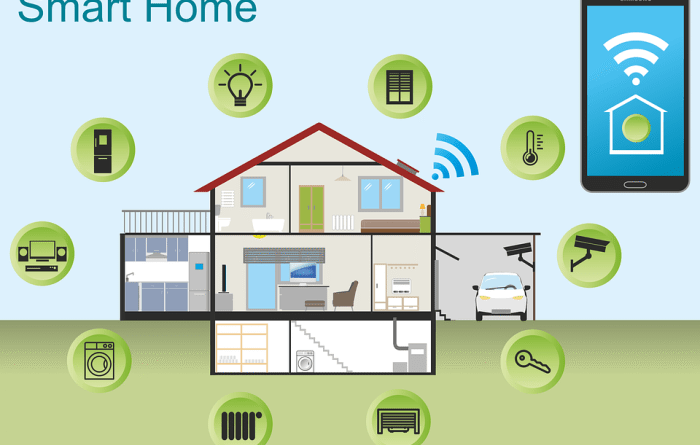
Home Automation Systems Smart Design Principles
Home automation systems smart design lays the groundwork for a future where homes seamlessly integrate technology, comfort, and security. This exploration delves into the intricacies of designing intelligent systems, encompassing everything from initial setup to future-proofing and security considerations.
The evolution of home automation systems from rudimentary controls to sophisticated, interconnected networks is detailed, showcasing the key components, design principles, and integration strategies. This discussion also covers essential aspects like security, privacy, and the role of user experience in crafting intuitive systems. We will also analyze the integration of various devices and the impact of emerging technologies, such as AI and IoT.
Introduction to Home Automation Systems
Home automation systems, also known as smart home systems, are rapidly transforming the way we interact with our living spaces. These systems integrate various devices and appliances to automate tasks, enhance comfort, and improve security. This evolution is driven by advancements in technology, particularly in the areas of internet connectivity, sensor technology, and artificial intelligence.
Definition of Home Automation Systems
Home automation systems encompass a collection of interconnected devices, appliances, and systems that are controlled and managed through a central interface. These systems leverage technology to automate tasks, enhance energy efficiency, and create a more convenient and secure living environment.
Evolution of Home Automation Systems
Early home automation systems were largely rudimentary and expensive, often relying on dedicated hardware and complex wiring. The evolution saw a shift towards centralized control systems and the use of programmable logic controllers. This paved the way for the development of user-friendly interfaces and the integration of various devices. The advent of internet connectivity and advancements in sensor technology have led to a dramatic increase in the sophistication and accessibility of home automation systems, making them more affordable and user-friendly.
Today’s smart homes are characterized by seamless integration of devices and a focus on user experience.
Types of Home Automation Systems
Home automation systems can be broadly categorized into several types:
- Smart Home Hubs: These systems use a central hub to manage and control various connected devices. The hub acts as a central communication point, receiving commands and relaying them to the relevant devices. Examples include Amazon Echo, Google Home, and Apple HomeKit. These systems often utilize a unified platform to manage devices from different manufacturers.
- Stand-alone Devices: These systems involve individual devices that control specific tasks without the need for a central hub. Examples include smart thermostats, security systems, and lighting controls. While offering specialized functionality, these systems lack the seamless integration and centralized control of hub-based systems.
- DIY Systems: These systems allow users to customize their home automation setups using various components, often with programmable logic controllers and specialized hardware. These systems provide maximum flexibility but may require advanced technical knowledge for implementation and maintenance.
Key Components of a Typical Home Automation System
A typical home automation system comprises several key components:
- Sensors: These detect changes in the environment, such as temperature, light, motion, or presence. Examples include motion detectors, temperature sensors, and light sensors.
- Actuators: These respond to sensor inputs, performing actions like turning lights on or off, adjusting temperature, or triggering alarms. Examples include smart switches, smart thermostats, and motorized blinds.
- Control System: This manages the interaction between sensors and actuators, executing commands and maintaining system functionality. This can be a smart home hub or a custom-built system.
- Communication Network: This facilitates the exchange of data between the various components of the system. Common networks include Wi-Fi, Ethernet, and Zigbee.
Organization of Home Automation Systems by Functionality
Home automation systems can be categorized based on their specific functionalities:
- Security Systems: These systems focus on monitoring and protecting a home from intrusion, often utilizing cameras, motion sensors, and alarms. This includes intrusion detection and prevention.
- Lighting and Entertainment Control: These systems automate the control of lights, music, and other entertainment systems, enabling users to adjust lighting and audio based on their preferences and needs. Examples include automated lighting schedules and smart audio systems.
