Dynamics 365 vs Salesforce: Enterprise CRM Comparison, a tale of two titans, a clash of innovative forces vying for the hearts and minds of businesses worldwide. Imagine a world where customer relationships are not just managed, but nurtured, where data sings a song of opportunity, and efficiency reigns supreme. This comparison isn’t merely a technical analysis; it’s an exploration into the very essence of business evolution, a journey to discover which platform holds the key to unlocking your company’s fullest potential.
Within this landscape, we’ll journey through the realms of Customer Relationship Management (CRM), witnessing the core functions that breathe life into businesses. We’ll uncover the histories and strengths of Dynamics 365 and Salesforce, examining their core features, from Sales Force Automation to marketing automation, and from deployment options to industry-specific solutions. Through each step, we’ll illuminate the unique strengths of each platform, equipping you with the knowledge to make an informed decision for your enterprise.
The power to choose is yours; the journey begins now.
Overview of CRM Systems: Defining the Landscape
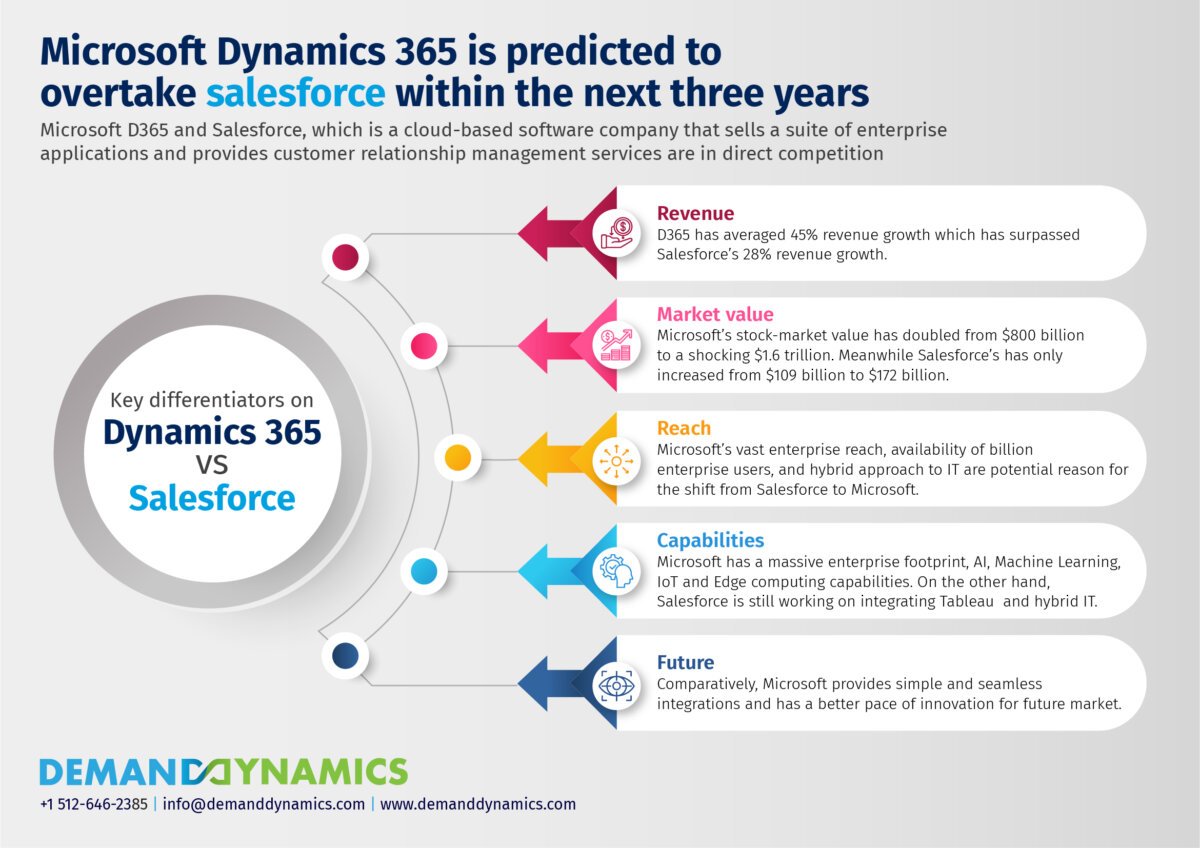
Source: demanddynamics.com
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems have become indispensable tools for businesses aiming to enhance customer interactions, streamline operations, and drive revenue growth. These systems provide a centralized platform for managing all customer-related data and interactions, offering a comprehensive view of the customer journey. Understanding the fundamentals of CRM is crucial for any organization considering implementing or upgrading its customer relationship strategies.
Defining Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems
CRM systems are software applications designed to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. They aim to improve business relationships with customers, assist in customer retention, and drive sales growth. A well-implemented CRM system allows businesses to understand their customers’ needs and behaviors, personalize interactions, and deliver superior customer service. The core principle of CRM is to centralize customer information, making it accessible and actionable across different departments within an organization.
Core Functions of a CRM System and Their Importance
CRM systems encompass a variety of core functions that are critical for effective customer relationship management. These functions, when implemented effectively, can significantly impact a business’s performance and customer satisfaction.
- Contact Management: This function involves storing and organizing customer contact information, including names, addresses, phone numbers, and email addresses. It also includes detailed information about interactions, such as past purchases, support tickets, and communication history. Contact management is the foundation of any CRM system, providing a centralized repository for all customer-related data.
- Sales Force Automation (SFA): SFA tools streamline the sales process by automating tasks such as lead tracking, opportunity management, and sales forecasting. This can include features like lead scoring, sales pipeline visualization, and automated email campaigns. SFA helps sales teams to work more efficiently, close deals faster, and improve sales performance.
- Marketing Automation: Marketing automation features enable businesses to automate marketing campaigns, personalize customer communications, and track marketing performance. This can include features like email marketing, social media integration, and lead nurturing. Marketing automation helps businesses to generate leads, nurture prospects, and improve the effectiveness of their marketing efforts.
- Customer Service and Support: CRM systems often include features for managing customer service and support interactions, such as ticketing systems, knowledge bases, and self-service portals. This helps businesses to provide faster and more efficient customer support, improve customer satisfaction, and reduce support costs.
- Analytics and Reporting: CRM systems provide powerful analytics and reporting capabilities, allowing businesses to track key performance indicators (KPIs), analyze customer behavior, and identify trends. This helps businesses to make data-driven decisions, optimize their customer relationship strategies, and improve overall business performance.
Common Benefits of Implementing a CRM System and Examples of Improved Efficiency
Implementing a CRM system offers numerous benefits to businesses across various industries. These benefits translate into improved efficiency, enhanced customer satisfaction, and ultimately, increased profitability. The following are key advantages and examples of how CRM systems improve efficiency:
- Improved Customer Satisfaction: CRM systems provide a 360-degree view of the customer, enabling businesses to personalize interactions and provide better customer service. For example, a customer service representative can quickly access a customer’s purchase history and past support tickets, allowing them to resolve issues more efficiently and effectively.
- Increased Sales Productivity: CRM systems automate sales processes, track leads, and manage opportunities, freeing up sales representatives to focus on closing deals. For instance, sales teams can automate follow-up emails, track the progress of sales pipelines, and generate sales forecasts, leading to improved sales performance.
- Enhanced Marketing Effectiveness: CRM systems allow businesses to segment their customer base, personalize marketing campaigns, and track marketing performance. For example, marketing teams can use CRM data to target specific customer segments with tailored messaging, leading to higher conversion rates.
- Streamlined Operations: CRM systems centralize customer data and automate various business processes, such as lead management, sales forecasting, and customer service. For example, a CRM system can automate the process of creating and assigning support tickets, reducing manual effort and improving response times.
- Better Decision-Making: CRM systems provide valuable data and insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing effectiveness. For example, businesses can use CRM analytics to identify trends, measure the success of their campaigns, and make data-driven decisions to improve their overall performance.
According to a study by Nucleus Research, CRM systems can increase sales productivity by an average of 14.6% and improve marketing ROI by 24.5%. This demonstrates the significant impact that CRM systems can have on a business’s bottom line.
Introduction to Dynamics 365 and Salesforce
This section delves into the origins and development of Dynamics 365 and Salesforce, two prominent enterprise CRM platforms. We will explore their respective histories, evolution, and initial market positioning to understand their core strengths and target audiences. This comparative analysis lays the groundwork for a deeper understanding of their capabilities and competitive landscape.
History and Evolution of Dynamics 365
Microsoft’s journey into the CRM space began with the acquisition of Great Plains Software in 2000, which brought Microsoft’s first foray into the enterprise resource planning (ERP) market. This acquisition set the stage for Microsoft’s later CRM endeavors. Microsoft officially entered the CRM market in 2003 with the launch of Microsoft Business Solutions – CRM. This early iteration focused on integrating CRM functionalities within the existing Microsoft ecosystem, targeting small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs).Over the years, Microsoft CRM underwent several iterations, evolving its feature set and platform architecture.
The product was rebranded as Microsoft Dynamics CRM, reflecting its integration with other Microsoft Dynamics products. A significant shift occurred with the introduction of Dynamics 365 in 2016. Dynamics 365 represented a move towards a more modular and cloud-first approach, integrating CRM and ERP functionalities into a unified platform. This evolution enabled customers to choose specific applications based on their business needs, promoting flexibility and scalability.
