Horas! CRM Pipeline Stages That Don’t Break Reports (2025 Templates) is a journey into the heart of sales management, a topic as vital as the rice harvest for our sustenance. This exploration is not merely about creating pipelines; it is about crafting systems that endure, much like the strong roots of a banyan tree. We shall delve into the stages, ensuring each one functions with precision and clarity, avoiding the pitfalls that lead to broken reports and wasted efforts.
We will examine how to construct pipelines that are resilient to errors, much like a sturdy rumah adat (traditional Batak house). We will also learn how to build customizable templates for diverse businesses, just as we adapt our farming practices to different terrains. The key is to maintain data integrity and provide reliable reports, which are essential for making good decisions.
Finally, we will examine how to integrate automation and visualization tools to optimize the process, ensuring that our sales strategies are as strong as a Batak warrior’s spirit.
Alright, so you’re diving into CRM Pipeline Stages That Don’t Break Reports (2025 Templates), yeah? Smart move. But hey, have you thought about how this plays out in healthcare? Things get real sensitive, real quick. That’s where understanding CRM for Healthcare 2025: HIPAA-Aware Workflows and Patient Journeys becomes crucial.
It’s all about data security and patient trust, which, in turn, affects your CRM reporting. Keep that in mind while building those templates!
CRM Pipeline Stages That Don’t Break Reports (2025 Templates)
In the ever-evolving landscape of customer relationship management (CRM), the ability to accurately track and analyze sales performance is paramount. This article delves into the creation and maintenance of robust CRM pipeline stages, specifically designed to prevent report corruption and provide actionable insights. We’ll explore how to define effective stages, design them to minimize errors, and build customizable templates for various business needs.
Alright, so you’re sorting through CRM Pipeline Stages That Don’t Break Reports (2025 Templates), yeah? Makes sense. But before you lock down those stages, think about the future. How accurate can your CRM be in 2025? That’s where Sales Forecasting With AI: How Accurate Can Your CRM Be in 2025?
comes in, helping you to refine those pipeline stages to deliver the best results. Consider those templates again!
The focus is on ensuring data integrity, automating processes, and ultimately, driving better sales outcomes.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of CRM pipeline stages, from defining the essential elements to implementing best practices for data integrity and reporting. By understanding and applying these principles, businesses can build a CRM system that not only streamlines sales processes but also delivers reliable and valuable data for strategic decision-making.
Defining CRM Pipeline Stages for 2025
A well-defined sales pipeline is the backbone of any successful CRM strategy. It provides a clear visual representation of the sales process, allowing businesses to track leads, manage opportunities, and forecast revenue. The key is to establish stages that are universally applicable and adaptable to different business models. These stages should be logical, sequential, and designed to capture the necessary information at each step.
- Lead Qualification: This initial stage focuses on identifying and qualifying potential customers. The purpose is to determine if a lead meets the criteria to become a viable opportunity. Actions include initial contact, needs assessment, and lead scoring. Key metrics include the number of leads qualified, qualification rate, and time to qualification.
- Discovery/Needs Analysis: Once a lead is qualified, the next step is to understand their specific needs and challenges. This involves in-depth conversations and research to tailor solutions. Actions include conducting demos, presenting proposals, and gathering detailed information. Key metrics include the number of discovery meetings, proposal acceptance rate, and time to proposal.
- Proposal/Presentation: This stage involves presenting a tailored solution to the prospect. The goal is to demonstrate the value of the product or service and secure their commitment. Actions include delivering proposals, conducting presentations, and addressing objections. Key metrics include the number of proposals sent, proposal win rate, and average deal size.
- Negotiation: This stage involves discussing terms, pricing, and any final adjustments to the proposal. The objective is to reach a mutually agreeable agreement. Actions include negotiating contracts, revising proposals, and addressing final concerns. Key metrics include the number of negotiations, negotiation success rate, and the average discount offered.
- Closed Won: This final stage signifies that the deal has been successfully closed, and the customer has agreed to purchase. Actions include contract signing, onboarding, and setting up the customer. Key metrics include the number of deals closed, total revenue generated, and the average sales cycle length.
- Closed Lost: This stage captures the deals that were not won. It’s crucial to understand why deals are lost to improve future performance. Actions include documenting the reasons for loss and updating the CRM. Key metrics include the number of deals lost, reasons for loss, and the average deal value lost.
Designing Stages That Prevent Report Corruption
To ensure the integrity of CRM reports, it’s essential to design pipeline stages that minimize data entry errors and maintain data accuracy. This involves implementing data validation techniques and carefully considering the structure of each stage to prevent inaccuracies.
- Data Validation Techniques:
- Required Fields: Make certain fields mandatory to ensure that crucial information is always captured.