- Climate Control: These systems automate the control of temperature, humidity, and ventilation, improving energy efficiency and occupant comfort. Examples include smart thermostats and ventilation systems.
- Home Appliances Management: These systems control and monitor various home appliances, including washing machines, refrigerators, and dishwashers, often optimizing energy usage and improving convenience.
Comparison of Home Automation Systems
| Feature | Smart Home Hubs | Stand-alone Devices | DIY Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | High | Moderate | Low |
| Cost | Moderate to High | Low to Moderate | Variable |
| Flexibility | Moderate | Low | High |
| Scalability | High | Low | High |
| Integration | High | Low | Variable |
Smart Design Principles for Home Automation
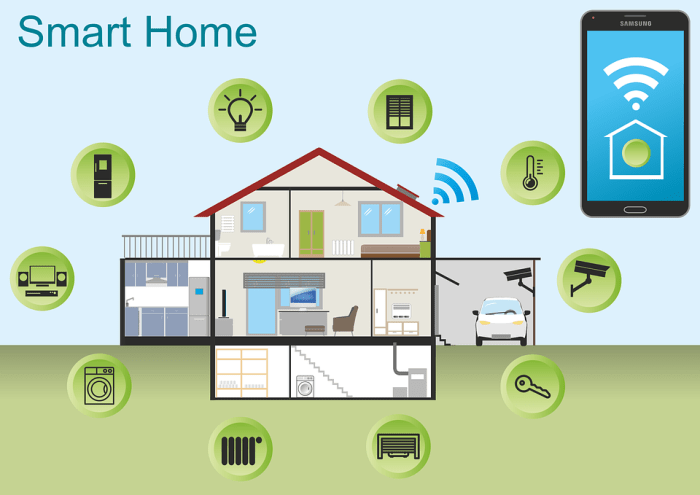
Source: highcountry.design
Creating a user-friendly and effective home automation system requires careful consideration of various design principles. A well-designed system not only enhances convenience but also ensures seamless integration and future-proof capabilities, ultimately leading to a more enjoyable and efficient living space. These principles are crucial for building robust, scalable, and secure systems that adapt to evolving needs and technologies.
Seamless Integration of Devices and Systems
Effective home automation hinges on the seamless integration of various devices and systems. This integration ensures that different components, such as lighting, temperature control, security systems, and entertainment, operate harmoniously and respond predictably to user commands. Compatibility standards and open communication protocols are vital for this. A robust API architecture facilitates the exchange of data between diverse components, enabling sophisticated interactions and automated workflows.
For example, a smart thermostat can adjust heating based on the lighting schedule set by the user, creating an interconnected and efficient environment.
Scalability and Future-Proofing Considerations
Designing a home automation system with scalability and future-proofing in mind is essential. The ability to easily add new devices or functionalities without significant reconfiguration is crucial. Utilizing a modular architecture allows for expansion without compromising existing system functionality. Employing open standards and protocols, as opposed to proprietary ones, enhances the long-term viability of the system. Choosing a cloud-based platform for data storage and control provides adaptability to future technological advancements and allows for remote management, making the system future-proof.
For instance, integrating a smart appliance into the existing system would be straightforward if the system was designed with scalability in mind.
User Experience (UX) in Smart Home Design
User experience (UX) is paramount in designing a successful home automation system. The user interface (UI) should be intuitive, visually appealing, and easy to navigate, regardless of technical proficiency. Intuitive controls, clear feedback mechanisms, and personalized configurations enhance the user experience. For instance, an intuitive interface that displays all connected devices and their status in a clear, visually appealing way is a key aspect of a good user experience.
Comparison of User Interfaces (UI) for Home Automation
Various UI options exist for home automation systems, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. These options include voice assistants, mobile apps, touchscreens, and smart hubs. Voice assistants offer hands-free control, while mobile apps provide greater flexibility and customization. Touchscreens offer a visually engaging interface for control, and smart hubs consolidate control of various devices in one location.
The best UI depends on individual preferences and the specific needs of the home. Voice assistants are particularly suitable for users who prefer hands-free control, whereas touchscreens provide a visually appealing and engaging interface for more complex configurations.
Implementing Security Measures in Smart Home Design
Security is a critical aspect of any home automation system. Robust security measures are essential to protect user data and prevent unauthorized access. Implementing multi-factor authentication, encryption, and regular security updates are crucial steps. Utilizing strong passwords, employing secure protocols for communication, and regularly updating software patches are vital for maintaining system security. Monitoring for suspicious activity and having a clear incident response plan are additional essential components.