- Key Milestones in Dynamics 365 Evolution:
- 2003: Launch of Microsoft Business Solutions – CRM.
- 2005: Introduction of Microsoft Dynamics CRM.
- 2016: Launch of Dynamics 365, marking a shift towards cloud-based, modular applications.
- Ongoing: Continuous updates and integrations, including AI-powered features and enhanced integrations with the Microsoft ecosystem (e.g., Microsoft 365, Power Platform).
The focus of Dynamics 365 has consistently been on integration with Microsoft’s broader suite of business applications and tools, offering a cohesive experience for users within the Microsoft ecosystem. Dynamics 365 has been designed to serve various industries, with tailored solutions available for sectors like manufacturing, retail, and financial services. The platform’s continuous evolution reflects Microsoft’s commitment to adapting to the changing needs of businesses and technological advancements.
Origins and Growth of Salesforce
Salesforce, founded in 1999, pioneered the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) CRM model. Marc Benioff, Parker Harris, and their team envisioned a cloud-based CRM solution that could be accessed from anywhere, eliminating the need for on-premise software installations. Salesforce’s initial target audience was SMBs, offering a user-friendly and affordable alternative to traditional, complex CRM systems.Salesforce’s growth has been remarkable, marked by strategic acquisitions and a focus on innovation.
The company expanded its offerings beyond core CRM functionalities to include marketing automation, sales force automation, customer service, and analytics. This expansion transformed Salesforce into a comprehensive platform for managing all aspects of customer relationships.
- Key Growth Drivers for Salesforce:
- Cloud-Based Delivery: Pioneering the SaaS model, providing accessibility and ease of use.
- Focus on Customer Success: Building a strong ecosystem of partners and developers.
- Strategic Acquisitions: Expanding capabilities through acquisitions like ExactTarget (marketing automation) and MuleSoft (integration).
- Innovation: Continuously introducing new features and technologies, including AI (Einstein) and industry-specific solutions.
Salesforce’s success is attributable to its early adoption of the SaaS model, its focus on customer success, and its commitment to innovation. Salesforce’s platform has been consistently ranked as the leading CRM provider in terms of market share, serving a diverse range of industries and company sizes. Salesforce’s approach is centered on fostering a strong ecosystem of partners and developers, which has contributed significantly to its widespread adoption and continued growth.
Initial Target Audience and Core Strengths of Each Platform
Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce initially targeted SMBs, but their core strengths and approaches differed.
| Feature | Dynamics 365 | Salesforce |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Target Audience | Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs), with a focus on integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem. | Small and Medium-sized Businesses (SMBs), with a focus on ease of use and cloud-based accessibility. |
| Core Strengths | Integration with Microsoft’s existing business applications (Office 365, Power Platform, etc.), strong ERP capabilities, and a comprehensive suite of applications. | User-friendliness, cloud-based accessibility, a robust AppExchange ecosystem, and a strong focus on sales and marketing automation. |
| Key Differentiators | Deep integration with the Microsoft ecosystem, offering a familiar interface and seamless data flow for Microsoft users. | A highly customizable platform, a vast marketplace of third-party applications (AppExchange), and a strong focus on sales and marketing automation capabilities. |
Dynamics 365 leveraged Microsoft’s existing presence in the business software market, particularly with products like Microsoft Office and Dynamics GP (Great Plains), to gain traction among businesses already using Microsoft products. Salesforce, on the other hand, emphasized its cloud-based, user-friendly approach, which made it attractive to companies seeking a CRM solution without the complexities of on-premise installations. Both platforms have evolved significantly since their inception, expanding their feature sets and target audiences.
The initial strategies, however, provided the foundation for their continued success in the competitive CRM market.
Core Features: Sales Force Automation (SFA)
Sales Force Automation (SFA) is a critical component of any Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system, streamlining sales processes and improving sales team efficiency. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce offer robust SFA capabilities, but they differ in their specific feature sets and implementation approaches. This section provides a detailed comparison of the SFA functionalities within each platform, focusing on lead management, opportunity tracking, and sales pipeline management.Salesforce and Dynamics 365, while offering comparable core SFA features, cater to different user preferences and business needs.
Salesforce is known for its extensive customization options and a large app ecosystem, providing flexibility for complex sales processes. Dynamics 365, integrated within the Microsoft ecosystem, emphasizes seamless integration with other Microsoft products and a user-friendly interface.
Sales Force Automation (SFA) Capabilities Comparison
Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce provide comprehensive SFA functionalities, including lead management, contact management, opportunity management, and sales forecasting. The core functionalities are designed to help sales teams manage their interactions with potential and existing customers, track sales activities, and ultimately, close more deals. The differences lie in the specific features, user interface, and the degree of customization offered.Salesforce provides a highly customizable platform with a vast ecosystem of applications.
This allows businesses to tailor their SFA processes to their specific requirements. Dynamics 365, on the other hand, focuses on seamless integration with other Microsoft products, such as Outlook and Excel, making it a strong choice for businesses already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
Lead Management in Dynamics 365 and Salesforce
Lead management is a crucial aspect of SFA, involving the capture, qualification, and nurturing of potential customers. Both platforms offer robust lead management capabilities, though they differ in their approach to lead scoring, lead assignment, and lead source tracking.* Dynamics 365:
Lead creation can be automated through web forms and integrations with marketing automation tools.
Lead scoring can be configured based on various criteria, such as website activity, email engagement, and demographic information.
Lead assignment rules can be set up to automatically route leads to the appropriate sales representatives.
Lead source tracking allows sales teams to identify the most effective lead generation channels. –
Salesforce
Salesforce provides similar lead capture capabilities, including web-to-lead forms and integrations with marketing platforms.
Lead scoring is available through its native features and the AppExchange, which offers a wide range of lead scoring apps.
Lead assignment rules are highly customizable, allowing for complex routing scenarios.
Detailed lead source tracking is available, providing insights into lead origin and performance.
Opportunity Tracking in Dynamics 365 and Salesforce
Opportunity tracking is the process of managing potential sales deals from initial contact through to closure. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce provide tools for tracking opportunities, including deal stages, estimated revenue, and close dates.* Dynamics 365:
Opportunities are tracked through a customizable sales process flow, guiding sales representatives through each stage of the sales cycle.
Users can define estimated revenue, close dates, and probability of winning for each opportunity.
Sales teams can easily track sales activities, such as calls, emails, and meetings, related to each opportunity.
Reporting and analytics provide insights into opportunity performance and sales pipeline health. –
Salesforce
Salesforce offers a similar opportunity management process, with a customizable sales pipeline.
Users can define deal stages, estimated revenue, and close dates.
Salesforce provides robust activity tracking capabilities, allowing sales teams to log and manage all interactions related to an opportunity.
Advanced reporting and dashboards provide real-time visibility into the sales pipeline.
Sales Pipeline Management: Creating and Managing Sales Pipelines
Effective sales pipeline management is critical for forecasting sales and managing the sales process efficiently. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce provide tools for creating and managing sales pipelines.* Dynamics 365:
The process begins with creating a new sales pipeline stage within the settings.
Define the stages of the sales process, such as “Qualify,” “Develop,” “Propose,” “Close,” and “Won/Lost.”
For each stage, define the expected activities, estimated revenue, and probability of winning.
Associate each opportunity with the relevant stage in the pipeline.
Track the progress of each opportunity through the sales cycle.
Regularly review and update the pipeline to ensure accuracy and identify potential bottlenecks. –
Salesforce
Salesforce’s pipeline management involves creating a sales process, which defines the stages of the sales cycle.
Create a new sales process within the Setup menu.
Customize the stages, such as “Prospecting,” “Qualification,” “Needs Analysis,” “Proposal/Quote,” “Negotiation/Review,” and “Closed Won/Lost.”
Define the expected activities, estimated revenue, and probability of winning for each stage.
Associate each opportunity with the appropriate sales process and stage.
Monitor the progress of opportunities through the pipeline.
Use reports and dashboards to analyze the pipeline and identify areas for improvement.
Core Features: Dynamics 365 Vs Salesforce: Enterprise CRM Comparison
Customer service and support are critical components of any Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system. Effective customer service enhances customer satisfaction, fosters loyalty, and ultimately contributes to business success. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce offer robust modules designed to manage and improve customer service interactions. This section delves into the specific features of each platform, comparing and contrasting their capabilities in areas such as case management, knowledge base functionality, and self-service portal offerings.
Dynamics 365 Customer Service and Support Modules
Dynamics 365 Customer Service provides a comprehensive suite of tools for managing customer interactions. These modules are designed to streamline service processes, improve agent productivity, and enhance customer satisfaction. Key features include:
- Case Management: This feature allows agents to log, track, and resolve customer issues. Cases can be created automatically from various channels (email, phone, chat, social media) and assigned to the appropriate agents or teams. The system supports escalation rules, service level agreements (SLAs), and automated workflows to ensure timely resolution.
- Knowledge Base: A central repository for articles, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides. Agents and customers can access this knowledge base to find answers to common questions and resolve issues independently. The knowledge base integrates seamlessly with case management, allowing agents to quickly find and share relevant information.