- Data Type Validation: Use specific data types (e.g., numbers, dates, currency) to prevent incorrect data entry.
- Dropdown Lists: Use dropdown lists for predefined options to standardize data and reduce free-text errors.
- Range Validation: Set limits on numerical fields to ensure data falls within acceptable ranges.
- Common Pitfalls and Avoidance:
- Inconsistent Data Entry: Standardize data entry formats and provide clear instructions.
- Duplicate Data: Implement duplicate detection rules to prevent redundant entries.
- Missing Data: Ensure all necessary fields are required and provide clear prompts.
Creating Customizable Templates (2025)
A flexible and adaptable CRM pipeline template is crucial for businesses of all sizes. These templates should allow users to customize stages, add custom fields, and integrate with other systems to meet their specific needs.
- Components of a CRM Pipeline Template:
- Stage Definitions: Predefined stages with descriptions, actions, and metrics.
- Custom Fields: Ability to add fields for specific data capture (e.g., product type, deal source).
- Workflow Automation: Pre-built automation to streamline tasks (e.g., email notifications, task creation).
- Reporting Dashboards: Customizable dashboards to visualize pipeline performance.
- Steps to Create a Customizable Template:
- Define Core Stages: Start with a set of essential stages applicable to most businesses.
- Implement Custom Fields: Allow users to add fields for specific needs.
- Develop Workflow Automation: Include options for automating tasks at each stage.
- Design Reporting Dashboards: Provide customizable dashboards to track performance.
- Methods for Modification and Integration:
- Stage Modification: Allow users to rename, reorder, and add/remove stages.
- Custom Field Addition: Provide an interface for users to create custom fields.
- System Integration: Offer integration options with email marketing, accounting, and other systems.
Data Integrity and Reporting Best Practices
Maintaining data integrity is critical for generating accurate and reliable reports. This involves implementing procedures for data cleansing, validation, and automated reporting dashboards.
- Best Practices for Data Accuracy:
- Regular Data Audits: Conduct periodic audits to identify and correct data inconsistencies.
- Data Governance Policies: Establish clear policies for data entry and management.
- User Training: Provide comprehensive training to ensure users understand data entry best practices.
- Data Cleansing and Validation Procedures:
- Duplicate Detection: Implement tools to identify and merge duplicate records.
- Data Standardization: Standardize data formats (e.g., addresses, phone numbers).
- Error Correction: Establish a process for correcting data errors and inconsistencies.
- Automated Reporting Dashboards:
- Real-time Data: Ensure dashboards display up-to-date data.