The security of a smart home system depends heavily on the robust implementation of these security measures.
Creating a Detailed Design Document for a Home Automation System
A well-structured design document is essential for a successful home automation system. This document should include a comprehensive overview of the system’s functionality, architecture, and security considerations. It should Artikel the scope of the project, including specific goals and objectives. A detailed breakdown of the system’s components, their interactions, and the data flow between them should be included.
A section dedicated to the user interface (UI) design, addressing navigation, usability, and aesthetics, should also be present. The design document should also include a clear security plan, outlining the measures to protect the system from potential vulnerabilities. For example, a detailed design document would clearly Artikel the communication protocols between devices, user interfaces, and security measures.
This comprehensive document serves as a blueprint for the entire system.
Integration and Interoperability

Source: wyredreams.com
Home automation systems strive for seamless control and integration of various devices. Interoperability is crucial for a truly smart home experience, enabling devices from different manufacturers to communicate and work together harmoniously. This section delves into the importance of interoperability, methods for integrating diverse systems, and challenges in achieving a unified smart home ecosystem.
Importance of Interoperability
Interoperability ensures that different home automation devices can communicate and exchange data effectively. This facilitates a streamlined user experience, enabling a user to manage multiple devices through a single interface. Without interoperability, users face the frustration of managing multiple apps and systems, and the potential for incompatibility issues between devices. A unified system reduces complexity and increases efficiency, leading to a more convenient and user-friendly smart home experience.
Methods for Integrating Home Automation Systems
Several methods facilitate the integration of diverse home automation systems. One common approach is utilizing open communication protocols, such as Z-Wave, Zigbee, or Thread. These protocols allow different devices to communicate with each other, even if they are from different manufacturers. Another method involves using smart hubs or controllers that act as intermediaries between various devices, translating commands and data between different systems.
A third approach is leveraging cloud-based platforms, which can aggregate data from various sources and provide a centralized control interface.
Example Smart Home Setup
A comprehensive smart home setup can integrate lighting, security, and temperature control. For instance, a motion sensor (security) could trigger the lights (lighting) to turn on automatically when someone enters a room. Simultaneously, the thermostat (temperature control) could adjust the temperature based on occupancy. This integrated system provides enhanced convenience and security.
Communication Protocols in Home Automation
The following table Artikels common communication protocols utilized in home automation systems:
| Protocol | Description | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Z-Wave | A low-power, mesh networking protocol | Reliable, robust, and cost-effective | Slower speeds compared to other options |
| Zigbee | Low-power, mesh networking protocol | Widely supported by manufacturers | Limited range compared to Z-Wave |
| Thread | Low-power, mesh networking protocol, designed for interoperability | Designed for enhanced scalability and interoperability | Smaller number of compatible devices compared to Z-Wave/Zigbee |
| Wi-Fi | High-speed wireless protocol | Fast data transmission | Higher power consumption compared to other options |
Challenges of Integrating Different Brands
Integrating different brands of home automation devices presents several challenges. One major obstacle is the lack of standardization in communication protocols and interfaces. This often leads to compatibility issues and the need for specific drivers or workarounds to bridge the gap between different systems. Another challenge is the complexity of configuring and managing different devices within a single ecosystem.
The variety of device functionalities and interfaces can require extensive knowledge and potentially increase the complexity of installation.
Ensuring Seamless Communication
Several methods can guarantee seamless communication between various smart home devices. A key factor is choosing devices that support the same or compatible communication protocols. Using a smart hub or controller can facilitate the translation of commands and data between different systems. Cloud-based platforms provide a centralized interface for managing and controlling various devices. Thorough research and planning during the initial setup can mitigate compatibility issues and ensure a smooth integration process.
Controlling Multiple Systems from a Single App
A user-friendly smart home app can integrate lighting, temperature, and security systems. The app provides a unified interface for controlling these systems, eliminating the need to navigate multiple applications. For instance, the app can allow users to schedule lighting to turn on and off automatically based on daily routines. Furthermore, the app can permit users to adjust the thermostat based on their preferences and monitor security cameras remotely.
Security and Privacy Considerations
Home automation systems, while enhancing convenience and comfort, introduce new security and privacy vulnerabilities. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate safeguards is crucial for responsible adoption and use. Protecting user data and ensuring the integrity of the system is paramount.