- Omnichannel Engagement: Dynamics 365 supports multiple communication channels, including live chat, email, phone, and social media. This allows agents to interact with customers through their preferred channels and provide a consistent service experience across all touchpoints.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): These agreements define the expected response times, resolution times, and other service level targets. The system monitors performance against SLAs and alerts agents and supervisors when targets are at risk of being missed.
- Customer Service Insights: This module provides analytics and insights into customer service performance. It offers dashboards and reports that track key metrics such as case resolution time, customer satisfaction scores, and agent productivity.
Salesforce Customer Service and Support Modules
Salesforce Service Cloud offers a comprehensive set of features for customer service and support, designed to provide a personalized and efficient service experience. The platform focuses on empowering agents and enabling self-service options for customers. Key features include:
- Case Management: Salesforce Service Cloud provides robust case management capabilities, allowing agents to track and resolve customer issues efficiently. Cases can be created from various channels, including email, phone, chat, and social media. Features such as case assignment rules, escalation rules, and workflow automation streamline the resolution process.
- Knowledge Base (Salesforce Knowledge): Salesforce Knowledge enables businesses to create and manage a comprehensive knowledge base. Agents and customers can access articles, FAQs, and troubleshooting guides to find answers to common questions. Salesforce Knowledge integrates with case management, allowing agents to quickly access and share relevant information.
- Service Console: A unified interface that provides agents with a 360-degree view of the customer, including case history, interactions, and relevant information. The service console streamlines agent workflows and improves productivity.
- Omnichannel Routing: Salesforce’s omnichannel routing intelligently directs customer inquiries to the most qualified agents, based on skills, availability, and priority. This ensures that customers receive prompt and efficient service across all channels.
- Self-Service Portals (Experience Cloud): Salesforce Experience Cloud allows businesses to create branded self-service portals where customers can access knowledge articles, submit cases, and interact with a community. This reduces the workload on agents and empowers customers to find answers independently.
Comparison of Customer Service Features
Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce offer comprehensive customer service modules. However, there are key differences in their approach and capabilities. This section compares and contrasts their features in key areas, including case management, knowledge base, and self-service portals.
- Case Management: Both platforms provide robust case management features. Dynamics 365 offers a streamlined interface for managing cases, with strong integration with other Dynamics 365 modules. Salesforce excels in its customization options and its ability to handle complex workflows. For example, Salesforce allows for more granular control over case assignment rules and escalation processes.
- Knowledge Base: Both platforms include knowledge base features. Dynamics 365 offers a straightforward knowledge base that integrates well with case management. Salesforce Knowledge offers more advanced features, such as article versioning, feedback, and analytics. Salesforce Knowledge also integrates more deeply with the broader Salesforce ecosystem, allowing for more sophisticated use cases, such as using knowledge articles to proactively address customer issues.
- Self-Service Portals: Both platforms offer self-service portal capabilities. Dynamics 365 allows for the creation of basic self-service portals, providing customers with access to knowledge articles and case submission options. Salesforce Experience Cloud offers a more robust and customizable self-service portal solution, allowing businesses to create branded portals with advanced features such as community forums, personalized content, and integration with other Salesforce applications.
For example, a company using Salesforce could create a portal where customers can track the status of their orders, access support articles, and connect with other customers in a community forum, all within a single, branded experience.
- Integration and Ecosystem: Salesforce, with its larger ecosystem, generally provides more third-party app integrations specifically for customer service functions. This includes integrations for advanced analytics, AI-powered chatbots, and specialized support tools. Dynamics 365 also offers integrations, but the breadth of third-party options may be slightly less extensive.
Core Features: Dynamics 365 Vs Salesforce: Enterprise CRM Comparison
Marketing automation is a critical component of modern CRM systems, enabling businesses to streamline marketing processes, nurture leads, and improve overall marketing ROI. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce offer robust marketing automation capabilities, though they differ in their approach and feature sets. This section provides a detailed comparison of these two platforms.
Dynamics 365 Marketing Automation Capabilities
Dynamics 365 Marketing provides a comprehensive suite of marketing automation tools designed to help businesses engage with customers and prospects. It is built directly within the Dynamics 365 ecosystem, offering seamless integration with other modules like Sales and Customer Service.The key features include:
- Customer Journey Orchestration: Dynamics 365 allows users to design and execute sophisticated customer journeys. These journeys can be triggered by various events, such as website visits, form submissions, or email opens. Users can create branching paths based on customer behavior, personalizing the experience at each touchpoint.
- Email Marketing: The platform offers a drag-and-drop email editor, enabling marketers to create visually appealing and responsive emails. Features include A/B testing, personalization, and detailed analytics to track email performance, such as open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates.
- Lead Scoring and Nurturing: Dynamics 365 enables lead scoring based on predefined criteria, such as website activity, email engagement, and demographic information. Automated lead nurturing campaigns can then be created to guide leads through the sales funnel. For example, a lead who downloads a whitepaper might automatically receive a series of emails offering further resources and eventually a sales call.
- Segmentation: Advanced segmentation capabilities allow marketers to target specific groups of contacts based on various criteria, including demographics, behavior, and purchase history. This ensures that marketing messages are relevant and effective.
- Event Management: Dynamics 365 facilitates the management of events, including webinars, conferences, and workshops. It provides tools for event registration, promotion, and post-event follow-up.
- Marketing Analytics and Reporting: The platform offers comprehensive analytics and reporting dashboards to track marketing performance. Users can monitor key metrics, such as campaign effectiveness, lead generation, and ROI. These insights can be used to optimize marketing strategies and improve results.
Salesforce Marketing Automation Capabilities
Salesforce offers a robust marketing automation solution through its Marketing Cloud, a separate platform that integrates with the core Salesforce CRM. Marketing Cloud provides a wide range of features designed to help businesses engage with customers across multiple channels.The key features include:
- Journey Builder: Salesforce’s Journey Builder is a visual interface for designing and automating customer journeys. It allows marketers to create personalized experiences across various channels, including email, SMS, and mobile push notifications. Journeys can be triggered by events, such as purchases, website activity, or social media interactions.
- Email Marketing: Marketing Cloud provides advanced email marketing capabilities, including a drag-and-drop email builder, A/B testing, and personalization features. Users can send targeted emails to segmented audiences and track email performance through detailed analytics.
- Lead Scoring and Nurturing: Salesforce enables lead scoring and lead nurturing through its Marketing Cloud. Leads are scored based on their engagement with marketing content and their demographic information. Automated nurture campaigns can be created to guide leads through the sales funnel, providing relevant content at each stage. For instance, a lead scoring high based on content interaction might be automatically added to a “hot lead” campaign.
- Segmentation: Salesforce’s segmentation capabilities allow marketers to target specific audiences based on various criteria, including demographics, behavior, and purchase history. This ensures that marketing messages are relevant and effective.
- Advertising Studio: Salesforce provides Advertising Studio, which allows marketers to manage advertising campaigns across various platforms, including Facebook, Instagram, Google, and LinkedIn. This enables marketers to reach a wider audience and drive traffic to their websites.
- Social Media Marketing: Salesforce offers tools for managing social media marketing campaigns, including social listening, content scheduling, and engagement tracking.
Comparison of Marketing Automation Features
Comparing Dynamics 365 Marketing and Salesforce Marketing Cloud reveals key similarities and differences. Both platforms offer robust marketing automation capabilities, but they differ in their approach and integration.The following table provides a direct comparison:
| Feature | Dynamics 365 Marketing | Salesforce Marketing Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Email Marketing | Drag-and-drop editor, A/B testing, personalization, detailed analytics | Drag-and-drop editor, A/B testing, personalization, detailed analytics |
| Campaign Management | Customer journey orchestration, event management, lead nurturing | Journey Builder, advertising studio, social media marketing |
| Lead Scoring | Based on predefined criteria, integrated with sales module | Based on engagement and demographics, integrated with sales module |
| Segmentation | Advanced segmentation based on demographics, behavior, and purchase history | Advanced segmentation based on demographics, behavior, and purchase history |
| Integration | Seamless integration within the Dynamics 365 ecosystem | Integration with Salesforce CRM and other platforms, often requiring additional configuration |
| Pricing | Based on the number of marketing contacts | Tiered pricing based on features and volume |
Both Dynamics 365 Marketing and Salesforce Marketing Cloud provide comprehensive features for email marketing, campaign management, and lead scoring. The choice between the two platforms depends on factors such as existing CRM infrastructure, integration needs, and budget. Dynamics 365 offers tight integration with its CRM, making it ideal for businesses already using the Dynamics 365 suite. Salesforce Marketing Cloud, while a separate platform, offers a broader range of features and integrations, making it suitable for businesses with complex marketing needs and diverse technology stacks.
Deployment Options and Pricing Models
Understanding the deployment options and pricing structures of Dynamics 365 and Salesforce is crucial for businesses evaluating CRM platforms. These factors significantly influence the total cost of ownership (TCO), scalability, and the level of control an organization has over its data and infrastructure. Choosing the right model ensures alignment with business needs, IT capabilities, and budgetary constraints.
