, complex customer journeys, and a strong emphasis on personalized experiences. They also typically have access to rich first-party data.
- Retail: Retailers collect vast amounts of data from online and offline channels, including purchase history, browsing behavior, loyalty program participation, and in-store interactions. This data can be leveraged to personalize product recommendations, target advertising, and optimize promotional campaigns.
- E-commerce: E-commerce businesses thrive on data-driven decision-making. A combined CRM and CDP approach allows them to understand customer preferences, personalize website experiences, and deliver targeted email marketing campaigns.
- Financial Services: Banks and financial institutions handle sensitive customer data. Using CRM and CDP allows for secure data management, personalized financial product recommendations, and improved customer service.
- Healthcare: Healthcare providers can use this strategy to improve patient engagement, personalize treatment plans, and streamline communication. Data privacy and security are paramount in this industry.
- Travel and Hospitality: Hotels and airlines can personalize customer experiences, from booking to post-stay interactions, by understanding customer preferences and travel patterns.
- Media and Entertainment: Media companies can use first-party data to personalize content recommendations, target advertising, and improve audience engagement across various platforms.
Retail: Personalized Product Recommendations and Targeted Advertising
Retail is a prime example of an industry that can significantly benefit from a combined CRM and CDP strategy. Retailers have access to rich customer data, including purchase history, browsing behavior, loyalty program participation, and in-store interactions.
A major apparel retailer, for example, implemented a combined CRM and CDP strategy to improve customer experience and drive sales. The CDP ingested data from various sources, including website activity, point-of-sale (POS) systems, and loyalty program data. This data was then used to create detailed customer profiles, which were synced with the CRM system. The CRM system enabled the retailer to manage customer interactions and personalize communications.
The results were impressive.
- Personalized Product Recommendations: By analyzing customer purchase history and browsing behavior, the retailer was able to deliver highly relevant product recommendations on its website and in email marketing campaigns.
- Targeted Advertising: The retailer used the CDP to segment its customer base and create targeted advertising campaigns on social media and search engines. For instance, customers who had previously purchased winter coats were targeted with ads for new winter accessories.
- Quantifiable Results:
- Increased Conversion Rates: Personalized product recommendations led to a 15% increase in conversion rates on the website.
- Higher Average Order Value: Customers who received personalized recommendations spent, on average, 10% more per order.
- Improved Customer Lifetime Value: By improving customer engagement and driving repeat purchases, the retailer saw a 12% increase in customer lifetime value.
- Key Takeaways:
- Data Integration is Crucial: Seamless integration between the CDP and CRM is essential for sharing customer data and enabling personalized experiences.
- Segmentation is Key: Effective segmentation allows for the creation of highly targeted marketing campaigns.
- Personalization Drives Results: Personalizing the customer experience is crucial for driving engagement, sales, and customer loyalty.
Financial Services: Personalized Product Recommendations and Improved Customer Service
Financial institutions handle sensitive customer data, making data security and personalized customer service paramount. A combined CRM and CDP strategy enables them to understand customer needs, personalize product recommendations, and improve customer service.
A large bank, for instance, implemented this strategy to enhance customer experience and increase product adoption. The CDP collected data from various sources, including transaction history, account activity, and customer interactions. This data was then used to create detailed customer profiles, which were synced with the CRM system. The CRM system was used to manage customer relationships and personalize communications.
The bank saw substantial improvements.
- Personalized Product Recommendations: The bank analyzed customer financial behavior to recommend relevant products and services, such as credit cards, loans, and investment opportunities.
- Improved Customer Service: The CRM system provided customer service representatives with a 360-degree view of each customer, enabling them to provide more personalized and efficient support.
- Quantifiable Results:
- Increased Product Adoption: The bank saw a 20% increase in the adoption of recommended financial products.
- Reduced Customer Churn: Personalized customer service and proactive communication led to a 10% reduction in customer churn.
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: The bank’s customer satisfaction scores increased by 15%.