Security Risks Associated with Home Automation Systems, Home automation systems smart design
Home automation systems are susceptible to various security threats due to their interconnected nature and reliance on internet connectivity. Malicious actors can exploit vulnerabilities in devices to gain unauthorized access to the home network, potentially leading to data breaches and physical harm. Compromised devices can be used to launch attacks on other systems, creating a cascading effect of security breaches.
Common Vulnerabilities in Home Automation Devices
Many home automation devices have inherent vulnerabilities due to factors like weak passwords, outdated firmware, and inadequate security protocols. Manufacturers may not prioritize security features in their designs, leading to easily exploitable weaknesses. Poorly configured devices can expose the entire home network to attacks. In some cases, default usernames and passwords are not changed, leaving devices vulnerable to brute-force attacks.
Another significant vulnerability is the lack of multi-factor authentication, making it easier for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Measures to Mitigate Security Risks
Robust security measures are essential to protect home automation systems. Regular firmware updates are crucial to address known vulnerabilities and patch security flaws. Strong passwords, combined with multi-factor authentication, are critical to securing access to the system. Restricting access to the home network and using a strong router with firewall protection can help defend against external attacks.
Employing intrusion detection systems can identify and respond to suspicious activities in real-time. Regular security audits can help identify and fix vulnerabilities before they are exploited.
Privacy Concerns Related to Home Automation Systems
Home automation systems collect and process vast amounts of data about the user’s habits, preferences, and activities. This data can be sensitive and could potentially be misused or leaked. Data breaches can expose personal information, potentially leading to identity theft and financial losses. Data collection practices need to be transparent and user-controlled. Users should be aware of what data is being collected, how it is used, and who has access to it.
Best Practices for Protecting User Data in a Home Automation System
Implementing strong privacy practices is essential for maintaining user trust. Data minimization principles should be applied, collecting only the necessary data to perform the intended functions. Data encryption should be used to protect sensitive information in transit and at rest. Users should be given clear control over their data, including the ability to access, modify, and delete their information.
Transparent data policies and practices are essential to build trust and maintain user privacy.
Security Protocols and Measures
| Protocol/Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| Strong Passwords | Use complex, unique passwords for all devices and accounts. |
| Multi-Factor Authentication | Implement additional security layers beyond passwords. |
| Regular Firmware Updates | Keep all devices updated with the latest security patches. |
| Network Segmentation | Isolate home automation devices from the main network. |
| Firewall Protection | Configure a robust firewall to block unauthorized access. |
Role of Encryption in Home Automation Systems
Encryption plays a vital role in securing data transmitted between devices and the cloud. Using end-to-end encryption ensures that only authorized parties can access the data. This protection is crucial to prevent unauthorized access and maintain user privacy. Encryption should be employed for both data at rest and in transit to provide comprehensive security. Examples include using HTTPS for communication with cloud services and encrypting data stored on local devices.
Future Trends and Innovations
Home automation systems are rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology. This section explores the emerging trends shaping the future of smart homes, focusing on the impact of artificial intelligence, cloud computing, renewable energy, and the Internet of Things. These innovations promise to enhance convenience, security, and sustainability within residential environments.
Emerging Trends in Home Automation
Home automation is transitioning from simple control systems to sophisticated ecosystems. The integration of various technologies, such as voice assistants, advanced sensors, and smart appliances, creates increasingly interconnected and responsive systems. This evolution is fostering greater user convenience and personalized control over home environments. Trends also include the increasing use of predictive analytics to anticipate needs and automate responses, such as adjusting temperature settings based on weather forecasts.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are revolutionizing home automation. AI-powered systems can learn user preferences and adapt to their routines, optimizing energy consumption and automating tasks. For example, a smart thermostat can learn the temperature preferences of occupants and adjust settings accordingly, reducing energy waste. Machine learning algorithms can analyze sensor data to detect potential issues, such as a leak or a malfunctioning appliance, and proactively alert users or initiate repairs.
This proactive approach enhances safety and reduces maintenance costs.
Role of Cloud Computing in Home Automation
Cloud computing plays a crucial role in the future of home automation by providing the necessary infrastructure for data storage, processing, and remote access. The cloud enables seamless integration of devices and services, allowing users to control their homes from anywhere in the world. It also allows for centralized data management, enabling personalized recommendations and proactive problem-solving. For example, cloud-based platforms can aggregate data from various sensors to provide insights into energy consumption patterns, leading to improved energy efficiency.