Dynamics 365 Deployment Options
Dynamics 365 offers a spectrum of deployment choices, providing flexibility to organizations with varying requirements. The primary options are cloud-based and, to a limited extent, on-premises.
- Cloud Deployment: Dynamics 365 is primarily a cloud-first solution, leveraging Microsoft’s Azure infrastructure. This is the most common deployment method, offering scalability, automatic updates, and reduced IT overhead. Data is hosted on Microsoft’s servers, and access is provided via a web browser or mobile apps. This deployment model allows businesses to focus on their core competencies rather than managing the underlying infrastructure.
- On-Premises Deployment: While less common, Dynamics 365 offers on-premises deployment for certain modules, particularly for older versions or specific compliance needs. This option provides greater control over data and infrastructure, as the software is installed on a company’s own servers. However, it requires the organization to manage the hardware, software, and security, increasing IT resource requirements and potentially the TCO. Microsoft is gradually moving away from on-premises deployments, prioritizing the cloud-first approach.
Salesforce Deployment Options
Salesforce, similar to Dynamics 365, primarily focuses on cloud-based deployment, offering scalability and ease of management.
- Cloud Deployment: Salesforce is a pure Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) platform, meaning it’s exclusively hosted in the cloud. Salesforce manages the infrastructure, software updates, and security. This deployment model offers a low barrier to entry, rapid deployment, and scalability. Salesforce provides a multi-tenant architecture, where multiple customers share the same infrastructure, which allows for cost efficiency.
- Private Cloud: Although Salesforce is primarily a public cloud solution, it offers private cloud options through partnerships or dedicated instances for large enterprises with specific security, compliance, or performance requirements. This option provides more control over the environment compared to the standard multi-tenant cloud.
Pricing Model Comparison
Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce employ subscription-based pricing models, with costs varying based on features, user licenses, and the chosen modules. The following table offers a comparison of the general pricing structures, acknowledging that specific pricing can change and vary depending on the specific editions, add-ons, and the volume of licenses purchased. The information provided is for illustrative purposes and based on publicly available information.
| Feature | Dynamics 365 Sales Professional | Dynamics 365 Sales Enterprise | Salesforce Sales Essentials | Salesforce Sales Professional |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Price per User/Month (approx.) | Around $65 | Around $95 | Around $25 | Around $75 |
| Core Features |
|
|
|
|
| Additional Features/Considerations |
|
|
|
|
| Target User | Small to Medium Businesses (SMBs) | Mid-size to Large Enterprises | Small Businesses and Teams | Growing Businesses and Teams |
Important Note: The pricing provided in the table is approximate and subject to change. Actual pricing can vary based on contract terms, add-ons, and special offers. Businesses should consult with Microsoft and Salesforce directly for the most up-to-date and accurate pricing information tailored to their specific needs.
Customization and Integration Capabilities
The ability to tailor a CRM system to specific business needs and seamlessly connect it with other critical applications is paramount for maximizing its value. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce offer extensive customization and integration capabilities, though they approach these functionalities with distinct strengths and weaknesses. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the platform that best aligns with an organization’s existing IT infrastructure and future growth plans.
Customization Options in Dynamics 365
Dynamics 365 provides a robust set of tools for customizing the CRM platform to fit specific business processes. This flexibility allows organizations to adapt the system to their unique requirements, improving user adoption and overall efficiency.
- Custom Fields: Users can add custom fields to any entity (e.g., Account, Contact, Opportunity) to capture specific data relevant to their business. This allows for tracking information not included in the standard CRM data model. For example, a manufacturing company might add fields to track product specifications or warranty information directly within the customer record.
- Custom Entities: Organizations can create entirely new entities to represent unique business objects or processes. This is useful for managing information not directly related to standard CRM functions. A healthcare provider, for example, could create a custom entity to track patient appointments or medical history.
- Forms and Views Customization: The user interface can be customized to improve user experience. Forms can be modified to display the most relevant information, and views can be created to filter and sort data according to specific needs. For instance, sales teams can create tailored views to focus on high-priority leads or opportunities.
- Business Rules: Business rules automate actions based on data changes. These rules can be used to validate data, set field values, show or hide fields, and display error messages. For example, a business rule could automatically update the status of an opportunity when a specific condition is met, reducing manual effort and ensuring data consistency.
- Workflows: Workflows automate business processes by defining a series of steps that are executed when a specific trigger occurs. Workflows can be used to send email notifications, update records, and perform other tasks. For example, a workflow could automatically notify a sales manager when a new lead is assigned to a sales representative.
- Power Platform Integration: Dynamics 365 seamlessly integrates with the Microsoft Power Platform, including Power Apps, Power Automate, and Power BI. This integration allows for the creation of custom applications, automated workflows, and insightful dashboards. For example, a custom Power App can be built to allow sales representatives to easily capture data on their mobile devices.
Customization Options in Salesforce
Salesforce also offers extensive customization options, providing businesses with the flexibility to tailor the platform to their specific needs. Salesforce’s customization capabilities are known for their depth and the vast ecosystem of applications available on the AppExchange.
- Custom Objects: Salesforce allows users to create custom objects to store data that is specific to their business needs. This is similar to custom entities in Dynamics 365, enabling the tracking of unique business processes. A financial services company, for example, might create a custom object to track investment portfolios.
- Custom Fields: Users can add custom fields to standard and custom objects to capture specific data points. This is a fundamental customization feature, enabling organizations to capture detailed information relevant to their operations. A retail company could add custom fields to track customer purchase history or product preferences.
- Page Layouts and Record Types: Salesforce provides tools to customize the user interface, allowing administrators to control which fields are displayed and in what order. Record types allow for different layouts and business processes based on the type of record. For example, a sales team could use different record types for different product lines.
- Process Builder and Flows: Salesforce offers the Process Builder and Flows for automating business processes. These tools enable users to create automated workflows without writing code. Process Builder is being phased out in favor of Flows, which offer more advanced capabilities. For example, a flow could automatically create a task for a sales representative when a new lead is created.
- Apex and Visualforce (Legacy): Salesforce supports Apex, a proprietary programming language, and Visualforce (now considered legacy), a framework for building custom user interfaces. These tools allow developers to create highly customized solutions and extend the functionality of the platform. Although Visualforce is still supported, Salesforce recommends using Lightning Web Components (LWC) for modern UI development.
- Lightning Web Components (LWC): LWC is a modern framework for building custom user interfaces within Salesforce. This framework allows developers to create reusable components that can be easily integrated into Salesforce pages. This is a more efficient and maintainable approach compared to Visualforce.
Integration Capabilities of Each Platform
Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce excel in integrating with other business systems, offering various options for connecting with existing infrastructure and data sources. The choice between the two often depends on the specific integration needs of the organization, including the existing technology stack and the desired level of customization.
- Dynamics 365 Integration Capabilities: Dynamics 365 has strong integration capabilities, especially within the Microsoft ecosystem. Its integration with other Microsoft products is seamless and out-of-the-box.
- Microsoft Ecosystem: Dynamics 365 integrates natively with other Microsoft products such as Microsoft 365 (Outlook, Teams, SharePoint), Power Platform (Power BI, Power Automate, Power Apps), and Azure services.
- Dataverse: Dynamics 365 uses Dataverse (formerly Common Data Service) as its underlying data platform. Dataverse provides a secure and scalable data storage solution that facilitates integration with other applications.
- Connectors: Dynamics 365 offers a wide range of pre-built connectors to integrate with third-party applications. Power Automate provides hundreds of connectors to popular services like Google Workspace, Dropbox, and social media platforms.
- APIs: Dynamics 365 provides robust APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow for custom integrations with other systems. These APIs support various protocols, including REST and OData, enabling developers to build custom solutions.
- Example Integrations:
- Outlook Integration: Seamlessly track emails, appointments, and contacts directly within Dynamics 365.
- SharePoint Integration: Store and manage documents related to customer records in SharePoint.
- Power BI Integration: Create insightful dashboards and reports using data from Dynamics 365.
- Third-party Applications: Integrate with marketing automation platforms (e.g., Marketo, HubSpot), ERP systems (e.g., SAP, Oracle), and other business applications.
- Salesforce Integration Capabilities: Salesforce offers extensive integration capabilities, supported by its robust API and the AppExchange, a marketplace with thousands of pre-built integrations.
- Salesforce APIs: Salesforce provides powerful APIs (REST API, SOAP API, Bulk API) for integrating with other systems. These APIs are highly flexible and can be used to build custom integrations.
- AppExchange: The AppExchange is a marketplace with thousands of pre-built applications and integrations. This allows organizations to easily connect Salesforce with various third-party applications, such as marketing automation platforms, ERP systems, and project management tools.
- MuleSoft Anypoint Platform: Salesforce owns MuleSoft, a leading integration platform that simplifies connecting applications, data, and devices. MuleSoft allows organizations to create and manage complex integrations.
- Example Integrations:
- Marketing Automation: Integrate with marketing automation platforms (e.g., Marketo, Pardot) to synchronize leads and track marketing campaigns.
- ERP Systems: Integrate with ERP systems (e.g., SAP, Oracle) to synchronize customer data, orders, and invoices.
- Financial Systems: Integrate with financial systems (e.g., NetSuite, QuickBooks) to manage financial transactions and reporting.