- Key Takeaways:
- Data Security is Paramount: Implementing robust data security measures is essential when handling sensitive customer data.
- Personalized Communication Builds Trust: Tailoring communications to individual customer needs fosters trust and loyalty.
- A Unified View of the Customer Improves Service: Providing customer service representatives with a comprehensive view of each customer improves their ability to assist customers.
E-commerce: Personalized Website Experiences and Targeted Email Marketing
E-commerce businesses can leverage first-party data to personalize website experiences and deliver targeted email marketing campaigns, leading to increased sales and customer loyalty.
An online fashion retailer, for example, implemented a combined CRM and CDP strategy to improve customer engagement and drive sales. The CDP ingested data from various sources, including website activity, purchase history, and email interactions. This data was then used to create detailed customer profiles, which were synced with the CRM system. The CRM system was used to manage customer interactions and personalize communications.
The results were significant.
- Personalized Website Experiences: The retailer used the CDP to personalize the website experience for each customer, including product recommendations, content suggestions, and dynamic pricing.
- Targeted Email Marketing: The retailer segmented its customer base and created targeted email marketing campaigns based on customer preferences, purchase history, and browsing behavior. For instance, customers who had viewed specific product categories were sent emails promoting related products.
- Quantifiable Results:
- Increased Conversion Rates: Personalized website experiences led to a 10% increase in conversion rates.
- Higher Click-Through Rates: Targeted email marketing campaigns had a 25% higher click-through rate compared to generic campaigns.
- Improved Customer Lifetime Value: By improving customer engagement and driving repeat purchases, the retailer saw a 18% increase in customer lifetime value.
- Key Takeaways:
- Website Personalization Drives Engagement: Personalizing the website experience can significantly improve customer engagement and conversion rates.
- Targeted Email Marketing is Effective: Segmenting customers and sending targeted emails can dramatically improve click-through rates and conversions.
- Data-Driven Decisions are Crucial: Making data-driven decisions is essential for success in the competitive e-commerce landscape.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Data Strategies
The landscape of first-party data management is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer expectations, and stricter data privacy regulations. Understanding these trends is crucial for businesses seeking to maintain a competitive edge and build lasting customer relationships. The convergence of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and enhanced data privacy controls will fundamentally reshape how organizations collect, manage, and utilize customer data in the years to come.
Emerging Trends in First-Party Data Management: AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are poised to revolutionize first-party data strategies. These technologies offer the potential to automate data processes, uncover hidden insights, and personalize customer experiences at scale. The application of AI and ML extends across various aspects of data management, from data collection and cleansing to predictive analytics and campaign optimization.
- Automated Data Enrichment and Cleansing: AI algorithms can automatically enrich customer profiles by integrating data from various sources, such as social media, website activity, and purchase history. These algorithms can also identify and correct data inaccuracies, ensuring data quality and consistency. For instance, a retail company could use AI to automatically update customer addresses based on real-time location data and purchase history, improving the accuracy of shipping and marketing campaigns.
- Predictive Analytics and Customer Segmentation: ML models can analyze vast datasets to predict customer behavior, such as churn, purchase propensity, and lifetime value. This enables businesses to create highly targeted customer segments and personalize marketing messages accordingly. A financial institution could use ML to identify customers at high risk of churn and proactively offer them tailored retention programs.
- Personalized Content Delivery and Recommendations: AI-powered recommendation engines can analyze customer preferences and behavior to deliver personalized content and product recommendations in real-time. This can significantly improve engagement and conversion rates. E-commerce platforms, for example, leverage AI to recommend products based on browsing history, purchase patterns, and similar customer behavior.
- Automated Campaign Optimization: AI can automate the optimization of marketing campaigns by analyzing performance data and adjusting targeting, bidding, and creative elements in real-time. This ensures that campaigns are constantly evolving to maximize their effectiveness. A marketing automation platform could use AI to dynamically adjust ad spend based on conversion rates and customer lifetime value.