Future of Home Automation and Renewable Energy
Integrating renewable energy sources into home automation systems is a significant advancement. Smart systems can optimize the use of solar panels, wind turbines, and other renewable energy sources to maximize energy generation and minimize reliance on the grid. For instance, a smart home system can adjust energy consumption based on real-time solar irradiance data, ensuring that energy is drawn from renewable sources whenever possible.
This integration promises a more sustainable and cost-effective approach to energy management.
Sustainable Smart Homes
Smart homes can be designed to be more sustainable through various strategies. Utilizing energy-efficient appliances and lighting systems is a fundamental aspect of sustainable design. Smart systems can automate the control of these appliances, ensuring they operate at peak efficiency. Integration with renewable energy sources, as discussed earlier, is another crucial element. Smart homes can also incorporate features like rainwater harvesting systems, optimized irrigation schedules, and waste management systems to minimize environmental impact.
Future Applications of Home Automation Systems
| Application Category | Specific Application | Description ||—|—|—|| Enhanced Security | Intrusion Detection and Prevention | Advanced sensors and AI-powered systems monitor the home environment, detect potential threats, and initiate appropriate responses, like sending alerts to owners or activating security measures. || Improved Accessibility | Automated Accessibility Features | Smart home systems can be configured to assist individuals with disabilities, enabling automated control of lighting, temperature, and other features, increasing independence and safety.
|| Optimized Comfort | Personalized Comfort Control | The system learns user preferences and adapts to their needs, such as adjusting lighting and temperature based on the time of day, activity, or weather conditions. || Enhanced Energy Efficiency | Dynamic Energy Management | Home automation systems can optimize energy consumption by dynamically adjusting energy usage based on factors like weather conditions, energy prices, and solar energy availability.
|| Enhanced Home Management | AI-driven Home Management | AI-powered systems can automate tasks like scheduling, ordering groceries, or managing household finances, streamlining everyday routines. |
Impact of the Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) is fundamentally changing home automation. The increasing number of connected devices expands the capabilities of smart homes. This interconnectedness allows for sophisticated control and automation of various aspects of the home environment, leading to increased convenience, efficiency, and safety. A wider range of appliances, lighting, and security systems can be seamlessly integrated into a single ecosystem.
The integration of IoT devices in homes creates a complex and responsive network that provides advanced features and personalized user experiences.
Case Studies and Examples

Source: acousticdesignlv.com
Home automation systems are rapidly evolving, offering homeowners sophisticated control over their living spaces. Real-world implementations demonstrate the practical applications and potential benefits of these technologies. Understanding successful deployments and common challenges provides valuable insights for designing and implementing robust and user-friendly home automation systems.
A Successful Home Automation Implementation
A prominent example of a successful home automation implementation involves a modern family home in a suburban area. The system integrated smart lighting, thermostats, security cameras, and a smart speaker for voice control. Key to the success was the thoughtful design process that prioritized user needs and system scalability. The system’s integration allowed for automated lighting schedules, optimized energy consumption, and improved home security.
Creating a Functional Home Automation System
A systematic approach is crucial for designing a functional home automation system. This involves defining specific needs and goals, conducting thorough research on available technologies, and meticulously planning the integration process. A detailed design document outlining the system architecture, device specifications, and communication protocols is essential. Furthermore, careful consideration of user experience and ease of use is paramount for long-term system adoption.
Smart Home Design Using Various Smart Devices
A comprehensive smart home design leverages a range of smart devices to create an integrated and automated environment. Smart lighting, such as LED bulbs controlled via a smartphone app, allows for customized lighting schemes. Smart thermostats automatically adjust temperature settings based on occupancy and weather conditions, optimizing energy use. Smart security systems, including motion sensors and video cameras, provide proactive protection.
A central hub, such as a smart home assistant, facilitates seamless communication and control between these diverse devices.
Benefits of a Central Hub
Employing a central hub significantly simplifies home automation. A central hub acts as a central control point for managing various smart devices, allowing users to monitor and control them through a single interface. This streamlines the user experience and enhances system reliability. A hub facilitates device communication, avoids conflicts, and ensures a consistent system experience. Furthermore, a hub often provides advanced features, like voice control, scheduling, and automation routines.
Potential Challenges and Solutions for a Smart Home Setup
Several challenges can arise in smart home setups. Compatibility issues between different devices and ecosystems are common. Addressing these challenges requires careful selection of compatible devices and integration platforms. Security vulnerabilities are another concern. Implementing strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular security updates mitigates these risks.
Interruptions in internet connectivity can disrupt the system. A reliable internet connection and redundant systems are crucial to minimize disruptions.