- Service Cloud Integrations: Integrate with telephony systems, live chat platforms, and knowledge bases to improve customer service.
User Interface and User Experience
The user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) are critical aspects of any CRM system, significantly impacting user adoption, productivity, and overall satisfaction. A well-designed UI facilitates efficient navigation and data access, while a positive UX ensures users enjoy interacting with the system. This section examines the UI and UX of Dynamics 365 and Salesforce, comparing their strengths and weaknesses.
User Interface of Dynamics 365, Dynamics 365 vs Salesforce: Enterprise CRM Comparison
Dynamics 365 offers a modern, intuitive user interface built on the Microsoft Power Platform. Its design emphasizes a clean layout and consistent user experience across different modules and devices. The UI adapts to various screen sizes, providing a responsive design that enhances usability on both desktops and mobile devices.The key elements of the Dynamics 365 UI include:
- Navigation Bar: Located at the top, the navigation bar provides access to various modules (Sales, Marketing, Customer Service, etc.), search functionality, and user settings. The navigation is designed to be customizable, allowing users to tailor the experience to their specific roles and needs.
- Command Bar: Situated at the top or within specific views, the command bar provides quick access to frequently used actions, such as creating new records, saving changes, and exporting data. The commands available change depending on the context of the current view.
- Forms and Views: Dynamics 365 utilizes forms to display and edit data, while views present data in a list format. Forms are customizable, allowing administrators to rearrange fields, add sections, and integrate custom controls. Views can be filtered, sorted, and grouped to provide tailored data displays.
- Dashboards: Dashboards offer a visual representation of key performance indicators (KPIs) and data insights. They are highly customizable and can include charts, graphs, and other visualizations to provide a comprehensive overview of business performance.
- Mobile Application: Dynamics 365 features a dedicated mobile application for iOS and Android devices. The mobile app provides a streamlined user experience, optimized for mobile access.
User Interface of Salesforce
Salesforce’s user interface has evolved over time, with a focus on providing a flexible and feature-rich platform. The UI offers a highly customizable experience, enabling organizations to tailor the system to their specific branding and operational requirements. Salesforce utilizes a component-based architecture, allowing for the creation of custom pages and applications.Key features of the Salesforce UI include:
- Navigation Menu: Typically located at the top or side, the navigation menu provides access to different Salesforce objects and applications. The menu can be customized to reflect the user’s role and preferred workflows.
- Utility Bar: The utility bar, located at the bottom, provides quick access to frequently used tools and features, such as recent items, notes, and utilities.
- Object Pages: Salesforce uses object pages to display and manage data related to specific objects (e.g., accounts, contacts, opportunities). These pages are highly customizable, allowing for the addition of custom fields, related lists, and custom components.
- Lightning Experience: Salesforce’s modern user interface, Lightning Experience, offers a more intuitive and visually appealing experience compared to the classic interface. It features a component-based architecture, allowing for the creation of custom pages and applications.
- Mobile Application: Salesforce provides a robust mobile application for iOS and Android devices, enabling users to access and manage their data on the go. The mobile app offers offline capabilities and a streamlined user experience.
Comparison of User Experience
Comparing the user experience of Dynamics 365 and Salesforce involves assessing ease of use, navigation, and mobile access. Both platforms offer comprehensive features and capabilities, but their approaches to UX differ.
- Ease of Use: Dynamics 365 is often praised for its intuitive interface and ease of navigation, particularly for users familiar with other Microsoft products. Salesforce, while powerful, can have a steeper learning curve due to its extensive features and customization options. Some users find the sheer number of options and customization possibilities in Salesforce overwhelming initially. Dynamics 365’s more streamlined approach can make it easier for new users to adopt the system quickly.
- Navigation: Both platforms offer robust navigation systems, but the specific implementations differ. Dynamics 365’s navigation is generally considered straightforward, with clear module divisions and easy access to core functionalities. Salesforce’s navigation, particularly within the Lightning Experience, provides a customizable experience. The ability to tailor the navigation menu and add custom components provides a flexible approach, but this can also lead to a more complex initial setup.
- Mobile Access: Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce offer well-developed mobile applications that provide access to core CRM functionalities on mobile devices. Both apps support offline access, allowing users to work even without an internet connection. Salesforce’s mobile app often gets praised for its feature-rich capabilities, but Dynamics 365’s mobile app provides a seamless experience, especially for organizations already invested in the Microsoft ecosystem.
Industry-Specific Solutions
CRM platforms are often more effective when tailored to specific industries. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce recognize this and offer solutions designed to address the unique needs and challenges of various sectors. This section examines the industry-specific strengths of each platform and compares their offerings.
Dynamics 365’s Industry Strengths
Dynamics 365 has carved a strong niche in several industries, often leveraging its deep integration with other Microsoft products like the Power Platform, Azure, and Office 365. This synergy provides significant advantages in data management, workflow automation, and business intelligence.
- Manufacturing: Dynamics 365 for Sales, coupled with Dynamics 365 for Supply Chain Management, provides comprehensive solutions for manufacturers. This includes features for sales order management, production scheduling, inventory tracking, and service management. For instance, companies like Thyssenkrupp have adopted Dynamics 365 to streamline their sales processes and improve customer relationships, highlighting its suitability for complex manufacturing environments.
- Financial Services: Dynamics 365 offers solutions for wealth management, banking, and insurance. These solutions focus on customer relationship management, regulatory compliance, and personalized client experiences. The platform’s robust security features and integration with financial data sources make it a compelling choice for financial institutions. For example, some financial institutions use Dynamics 365 to manage client interactions and provide personalized financial advice.
- Retail: Dynamics 365 Commerce provides tools for managing sales, marketing, and customer service across multiple channels, including physical stores, e-commerce platforms, and mobile apps. It supports features like point-of-sale (POS) systems, inventory management, and personalized customer experiences. Companies like Starbucks utilize Dynamics 365 for retail management, including order management and customer loyalty programs.
- Healthcare: Dynamics 365 for Healthcare offers features to manage patient relationships, streamline administrative tasks, and improve care coordination. It helps healthcare providers improve patient engagement, enhance operational efficiency, and maintain regulatory compliance.
Salesforce’s Industry Strengths
Salesforce, with its extensive ecosystem and broad market presence, also excels in specific industries. Its AppExchange marketplace provides a vast array of industry-specific applications and integrations, allowing for highly customized solutions.
- Financial Services: Salesforce Financial Services Cloud is designed for wealth management, retail banking, and insurance. It provides features for relationship management, client onboarding, and regulatory compliance. Companies like USAA use Salesforce to improve customer service and provide personalized financial services.
- Healthcare and Life Sciences: Salesforce Health Cloud helps healthcare providers and life sciences companies manage patient relationships, improve care coordination, and streamline clinical trials. It focuses on patient engagement, data security, and regulatory compliance. Notable users include large healthcare providers.
- Retail: Salesforce Commerce Cloud offers comprehensive solutions for e-commerce, in-store experiences, and customer relationship management. It provides features for product catalog management, order management, and personalized marketing. Retailers such as Adidas use Salesforce to manage their online and in-store sales operations.
- Manufacturing: Salesforce Manufacturing Cloud provides tools for sales and operations planning, channel management, and partner relationship management. It integrates with other systems to improve supply chain visibility and optimize manufacturing processes.
Comparing Industry-Specific Solutions and Pre-Built Templates
The availability of industry-specific solutions and pre-built templates is a critical factor in choosing a CRM platform. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce offer these resources, but their approaches and strengths differ.
- Dynamics 365: Dynamics 365 offers pre-built industry templates and solutions that often integrate seamlessly with other Microsoft products. This integration can provide a more streamlined implementation process and reduce the need for extensive customization. The Power Platform, with its low-code/no-code capabilities, allows businesses to easily customize and extend these solutions to meet their specific needs.
- Salesforce: Salesforce has a broader ecosystem of industry-specific applications available through its AppExchange marketplace. This provides a wider range of choices and allows businesses to select solutions that precisely match their requirements. However, the integration of these third-party applications can sometimes require more effort and technical expertise. Salesforce’s robust API also allows for highly customized solutions.
The choice between Dynamics 365 and Salesforce depends on the specific industry and the desired level of customization. Dynamics 365 excels in industries where Microsoft product integration is crucial, while Salesforce provides a more extensive marketplace of third-party applications.
Reporting and Analytics
Reporting and analytics are crucial for understanding CRM performance, identifying trends, and making data-driven decisions. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce offer robust reporting and analytics capabilities, but they differ in their approach and specific tools. This section explores the reporting and analytics tools within each system and provides a practical demonstration of creating a basic sales performance report.
Reporting and Analytics Tools in Dynamics 365
Dynamics 365 provides a suite of reporting and analytics tools designed to provide insights into various business operations. These tools enable users to visualize data, track key performance indicators (KPIs), and make informed decisions.
- Power BI Integration: Dynamics 365 deeply integrates with Microsoft Power BI, a powerful business intelligence platform. This integration allows users to create interactive dashboards, perform advanced data analysis, and share insights across the organization. Power BI can connect to a wide variety of data sources, including Dynamics 365 data, and offers extensive data visualization options.