- Customizable Views: Allow users to customize dashboards based on their roles and needs.
- Alerts and Notifications: Set up alerts for key metrics and performance indicators.
Implementing Stages with Minimal Impact on Reports
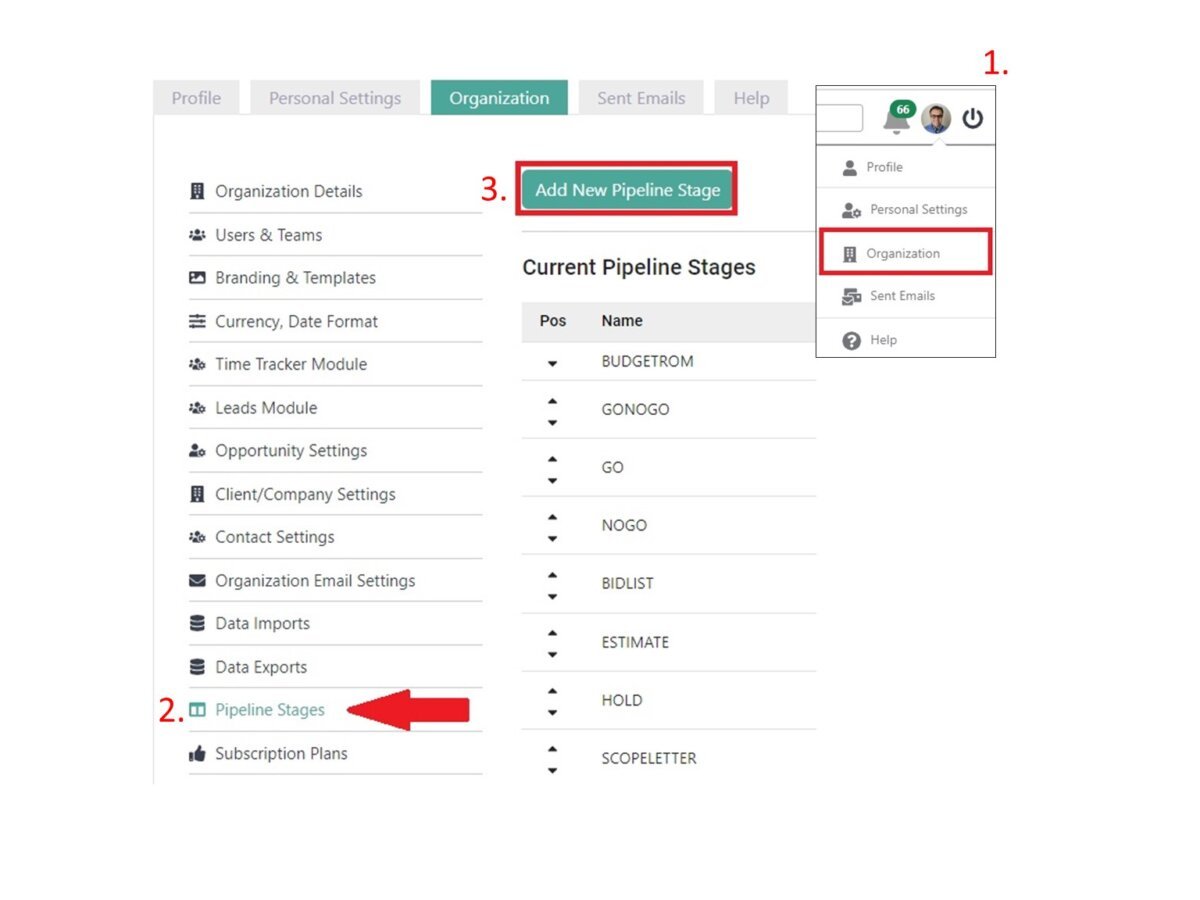
Source: idealcrm.app
When introducing new pipeline stages or making modifications, it’s crucial to minimize the impact on existing reporting structures. This involves careful planning, data migration strategies, and thorough testing.
- Strategies for Integrating New Pipeline Stages:
- Phase Implementation: Introduce new stages gradually to avoid disrupting existing workflows.
- Data Mapping: Map existing data to new stages to ensure continuity.
- Testing and Validation: Test new stages thoroughly before deploying them to a live environment.
- Data Migration when Modifying or Adding Stages:
- Backup Data: Always back up data before making any changes.
- Data Transformation: Use data transformation tools to move data between stages.
- Data Validation Post-Migration: Verify data accuracy after migration.
- Testing and Validation Techniques:
- User Acceptance Testing (UAT): Involve users in testing to ensure the changes meet their needs.
- Regression Testing: Test existing reports to ensure they still function correctly.
- Performance Testing: Test the performance of the system after the changes.
Stage-Specific Metrics and KPIs
Tracking the right metrics and KPIs is essential for measuring pipeline performance and identifying areas for improvement. Each stage requires specific metrics to evaluate its effectiveness.
- Critical Performance Indicators (KPIs) by Stage:
- Lead Qualification: Qualification Rate, Time to Qualification, Lead Source Conversion Rate.
- Discovery/Needs Analysis: Number of Discovery Meetings, Conversion Rate from Discovery to Proposal, Time to Proposal.
- Proposal/Presentation: Proposal Win Rate, Average Deal Size, Time to Close (Proposal).
- Negotiation: Negotiation Success Rate, Average Discount Offered, Deal Cycle Time.
- Closed Won: Total Revenue, Sales Cycle Length, Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC).
- Closed Lost: Reasons for Loss, Lost Deal Value, Lost Deal Conversion Rate.
- Methods for Calculating Conversion Rates:
- Stage-to-Stage Conversion: (Number of Opportunities in Next Stage / Number of Opportunities in Current Stage)
– 100. - Overall Conversion Rate: (Number of Closed Won Deals / Number of Leads)
– 100. - Cohort Analysis: Analyze conversion rates over time for specific groups of leads.
- Stage-to-Stage Conversion: (Number of Opportunities in Next Stage / Number of Opportunities in Current Stage)
- Using Metrics to Optimize the Pipeline:
- Identify Bottlenecks: Analyze conversion rates to pinpoint areas where leads are stalling.
- Optimize Processes: Adjust processes to improve conversion rates at each stage.
- Refine Sales Strategies: Use data to refine sales strategies and improve overall performance.