Predictions for the Future of Data Privacy and Marketing Strategies
Data privacy regulations are becoming increasingly stringent worldwide, impacting how businesses collect, use, and share customer data. The future of data privacy will likely involve stricter enforcement of existing regulations, increased consumer control over their data, and the adoption of privacy-enhancing technologies. Marketing strategies will need to adapt to this changing environment, prioritizing transparency, consent, and data minimization.
- Increased Data Privacy Regulations: The trend towards stricter data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, will continue globally. Organizations will need to invest in robust data governance frameworks and ensure compliance with evolving legal requirements. Further legislation is expected, potentially with global implications, forcing organizations to adopt privacy-by-design principles.
- Enhanced Consumer Control: Consumers will demand greater control over their data, including the right to access, rectify, and delete their personal information. Businesses will need to provide clear and concise privacy policies, obtain explicit consent for data collection, and offer easy-to-use tools for managing privacy preferences. A shift is expected towards platforms that allow users to easily manage their data and opt-out of data sharing.
- Privacy-Enhancing Technologies (PETs): PETs, such as differential privacy, federated learning, and secure multi-party computation, will become increasingly important for protecting customer data while enabling data-driven insights. These technologies allow businesses to analyze data without directly accessing or storing sensitive information. Examples include the use of homomorphic encryption, allowing data processing without decrypting it.
- Shift to Zero-Party Data: Businesses will increasingly focus on collecting zero-party data – data that customers intentionally and proactively share with a brand. This includes preferences, purchase intentions, and personal information provided directly by the customer. This shift will require companies to build trust, offer value in exchange for data, and create engaging experiences that encourage data sharing. For example, brands might use quizzes or surveys to gather customer preferences.
- Contextual Marketing: As third-party cookies phase out, contextual marketing, which targets ads based on website content rather than user data, will become more prevalent. This approach prioritizes delivering relevant messages based on the context of the user’s browsing session. The rise of contextual marketing will also involve the development of advanced AI-powered content analysis tools.
Conceptual Illustration of a Future-State Data Ecosystem
The future-state data ecosystem will be characterized by a connected, intelligent, and privacy-centric architecture. CRM and CDP will continue to be central to this ecosystem, integrated with AI-powered tools, data governance platforms, and a focus on zero-party data collection.
Imagine a diagram depicting a circular ecosystem, with the following elements:
- Center: Customer at the core, surrounded by a circle.
- CRM (Central Hub): Positioned within the first ring around the customer. It integrates customer interactions, sales data, and service records.
- CDP (Data Orchestration Layer): Positioned in the second ring, surrounding the CRM. It collects, unifies, and analyzes data from various sources, including the CRM, marketing automation platforms, and other third-party systems.
- AI/ML Engines (Intelligence Layer): Positioned in the third ring. These engines drive predictive analytics, personalization, and automated decision-making across the ecosystem.
- Data Governance & Privacy Platform (Compliance Layer): Positioned in the third ring, alongside the AI/ML engines. It ensures data compliance, manages consent, and enforces privacy policies.
- Data Sources (External Ring): Surrounding the entire ecosystem, represented as spokes connecting to the CDP. This includes:
- Website & App Data
- Social Media
- Email Marketing
- Customer Service Interactions
- Point of Sale (POS) Data
- Zero-Party Data Collection Tools (surveys, preferences)
- Output & Action (Arrows pointing outwards): From the CRM, CDP, and AI/ML engines, arrows point towards the customer experience, including personalized marketing campaigns, targeted product recommendations, and proactive customer service.
This future ecosystem illustrates a holistic approach to data management, where customer data is collected, analyzed, and utilized in a privacy-conscious manner to deliver personalized and relevant experiences. The integration of AI and ML ensures continuous improvement and optimization, while the data governance platform safeguards customer privacy and ensures compliance with regulations. Zero-party data plays a key role, providing valuable insights while respecting customer preferences.