- Built-in Reporting: Dynamics 365 includes built-in reporting features that allow users to generate standard reports on sales, marketing, customer service, and other areas. These reports can be customized to meet specific needs and can be exported in various formats, such as Excel and PDF.
- Advanced Find: Advanced Find enables users to query data within Dynamics 365 based on specific criteria. This tool is useful for creating ad-hoc reports and identifying specific data sets. The results of an Advanced Find query can be exported to Excel for further analysis.
- Custom Reports: Users can create custom reports using the Dynamics 365 reporting engine. This provides flexibility in designing reports tailored to specific business requirements. Custom reports can incorporate complex calculations and data visualizations.
- Dashboards: Dynamics 365 dashboards provide a centralized view of key performance indicators and other important data. Users can customize dashboards to display the information most relevant to their roles. Dashboards can include charts, graphs, and other visualizations.
Reporting and Analytics Tools in Salesforce
Salesforce also offers comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities. Its tools are designed to provide users with a 360-degree view of their customers and business performance.
- Salesforce Reports: Salesforce Reports is a core feature that allows users to generate reports based on their data. Users can create reports using a drag-and-drop interface and customize them with filters, groupings, and formulas.
- Salesforce Dashboards: Salesforce Dashboards provide a visual representation of key metrics and trends. Dashboards can include charts, graphs, and tables, and they can be customized to display the information most relevant to each user’s role.
- Salesforce Einstein Analytics (Tableau CRM): Salesforce Einstein Analytics (now Tableau CRM) is a powerful analytics platform that provides advanced data visualization, data discovery, and predictive analytics capabilities. It allows users to analyze large datasets, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions.
- Custom Report Types: Salesforce allows users to define custom report types, which determine the objects and fields that are available in reports. This provides flexibility in creating reports that meet specific business needs.
- AppExchange: Salesforce AppExchange offers a wide range of third-party reporting and analytics apps that can be integrated with Salesforce to extend its capabilities.
Creating a Basic Sales Performance Report
Creating a basic sales performance report provides a practical demonstration of the reporting capabilities within each system. This example will illustrate how to generate a report showing the total value of closed won opportunities within a specific timeframe.
- Dynamics 365:
- Access the Reports Section: Navigate to the Sales area and select “Reports.”
- Create a New Report: Click on “New” to create a new report.
- Choose Report Type: Select “Report Wizard” or “Power BI” depending on your preference and available licenses. If using the Report Wizard, select the appropriate entity (e.g., Opportunity) and fields for the report. If using Power BI, select the Dynamics 365 data source.
- Define Filters: Set filters to include only opportunities with a “Closed Won” status and a date range (e.g., “Created On” within the last quarter).
- Configure Columns: Add columns to the report, such as “Opportunity Name,” “Close Date,” and “Estimated Revenue.”
- Summarize Data: Use the report wizard to calculate the sum of the “Estimated Revenue” field to get the total value of closed won opportunities.
- Save and Run: Save the report and then run it to view the results. The report will display a list of closed won opportunities and their total value.
- Salesforce:
- Access the Reports Tab: From the navigation menu, select the “Reports” tab.
- Create a New Report: Click on “New Report.”
- Choose Report Type: Select the “Opportunities” report type.
- Define Filters: In the report builder, add filters to include only opportunities with a “Closed Won” stage and a date range for the “Close Date” field.
- Add Columns: Add columns such as “Opportunity Name,” “Close Date,” and “Amount.”
- Summarize Data: Group the data by “Close Date” and then add a summary formula to calculate the sum of the “Amount” field.
- Save and Run: Save the report and run it. The report will show a list of closed won opportunities and their total amount, grouped by the selected criteria.
Security and Compliance
Security and compliance are paramount considerations for any enterprise CRM implementation. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce provide robust security features and adhere to stringent compliance standards. The choice between the two often depends on specific industry requirements and organizational risk tolerance. This section examines the security measures, compliance certifications, and data privacy features of both platforms.
Dynamics 365 Security Measures
Dynamics 365 employs a multi-layered approach to security, encompassing various features to protect data and ensure system integrity. These measures are crucial for safeguarding sensitive customer information and maintaining regulatory compliance.
- Data Encryption: Dynamics 365 utilizes encryption at rest and in transit. At rest, data stored in Microsoft’s data centers is encrypted using BitLocker or other technologies. In transit, data is encrypted using Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure communication between users and the platform. This prevents unauthorized access to data during transmission.
- Identity and Access Management: Role-based security allows administrators to control user access to data and functionality based on their roles within the organization. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is supported to add an extra layer of security, requiring users to verify their identity using a second factor, such as a code from a mobile app.
- Threat Detection and Protection: Microsoft Defender for Cloud (formerly Azure Security Center) provides threat detection and response capabilities, including monitoring for suspicious activity, identifying vulnerabilities, and providing recommendations for security improvements.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): DLP policies can be implemented to prevent sensitive information from leaving the organization. This includes preventing users from sharing confidential data through email, cloud storage, or other channels.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Microsoft conducts regular security audits and penetration testing to identify and address vulnerabilities. These tests are performed by both internal teams and third-party security experts.
Salesforce Security Measures
Salesforce offers a comprehensive suite of security features designed to protect customer data and maintain the integrity of the platform. These measures are essential for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data within the Salesforce ecosystem.
- Platform Encryption: Salesforce provides native encryption capabilities, allowing customers to encrypt sensitive data at rest within the Salesforce platform. This ensures that even if unauthorized access occurs, the data remains protected.
- Identity Verification: Salesforce supports various identity verification methods, including multi-factor authentication (MFA), to secure user access. MFA helps prevent unauthorized users from accessing the platform.
- Access Controls: Salesforce offers granular access controls, including role-based access control (RBAC) and permission sets, to manage user access to data and functionality. Administrators can define user profiles and permissions to restrict access based on job roles.
- Monitoring and Auditing: Salesforce provides comprehensive audit trails that track user activity and data changes. This allows administrators to monitor user behavior, identify potential security breaches, and ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Security Assessments and Compliance Programs: Salesforce undergoes regular security assessments and maintains compliance with various industry standards, such as ISO 27001 and SOC 2. These assessments validate the effectiveness of Salesforce’s security controls.
Compliance Certifications and Data Privacy Comparison
Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce have achieved numerous compliance certifications and offer features to support data privacy regulations. A comparison highlights the key differences and similarities.
- Compliance Certifications: Both platforms adhere to a wide range of industry standards and regulations, including:
- ISO 27001: An internationally recognized standard for information security management systems.
- SOC 2: A standard for service organizations that ensures data is managed securely to protect the interests of the organization and the privacy of its clients.
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): Relevant for organizations that handle protected health information (PHI).
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): A regulation in EU law on data protection and privacy in the European Union and the European Economic Area.
- CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act): A state law that provides California consumers with the right to control their personal information.
- Data Privacy Features:
- Data Residency: Both platforms offer data residency options, allowing customers to choose the geographic location where their data is stored. This is crucial for compliance with data sovereignty regulations.
- Data Subject Rights: Both platforms support data subject rights, such as the right to access, rectify, and erase personal data. These features help organizations comply with GDPR and other data privacy regulations.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Both platforms provide data loss prevention capabilities to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization.
- Privacy Controls: Salesforce provides features like Privacy Center to centralize privacy-related settings and activities, while Dynamics 365 integrates with Microsoft’s broader compliance offerings.
- Key Differences:
- Integration with Ecosystems: Dynamics 365 benefits from seamless integration with the Microsoft ecosystem, including Azure and Microsoft 365, which can streamline compliance efforts.
- Specific Industry Solutions: Both platforms offer industry-specific solutions that address the unique compliance requirements of various sectors, such as healthcare, finance, and government.
Ecosystem and Community Support
Understanding the ecosystem and community support for Dynamics 365 and Salesforce is crucial for businesses. A strong ecosystem provides access to a vast network of partners, developers, and resources, which can significantly enhance the CRM platform’s capabilities and facilitate its successful implementation and ongoing management. This support network offers valuable assistance with customization, integration, training, and troubleshooting, ultimately influencing the overall return on investment.
Ecosystem and Community Support for Dynamics 365
Dynamics 365 benefits from Microsoft’s extensive ecosystem, providing a robust support network for users. This ecosystem encompasses a large number of partners, a dedicated online community, and comprehensive training resources.The Dynamics 365 ecosystem is vast and well-established.
- Microsoft Partner Network: This network provides access to a global community of partners specializing in Dynamics 365 implementations, customizations, and integrations. These partners offer a wide range of services, from initial consultation and deployment to ongoing support and development. Microsoft categorizes partners based on their expertise and certifications, allowing businesses to find partners that align with their specific needs.
- Microsoft AppSource: This online marketplace offers a wide variety of third-party applications and solutions that integrate with Dynamics 365. These apps extend the platform’s functionality, covering areas such as marketing automation, customer service, and industry-specific solutions. This marketplace provides a streamlined way for businesses to discover and implement solutions that complement their Dynamics 365 implementation.
- Dynamics 365 Community: Microsoft hosts an active online community where users, partners, and Microsoft employees can connect, share knowledge, and seek assistance. This community offers forums, blogs, and other resources for troubleshooting issues, learning best practices, and staying up-to-date on the latest features and updates.