Using HTML Tables for Stage Breakdown
An HTML table can effectively illustrate the different stages of a CRM pipeline, along with their descriptions, actions, and key metrics. This format provides a clear and organized way to present the information.
| Stage | Description | Associated Actions | Key Metrics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead Qualification | Identifying and qualifying potential customers. | Initial contact, needs assessment, lead scoring. | Qualification Rate, Time to Qualification, Leads Qualified. |
| Discovery/Needs Analysis | Understanding customer needs and challenges. | Demos, presentations, gathering information. | Number of Discovery Meetings, Conversion Rate, Time to Proposal. |
| Proposal/Presentation | Presenting a tailored solution to the prospect. | Delivering proposals, conducting presentations, addressing objections. | Proposal Win Rate, Average Deal Size, Proposals Sent. |
| Negotiation | Discussing terms and pricing. | Negotiating contracts, revising proposals. | Negotiation Success Rate, Average Discount, Deals Negotiated. |
| Closed Won | Deal successfully closed. | Contract signing, onboarding. | Total Revenue, Sales Cycle Length, Deals Closed. |
| Closed Lost | Deal not won. | Documenting reasons for loss. | Reasons for Loss, Lost Deal Value, Deals Lost. |
The structure of the HTML table is straightforward. The <table> tag defines the table, <thead> holds the header row, and <tbody> contains the table data. Each row is defined by <tr>, and each cell by <th> (header) or <td> (data). This structure allows for easy modification and expansion.
Data visualization elements can be incorporated within the table using CSS or JavaScript. For example, progress bars can be used to visually represent the percentage completion of each stage, or color-coding can highlight key metrics.
Examples of CRM Pipeline Stages for Different Industries
The following examples illustrate how CRM pipeline stages can be tailored for specific industries. Each industry has unique sales processes and requirements.
- SaaS Industry:
- Awareness: Initial contact and marketing efforts.
- Evaluation: Free trials, demos, and product evaluations.
- Negotiation: Pricing discussions and contract terms.
- Closed Won: Subscription signed.
- Onboarding: Customer setup and training.
- Renewal: Contract renewal and upselling.
- E-commerce Industry:
- Visitor: Website visitor.
- Lead: Customer who shows interest (e.g., signs up for newsletter).
- Cart Abandonment: Customer adds items to cart but doesn’t complete purchase.
- Checkout: Customer starts checkout process.
- Order Placed: Order completed.
- Customer Retention: Post-purchase follow-up, repeat purchases.
- Real Estate Industry:
- Prospect: Initial contact and qualification.
- Showing: Property viewing.
- Offer: Offer submitted.
- Negotiation: Offer negotiation.
- Under Contract: Contract signed.
- Closed: Sale completed.
Automation and Integration within Pipeline Stages
Automation and integration are essential for streamlining tasks and improving data accuracy within each pipeline stage. These features reduce manual effort and provide a seamless workflow.
- Use of Automation:
- Automated Emails: Send automated follow-up emails based on stage progression.
- Task Creation: Automatically create tasks for sales reps based on stage changes.
- Lead Scoring: Automate lead scoring based on behavior and engagement.
- Integration with Other Business Systems:
- Email Marketing: Integrate with email marketing platforms to send targeted campaigns.
- Accounting Systems: Integrate with accounting systems for invoice generation and revenue tracking.
- Project Management: Integrate with project management tools to manage customer projects.
- Improving Data Accuracy and Reducing Manual Effort:
- Reduced Errors: Automation minimizes manual data entry errors.
- Faster Data Entry: Automated workflows streamline data input.
- Improved Efficiency: Automation frees up sales reps to focus on selling.
Illustrative Graphics for Pipeline Representation, CRM Pipeline Stages That Don’t Break Reports (2025 Templates)
Visual representations are crucial for understanding and communicating the sales pipeline. Here are descriptions of illustrative graphics to enhance understanding.
Description 1: A multi-stage sales pipeline illustration showing a funnel-shaped diagram. The funnel is divided into distinct stages, starting with “Lead Generation” at the top, followed by “Qualification,” “Needs Analysis,” “Proposal,” “Negotiation,” and finally, “Closed Won” at the bottom. Each stage is visually distinct, with arrows indicating the flow of leads through the pipeline. The illustration also includes the percentage of leads that progress from one stage to the next, providing a clear visual representation of conversion rates.
Description 2: An illustration showcasing a horizontal bar chart that represents different pipeline stages. Each bar represents a stage (e.g., “Prospecting,” “Qualification,” “Proposal,” “Closing”). The height of each bar corresponds to the number of opportunities or deals at that stage. Above each bar, a conversion rate percentage is displayed, showing the likelihood of a deal moving to the next stage. Arrows connect the bars to illustrate the flow of leads.
The chart includes labels for each stage, clearly indicating the progression and conversion rates.
Description 3: An infographic that depicts the sales pipeline with a focus on data entry points and validation steps. The infographic starts with a lead at the top, progressing through various stages (e.g., “Lead Captured,” “Qualified,” “Proposal Sent,” “Closed Won”). Each stage is represented by a distinct section. Within each section, there are labeled data entry fields (e.g., “Lead Name,” “Contact Information,” “Deal Value”).
Validation steps are illustrated by icons or labels (e.g., “Required Field,” “Data Type Check”). Arrows and visual cues highlight the importance of data accuracy at each step, and how validation ensures data integrity throughout the pipeline.