Troubleshooting Common Issues in Home Automation Systems
Troubleshooting home automation systems requires a methodical approach. First, thoroughly understand the system’s architecture and functionality. Second, identify the specific issue by carefully examining error messages and system logs. Third, check the connectivity of devices and ensure they are properly configured. Fourth, consider updating the firmware of devices and software to address any known bugs.
Fifth, seek professional assistance if the problem persists.
Comparison of Smart Home Ecosystems
| Ecosystem | Devices Supported | Integration Platform | Security Features | Pricing ||—|—|—|—|—|| Ecosystem A | Wide range of smart home devices | Cloud-based platform | Advanced security protocols | Moderate || Ecosystem B | Limited device selection | Local network-based platform | Basic security protocols | Low || Ecosystem C | Wide range of devices | Hybrid cloud/local platform | Strong security protocols | High |
User Interface and User Experience: Home Automation Systems Smart Design
A user-friendly interface is paramount to the success of any home automation system. A seamless and intuitive experience empowers users to effortlessly control and manage their smart home environment. This section delves into the critical aspects of designing effective user interfaces and experiences for home automation, encompassing app design, user testing, and visual interface considerations.Effective user interface design translates into a positive user experience, making the smart home accessible and enjoyable for all.
A well-designed interface fosters a sense of control and comfort, enabling users to interact with their home environment efficiently and intuitively.
Importance of a User-Friendly Interface
A user-friendly interface is essential for user adoption and satisfaction. A poorly designed interface can lead to frustration and abandonment of the system. Intuitive controls and clear visual cues facilitate easy navigation and comprehension of functionalities, promoting a positive user experience.
Elements of a Good User Experience
A positive user experience hinges on several key elements. These include intuitive navigation, clear visual cues, feedback mechanisms, and personalized customization options. The system should provide immediate feedback on user actions, minimizing confusion and ensuring a sense of control. Users should be able to tailor the interface to their specific needs and preferences, enhancing personalization and engagement.
Best Practices for Designing Intuitive Controls
Designing intuitive controls involves considering several best practices. These include using familiar icons and terminology, providing clear and concise instructions, and incorporating visual cues that enhance comprehension. The design should be adaptable to different user skill levels, making the system accessible to all. Employing a consistent design language across all screens and devices contributes to a coherent and recognizable experience.
Examples of Different Home Automation App Designs
Numerous app designs exist, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Some apps feature a highly visual dashboard with intuitive controls for lighting, temperature, and security. Others opt for a more minimalist approach, focusing on a streamlined experience for simple tasks. The choice of design should be aligned with the target user base and the intended functionalities of the system.
Examples of visual dashboards might include interactive maps that allow users to monitor and control devices throughout their homes, along with dedicated sections for security cameras and access control. Alternatively, a streamlined app could present a list of connected devices, with a toggle switch for on/off functionality.
Method for Conducting User Testing and Feedback Analysis
User testing is crucial for identifying areas for improvement in the user interface. This involves recruiting representative users, observing their interactions with the system, and gathering feedback on their experience. Analyzing this feedback provides valuable insights into user needs and pain points, guiding design iterations to enhance usability. Quantitative data such as task completion rates and time-on-task can be used alongside qualitative feedback, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation.
Table Comparing Different User Interface Designs
| Design Feature | Design A | Design B | Design C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Navigation | Intuitive, hierarchical structure | Flat, visually appealing layout | Context-sensitive menus |
| Visual Cues | Clear icons and color coding | Minimalist aesthetic, subtle cues | Interactive elements for feedback |
| Feedback Mechanisms | Immediate visual and auditory feedback | Haptic feedback on touchscreens | Animated transitions and progress indicators |
| Customization Options | Extensive personalization settings | Limited but effective customization | Dynamic adjustment based on user behavior |
Designing a Visual Interface for a Smart Home
Designing a visual interface for a smart home requires careful consideration of visual elements and their impact on user experience. A well-designed visual interface should be aesthetically pleasing, easy to navigate, and provide clear and concise information. The use of color, typography, and imagery should enhance comprehension and minimize cognitive load. Visual elements should be consistently used to convey information and actions, fostering a seamless user experience.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, creating a smart home hinges on a meticulous understanding of design principles, interoperability, and security measures. This comprehensive overview provides a framework for building intelligent and secure home automation systems, considering future needs and technological advancements. By embracing these principles, homeowners can create homes that are not only technologically advanced but also intuitive, user-friendly, and secure.