- Microsoft Learn: Microsoft Learn offers extensive training resources for Dynamics 365, including self-paced learning paths, modules, and certifications. These resources cover various aspects of Dynamics 365, from basic user training to advanced development and administration. The platform is regularly updated to reflect the latest features and functionalities of the platform.
Ecosystem and Community Support for Salesforce
Salesforce has cultivated a mature and extensive ecosystem that is one of its core strengths. This ecosystem provides a comprehensive support system for users, including a large partner network, an active online community, and a wealth of training resources.Salesforce’s ecosystem is renowned for its breadth and depth.
- Salesforce AppExchange: The AppExchange is Salesforce’s marketplace for third-party applications and solutions. It offers a vast library of apps that extend the functionality of the Salesforce platform, covering a wide range of business needs, including sales, marketing, customer service, and more. The AppExchange facilitates seamless integration with Salesforce.
- Salesforce Partner Program: Salesforce’s partner program includes a diverse network of consulting partners, technology partners, and system integrators. These partners provide implementation services, customization, integration, and ongoing support. Salesforce categorizes partners based on their expertise and performance, allowing businesses to easily find partners with relevant experience.
- Salesforce Trailhead: Trailhead is Salesforce’s online learning platform, offering interactive modules and trails that teach users how to use Salesforce. It covers various topics, from basic user training to advanced development and administration. Trailhead is gamified, allowing users to earn badges and points as they complete modules, making the learning process engaging and effective.
- Salesforce Community: Salesforce hosts a vibrant online community where users can connect, share knowledge, and seek assistance. This community includes forums, blogs, and user groups, providing a platform for users to ask questions, share best practices, and collaborate.
Resources Available for Users
Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce provide users with extensive resources to facilitate successful implementation and ongoing use of their CRM platforms. These resources include online communities, training programs, and partner networks. The availability and quality of these resources can significantly impact the user experience and the overall success of a CRM implementation.To highlight the resources, a comparative overview can be presented.
| Resource | Dynamics 365 | Salesforce |
|---|---|---|
| Online Communities | Dynamics 365 Community, Microsoft Forums | Salesforce Community, Success Community |
| Training Programs | Microsoft Learn, Partner training | Trailhead, Salesforce University, Partner training |
| Partner Networks | Microsoft Partner Network, Microsoft AppSource | Salesforce Partner Program, AppExchange |
| Documentation | Microsoft documentation, TechNet | Salesforce documentation, Help and Training |
Scalability and Performance
Scalability and performance are crucial aspects of any enterprise CRM system, determining its ability to handle increasing data volumes, user loads, and complex operations. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce offer robust solutions in this area, but they approach scalability and performance with distinct architectural designs and service offerings. Understanding these differences is vital for businesses planning for growth and anticipating evolving CRM demands.
Scalability of Dynamics 365
Dynamics 365 is built on Microsoft’s Azure cloud platform, providing a highly scalable infrastructure. The platform’s scalability is a key selling point, offering several advantages for businesses.
- Horizontal Scalability: Azure allows Dynamics 365 to scale horizontally by adding more resources, such as compute power and storage, as needed. This means that the system can handle increasing user loads and data volumes without significant performance degradation. For instance, a company experiencing a sudden surge in sales due to a successful marketing campaign can quickly scale up its Dynamics 365 instance to accommodate the increased activity.
- Elasticity: Dynamics 365 leverages Azure’s elastic capabilities, which means the system can automatically adjust resources based on demand. This helps optimize costs by ensuring resources are only used when necessary.
- Database Scalability: Dynamics 365 uses SQL Server in the backend, which offers scalability options such as sharding and partitioning to manage large datasets efficiently. This architecture allows for the distribution of data across multiple servers, improving performance and reducing the load on any single server.
- Geographic Distribution: Azure’s global network of data centers allows Dynamics 365 to be deployed in various geographic regions, bringing the application closer to users and improving response times. This is particularly beneficial for multinational corporations with users spread across different continents.
Scalability of Salesforce
Salesforce also provides strong scalability, utilizing its own cloud infrastructure to manage large volumes of data and user activity. The platform’s scalability is a core design principle, allowing it to support some of the largest organizations globally.
- Multi-tenant Architecture: Salesforce operates on a multi-tenant architecture, where multiple customers share the same infrastructure and resources. This design enables Salesforce to efficiently manage resources and scale its platform.
- Automatic Scaling: Salesforce automatically scales its infrastructure to meet customer demands. The platform continuously monitors resource usage and adjusts its capacity to handle increasing loads.
- Database Scalability: Salesforce employs a sophisticated database architecture optimized for handling large datasets. The platform uses techniques like data partitioning and caching to improve performance.
- API Limits and Governance: Salesforce implements API limits and governance rules to manage resource usage and prevent individual customers from negatively impacting the performance of the platform for other users. These limits help ensure that the platform remains stable and performant, even during peak usage times.
Performance Characteristics of Both Platforms
Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce exhibit different performance characteristics, particularly in load times and handling of large datasets. Several factors influence these characteristics, including data volume, the complexity of customizations, and the number of concurrent users.
- Load Times:
- Dynamics 365: Load times in Dynamics 365 can vary depending on the complexity of the customizations, the number of plugins, and the size of the datasets. Generally, Dynamics 365 provides good performance, especially with optimized configurations. Microsoft regularly releases updates and performance improvements to enhance load times.
- Salesforce: Salesforce, with its multi-tenant architecture, generally offers consistent load times. However, performance can be affected by the complexity of the Salesforce instance and the number of customizations. Salesforce invests heavily in optimizing its platform for performance and provides tools for customers to improve performance, such as query optimization and efficient data modeling.
- Handling of Large Datasets:
- Dynamics 365: Dynamics 365 excels at handling large datasets due to its underlying Azure infrastructure and SQL Server database. The platform offers features like data partitioning, indexing, and asynchronous processing to manage large volumes of data efficiently.
- Salesforce: Salesforce is also well-equipped to manage large datasets. The platform employs various techniques to optimize performance, including data partitioning, caching, and optimized database queries. Salesforce provides tools and best practices for customers to effectively manage large datasets.
- Examples and Data:
- Dynamics 365: A global manufacturing company using Dynamics 365 reported a 20% improvement in data processing speed after implementing data partitioning and optimizing database queries.
- Salesforce: A large financial services firm using Salesforce experienced a 15% reduction in report generation time after optimizing their Salesforce instance by implementing caching and improving data modeling.
- Key Considerations:
- Customizations: Extensive customizations can impact the performance of both platforms. It is essential to design customizations efficiently and follow best practices to minimize performance degradation.
- Integrations: Integrations with other systems can also affect performance. The complexity and efficiency of the integrations should be carefully considered.
- User Training: Proper user training and adoption of best practices can improve performance. Users should be trained on how to use the platform effectively and avoid practices that could negatively impact performance.
Data Migration and Implementation

Source: technologyadvice.com
Data migration and implementation are critical phases in the transition to a new CRM system, significantly impacting its success. This section explores the specific processes for Dynamics 365 and Salesforce, followed by a comprehensive step-by-step implementation guide. A well-executed migration ensures data integrity and a smooth transition, while a well-planned implementation maximizes user adoption and the CRM’s overall effectiveness.
Data Migration Process for Dynamics 365
Dynamics 365 offers various data migration options, enabling organizations to choose the method best suited to their needs and technical capabilities. These methods vary in complexity and the level of control they provide.Dynamics 365 data migration generally involves the following stages:
- Planning and Assessment: This initial phase involves identifying the data sources, understanding data structures, and defining the scope of the migration. A comprehensive assessment helps to determine the data quality, volume, and complexity. This stage also includes selecting the appropriate migration tools and strategies. For instance, a company migrating from a legacy CRM system would need to carefully map the fields and data types to Dynamics 365 equivalents, identifying potential data cleansing requirements.
- Data Extraction: Data extraction involves retrieving data from the source systems. Dynamics 365 supports various data connectors and import tools. Data can be extracted from various sources, including CSV files, Excel spreadsheets, and databases. The choice of extraction method depends on the source system’s capabilities and the data’s format.
- Data Transformation: Data transformation is the process of cleaning, mapping, and converting the extracted data to align with Dynamics 365’s data structure. This may involve data cleansing (e.g., removing duplicates, standardizing formats), data mapping (matching source fields to Dynamics 365 fields), and data conversion (e.g., converting date formats). Transformation tools, such as Power Query, can be used to automate these processes.
- Data Loading: Data loading involves importing the transformed data into Dynamics 365. Dynamics 365 provides import tools, such as the Data Import Wizard and the Data Management Framework, to facilitate data loading. The Data Import Wizard is suitable for smaller datasets, while the Data Management Framework is more efficient for larger volumes of data.
- Data Validation and Testing: After data loading, validation and testing are crucial to ensure data accuracy and integrity. This involves verifying the data against the expected values and identifying any discrepancies. Data validation typically includes checks for data completeness, accuracy, and consistency. Testing may involve running reports and queries to verify the data’s functionality.
- Go-Live and Post-Migration Support: Once data validation is complete, the system is ready to go live. Post-migration support involves addressing any issues that arise after the go-live and providing ongoing data maintenance and updates. Regular audits and data cleansing are essential to maintain data quality over time.
Data Migration Process for Salesforce
Salesforce offers a range of data migration tools and strategies, catering to diverse migration needs and complexities. These options allow organizations to tailor their migration approach based on factors such as data volume, source system, and technical expertise.The data migration process in Salesforce typically includes the following steps:
- Planning and Strategy: The initial step involves defining the migration scope, identifying data sources, and determining the data migration strategy. This includes selecting the appropriate Salesforce data migration tools and assessing data quality. A detailed plan ensures a structured approach, minimizing risks and maximizing efficiency.
- Data Extraction: Data extraction involves retrieving data from the source systems. Salesforce provides various tools and options for data extraction, including the Data Loader, the Salesforce API, and third-party integration tools. The method chosen depends on the source system’s capabilities and the data format. For example, the Data Loader is suitable for importing and exporting large volumes of data.
- Data Cleansing and Transformation: This phase focuses on cleaning, mapping, and transforming the extracted data to align with Salesforce’s data structure. This may include removing duplicates, standardizing formats, and mapping fields from the source system to Salesforce fields. Data transformation tools and techniques are used to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
- Data Loading: The transformed data is then loaded into Salesforce. Salesforce provides tools such as the Data Loader, the Import Wizard, and third-party tools for data loading. The choice of tool depends on the data volume and the required level of automation.
- Data Validation and Testing: Data validation is essential to verify the accuracy and integrity of the migrated data. This involves running tests and queries to ensure that the data has been loaded correctly and that it meets the required standards.
- Deployment and Go-Live: Once data validation is complete, the system is ready to go live. This phase involves deploying the CRM system and training users on its functionality. Post-migration support ensures that any issues are addressed promptly.
Step-by-Step Guide for Implementing a CRM System
Implementing a CRM system involves a series of well-defined steps, encompassing data migration, configuration, and user training. This structured approach ensures a successful CRM deployment, maximizing user adoption and the system’s overall effectiveness.
- Project Planning and Scope Definition: Define clear project goals, objectives, and scope. Identify key stakeholders, establish a project timeline, and allocate resources. This includes documenting current business processes and identifying areas for improvement.
- Requirement Gathering and Analysis: Collect and analyze business requirements, including user needs, data requirements, and integration needs. Document these requirements in a detailed specification document. This stage involves workshops and interviews with stakeholders to gather comprehensive insights.
- CRM System Selection: Evaluate and select the CRM system that best meets the organization’s requirements. Consider factors such as features, scalability, cost, and vendor reputation. A proof of concept (POC) may be conducted to validate the chosen system.
- Data Migration Planning: Develop a detailed data migration plan, including data mapping, data cleansing, and data transformation strategies. Identify data sources, assess data quality, and choose the appropriate data migration tools. This plan should include a rollback strategy in case of issues.
- Data Migration Execution: Extract data from the source systems, transform the data to match the CRM system’s data structure, and load the data into the CRM system. Validate the data to ensure accuracy and completeness. Regular progress checks and data validation are crucial during this stage.
- System Configuration and Customization: Configure the CRM system to align with the organization’s business processes. Customize the system by adding custom fields, workflows, and integrations. Test the configuration to ensure that it functions as expected.
- Integration with Other Systems: Integrate the CRM system with other business systems, such as ERP, marketing automation, and email systems. This integration ensures data synchronization and seamless workflows. Thorough testing of the integration is essential.
- User Training and Adoption: Provide comprehensive training to users on how to use the CRM system effectively. Develop training materials, conduct training sessions, and provide ongoing support. User adoption is critical for the CRM’s success.
- Testing and Quality Assurance: Conduct thorough testing to ensure that the CRM system functions as expected. Test the system’s functionality, performance, and security. This includes user acceptance testing (UAT) to validate the system’s usability.
- Deployment and Go-Live: Deploy the CRM system to the production environment. Provide post-implementation support to address any issues that arise. Monitor the system’s performance and provide ongoing maintenance and updates.
- Post-Implementation Review and Optimization: Review the CRM system’s performance and identify areas for improvement. Continuously optimize the system to meet evolving business needs. This includes regular data audits and system updates.
Future Trends and Innovations
The CRM landscape is in constant flux, driven by technological advancements and evolving customer expectations. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce are actively investing in research and development to remain at the forefront of these trends. These innovations are aimed at enhancing user experience, improving efficiency, and delivering more personalized customer interactions. The integration of AI, machine learning, and other cutting-edge technologies is reshaping how businesses manage their customer relationships.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in Dynamics 365
Dynamics 365 is heavily focused on integrating with the Microsoft ecosystem and leveraging its AI capabilities through services like Azure. This approach enables businesses to personalize customer interactions and automate complex business processes.
- AI-Powered Insights and Automation: Dynamics 365 utilizes AI to provide predictive analytics, personalized recommendations, and automated workflows. For example, Dynamics 365 Sales leverages AI to score leads, predict deal outcomes, and provide sales representatives with insights on the best course of action. Microsoft’s “Sales Copilot” is a prime example, offering real-time recommendations and context-aware suggestions directly within the sales workflow.
- Integration with Microsoft Power Platform: The tight integration with Power BI, Power Apps, and Power Automate allows for highly customizable solutions. Power BI enables advanced data visualization and reporting, Power Apps allows for the creation of custom applications, and Power Automate facilitates workflow automation. For instance, a company can use Power Automate to automatically update a customer’s information in Dynamics 365 based on interactions detected through email or social media.
- Mixed Reality and IoT Integration: Microsoft’s investments in mixed reality through HoloLens and its Azure IoT platform are poised to revolutionize how businesses interact with customers in the field. Imagine a service technician using HoloLens to access real-time data and step-by-step instructions for repairing equipment, all integrated with Dynamics 365 Field Service. This enhances efficiency and provides better customer support.
- Industry-Specific Solutions: Dynamics 365 continues to expand its portfolio of industry-specific solutions, tailoring features and functionalities to meet the unique needs of various sectors such as retail, manufacturing, and healthcare. This approach allows for quicker implementations and more relevant features from the start.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in Salesforce
Salesforce, as a pioneer in cloud-based CRM, consistently innovates to maintain its market leadership. Salesforce is focused on AI-driven insights, enhanced user experiences, and seamless integrations.
- Einstein AI: Salesforce Einstein is the core AI platform that powers various features within the Salesforce ecosystem. It provides predictive analytics, personalized recommendations, and automated tasks. Einstein Sales Cloud, for example, analyzes sales data to predict which leads are most likely to convert, identifies the best next steps, and automates routine tasks.
- Hyperforce and Multi-Cloud Strategy: Salesforce has invested heavily in its Hyperforce infrastructure, a scalable and secure cloud platform. This allows Salesforce to deploy its services across various public cloud providers globally, improving performance, and meeting local data residency requirements. Salesforce also emphasizes a multi-cloud strategy, enabling customers to choose the specific Salesforce clouds and services that best meet their needs.
- Enhanced User Experience: Salesforce is constantly refining its user interface and user experience, focusing on features like the Salesforce Lightning Experience, which provides a modern, intuitive interface. They also focus on mobile-first design, ensuring users can access and manage customer data on the go.
- Customer 360: This initiative aims to provide a unified view of the customer across all Salesforce clouds and connected systems. It integrates data from sales, service, marketing, and commerce to provide a comprehensive understanding of each customer, enabling more personalized and effective interactions.
Future Evolution of Dynamics 365 and Salesforce
Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce are poised for significant evolution, driven by AI, machine learning, and other emerging technologies. The competitive landscape will likely see increased focus on providing even more personalized customer experiences, automation of complex processes, and deeper integrations with other business applications.
- AI and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning will play an increasingly central role in both platforms. Expect to see:
- More sophisticated predictive analytics, enabling businesses to anticipate customer needs and proactively address them.
- Advanced automation, streamlining workflows and freeing up human agents to focus on more strategic tasks.
- Personalized recommendations, tailoring products, services, and content to individual customer preferences.
- Hyper-Personalization: Businesses will strive to deliver hyper-personalized experiences, tailoring interactions to individual customer preferences, behaviors, and needs. Both platforms will offer more tools and capabilities to support hyper-personalization, including advanced segmentation, dynamic content, and real-time personalization engines.
- Low-Code/No-Code Development: The demand for low-code/no-code development platforms will continue to grow, allowing business users to create and customize applications without extensive coding knowledge. Both Dynamics 365 (with Power Platform) and Salesforce (with Salesforce Platform) are investing heavily in these capabilities, empowering citizen developers and accelerating innovation.
- Industry-Specific Solutions: Both vendors will continue to expand their industry-specific solutions, providing pre-built functionalities and customizations tailored to the unique needs of various sectors. This will allow businesses to implement CRM solutions more quickly and efficiently.
- Enhanced Integrations: Seamless integration with other business applications, such as ERP systems, marketing automation platforms, and communication tools, will become even more critical. Both Dynamics 365 and Salesforce will focus on improving their integration capabilities, allowing businesses to create a unified view of their customer data and streamline their workflows.
- Focus on Sustainability: As environmental concerns become more prominent, both companies are likely to incorporate sustainability features into their CRM offerings. This could include tools for tracking carbon emissions, optimizing resource usage, and supporting eco-friendly business practices.